Reference no: EM132804153
Question 1
A) Find the completely reduced rate of formation of HBr for the following mechanism.
Br2 + M ↔ 2Br + M k1 and k-1 for forward and reverse reaction
Br + H2 ↔ HBr + H k2 and k-2 for forward and reverse reaction
H + Br2 →k3 HBr + Br
Specifically state the rate constants.
B) Propose a mechanism for the reaction:
H2O2 + 2H+ + 2I- → I2 + 2H2O
For the rate r = k[H+][H2O2][I-]
C) Apply the Steady-State approximation to the Br- catalyted reaction we discussed in class and compare the new rate equation to the original.
HNO2 + 2H+ + C6H5NH2 C6H5NH2 + 2H2O r = k[H+][HNO2][Br+]
Question 2
Assume the first step is a catalyst mediated reaction. The reactor runs at 350 K and 1 atm and only 1 molecule per mol will collide with an active site, of with 1 in 100 will stick to the surface (assume kinetic theory). Upon bonding to the surface, the molecule rapidly decompose. Calculate the rate of (H2O)5CrR2+ decomposition per unit surface area and length of a PFR reactor that is 5 cm in diameter for 87% conversion at a flow rate of 1 cm s-1.
Question 3
Unfortunately, The SCN group can react with the (H2O)5CrR2+ and extract an ethoxy molecule which poisons the catalyst in an elementary reaction. What factor would you chose to maximize product? Set up the equation for the critical dimension(length/volume/concentration) in terms of symbols (k1, k2, []), etc..), do not solve.
Question 4 California Professional Engineering Exam
Compound A undergoes a reversible, elementary isomerization reaction. A ↔ B. over a metal catalyst. A and B are liquid, miscible, and nearly identical density. The equilibrium constant for the reaction is 5.8. In an isothermal fixed bed reactor with no backmixing, a feed of pure A undergoes a net conversion to B of 55%. If a second identical reactor is placed downstream, what is the overall expected conversion when:
A) The reactors are in series?
B) The products are separated and only unconverted A is fed into the second reactor?
Question 5
Develop the solution for the following problem but do not solve.
The following reactions take place in the liquid phase
A + B → 2C rtC = k1C[A][B]; k1C = 0.0.043 dm3/mol s at 400 K
2B + C → D r2D= k2D[B][C]; K2D= 0.4dm3/mols exp [5000 K (1/500 - 1/T)]
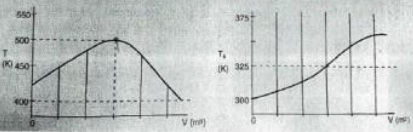
The concentrations of the four molecules were measured at the point where T is maximum and found to be [A]=0.1. [B]=0.2. [C]=0.5, and [D]=1.5 in mol/dm3. The overall heat-transfer coefficient times the heat-exchanger area per unit volume (UA) is 10 cal/s dm3 K and an equimolar feed rate for A and B at 10 mol/s. What is the activation energy of Reaction 1?
CPA = CPB = CPC=20 cal/ mol K; CPD 90 cal/mol K: CP1 100 cal/mol K
ΔH1A° = -50 kcal/ mol A: ΔH2B° = 5 kcal/ mol B