Reference no: EM133101101
Unit 3 Engineering Science - Higher National Certificate in Engineering
Unit reference - T/615/1477
Assignment - Scientific Data and Material Properties
Learning Outcome 1: Examine scientific data using both quantitative and qualitative methods
Learning Outcome 2: Explore the characteristics and properties of engineering materials
Assignment Brief:
Case Scenario:
You have secured a position as a trainee engineer within a research and development (R&D) company that support a range of customers who require specialist engineering technical support. As part of your training, you have been asked to complete a range of tasks as set out below. These tasks cover a range of scientific data gathering methods along with an understanding of the characteristics and properties of engineering materials. You are required to complete the tasks set below and present your findings using variety of methods. This activity will form part of your next appraisal.
A company has lately been receiving customer complaints about one of their products, the complaints being related to the mechanical parts they supply to a skateboard manufacture. The supplied parts have been failing early in service and they have requested your company carries out independent testing on the samples supplied along with the results from a customer survey from the complaints received by the skateboard manufacturer.
Task 1:
Tensile testing (destructive) has been carried out on the supplied parts by your company's inspection department and the results sent on for your analysis. You are required to demonstrate your knowledge and understanding by producing a formal laboratory report based on the tasks below.
In the accompanying sheet there are three sets of test data generated form Tensile tests see Canvas for the test data and a Dye Penetrant test image see (figure 1) carried out on materials that may have been suitable for manufacture of the parts for a skateboard.
The Tensile test specimens are:
Specimen 1 -Ferrous metal, diameter of 9.50 mm and original gauge length of 50 mm.
Specimen 2 - Non-ferrous metal, width of 40 mm, breadth of 2.5 mm and original gauge length of 120 mm.
Specimen 3 - Non-metal, width of 12.61 mm, thickness of 3.47 mm and original gauge length of 50 mm.
By comparing and contrasting results obtained from the testing with theoretical material properties you should be able to draw appropriate conclusions. To do this the laboratory report must by structured to follow formal scientific methods thus ensuring your analysis can be relied upon to be scientifically sound.
You should ensure that your report includes the following elements:
a) Describe SI units and prefix notation, ensure the correct SI units are used within this laboratory report.
b) Examine both quantitative and qualitative data and ensure appropriate software is used to give graphical representation including:
i) Plotting an engineering stress strain (or force extension) curve for the data,
ii) Calculation of the Young's Modulus for each material,
iii) Determining the approximate ultimate tensile strength for each material,
iv) Comparison quantitative and qualitative data gathered from the three specimens to theoretical data from authorised published resources and report your findings.
c) Investigate and explain how the application of a scientific method impacts on the rigour of data analysis.
d) Analyse the data further using both quantitative and qualitative methods.
Task 2:
Dye penetrant testing (non-destructive) have been carried out on the supplied parts as shown in figure 1 as part of the skateboard for your analysis. You are required to demonstrate your knowledge and understanding by producing a formal laboratory report based on the tasks below.
a) Figure 1 shows the dye penetrant testing; use your understanding of material properties and report on why skateboard truck casting is failed within 3 months of manufacture rather than minimum of 15 months from manufacture.
b) Hysteresis in materials has implications for the design engineer, review elastic and electromagnetic hysteresis in different materials and relate your findings to Task 2(a) figure 1.
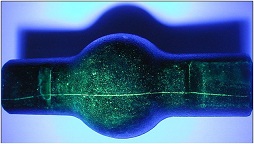
Figure 1: Dye Penetrant test image for Skateboard Truck Casting
Task 3:
All engineers need a fundamental understanding of material characteristics and their properties; for someone entering the field of R&D and working within a scientific field it is essential their understanding goes much deeper and underpins their methods of analysis whether this is through testing or observation. In preparation for your appraisal and to demonstrate you full understanding a typical material for consider the containers are used in everyday life such drink pops, milk, beer, etc.,you have been asked to investigate the characteristics and properties of engineering materials, in compliance with the Food and Drug standard; and write a formal report set against the tasks below:
a) Carryout research into the structural and mechanical properties of metals and non-metals go on to describe this relationship of how the structural properties give metals and non-metals their mechanical properties.
b) Explain the meaning of the following terms, describing if they have mechanical, physical, thermal, or electrical and magnetic properties.
i) Density
ii) Elasticity
iii) Hardness
iv) Toughness
v) Ductility
vi) Malleability
vii) Brittleness
viii) Plasticity
ix) Electrical conductivity
x) Thermal conductivity
c) Explain the types of degradation found in metals and non-metals.
Attachment:- Engineering Science.rar