Reference no: EM135407
Question 1: One subway station in Toronto has 6 turnstiles, each of which can be controlled by the station manager to be used for either entrance or exit control - however never for both. The manager should decide at different times of the day just how many turnstiles to use for entering passengers and how many to be set up to permit exiting passengers.
Assume that passengers enter the station at a rate of around 84 per minute between the hours of 7 and 9 A.M. Passengers exiting trains at the stop reach the exit turnstile area at a rate of around 48 per minute throughout the same morning rush hours. Each turnstile can permit an average of 30 passengers per minute to enter or exit. Arrival and service times have been thought to follow Poisson and exponential distributions, respectively. Suppose that riders form a common queue at both entry and exit turnstile areas and proceed to the first empty turnstile.
The station manager doesn't want the average passenger at his station to have to wait in the turnstile line for more than 6 seconds, nor does he want more than 8 people in any queue at any average time.
a) How many turnstiles must be opened in each direction every morning?
b) Describe the suppositions underlying the solution of this problem by using queuing theory.
Question 2: Consider the given network, where the numbers symbolize actual distance between the corresponding nodes.
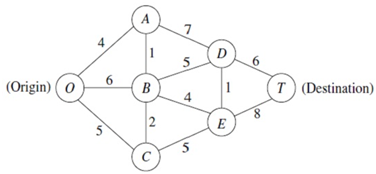
a) Use algorithm to find out the shortest path from O to T.
b) Formulate this shortest path problem as an integer programming problem and solve it in EXCEL.
Question 3: A computer engineer lives in town A and needs to visit each of the towns B, C, D, and E to service different installations. He should visit each town once and return to town A. The distances in miles between the towns are illustrated in the table.
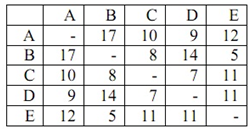
a) Use the nearest neighbor algorithm to find out a tour, starting at town A.
b) Use the nearest insertion algorithm to find out a tour, starting at town A.
c) Use Clarke and Wright savings algorithm to find out a tour, starting at town A.
|
Indicate if gdp is affected
: Indicate if GDP is affected, under what category and what happens to GDP Oklahoma cleans up after a devastating tornado.
|
|
Given the demand and cost conditions
: Given the demand and cost conditions, what price, output and profits result in the short run? What will happen as the firm moves from the short to the long run
|
|
Explain the short-run phillips curve
: Explain how the short-run Phillips curve, the long-run Phillips curve, the short-run aggregate supply curve, the long-run aggregate supply curve, and the natural rate hypothesis are all related.
|
|
Do protectionist policies benefit producers
: Do protectionist policies benefit producers, consumers, workers, or the government
|
|
Queuing theory-clarke and wright algorithm
: How many turnstiles must be opened in each direction every morning and describe the suppositions underlying the solution of this problem by using queuing theory.
|
|
Introduction to statistical process control
: Write introduction to STATISTICAL PROCESS CONTROL and Explain the use of SPC tools used at D2D
|
|
Accounting and financial statements
: Demonstrate an understanding of governmental and not-for-profit accounting and financial statements. Analyze transactions unique to governmental and not-for-profit entities to determine potential outcomes
|
|
Explain the objectives of a budgetary control system
: Identify and explain the objectives of a budgetary control system and discuss the concept of a participative style of budgeting.
|
|
What is the unregulated competitive equilibrium
: What is the unregulated competitive equilibrium and what is the social optimum specific tax (per unit of output of gunk) results in the social optimum
|