Reference no: EM13376564
Questions 1 to 20: Select the best answer to each question. Note that a question and its answers may be split across a page break, so be sure that you have seen the entire question and all the answers before choosing an answer.
1. An operation costing system is
A. the same as a process-costing system, except that direct materials costs are accounted for in the same way as in job-order costing.
B. the same as a job-order system, except that direct materials costs are accounted for in the same way as in process costing.
C. identical to a process-costing system, except that actual manufacturing overhead costs are traced to units of product.
D. identical to a job-order costing system, except that actual manufacturing overhead costs are traced to units of product.
The Lee Company uses a job-order costing system. The following data were recorded for June:
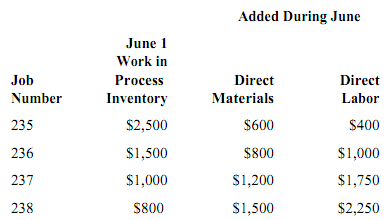
Overhead is charged to production at 80% of direct materials cost. Jobs 235, 237, and 238 were completed during June and transferred to finished goods. Jobs 235 and 238 have been delivered to customers.
2. Lee Company's work-in-process inventory balance on June 30 was
A. $9,450.
B. $4,100.
C. $3,940.
D. $3,300.
3. The Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 contains all of the following provisions except which one?
A. Both the CEO and CFO must certify in writing that their company's financial statements and accompanying disclosures fairly represent the results of operations.
B. Severe penalties are established for altering or destroying documents that may eventually be used in an official proceeding.
C. A CFO must be a CPA or CMA.
D. The audit committee of the board of directors of a company must hire, compensate, and terminate the public accounting firm that audits the company's financial reports.
4. When would the direct method and the step-down method of service department cost allocation result in identical allocations being made to the operating departments?
A. The only time is when there is just one service department.
B. That can happen only if there's an equal amount of service departments and operating departments.
C. The only time is when all costs in the service departments are fixed costs.
D. That can happen if there is only one service department or, if the company has more than one service department, if all the costs in those departments are fixed costs.
5. Which of the following is not one of the five steps in the lean-thinking model discussed in the text?
A. Identify the business process that delivers value.
B. Organize work arrangements around the flow of the business process.
C. Create a pull system that responds to customer orders.
D. Automate the business process.
6. Becky works on the assembly line of a manufacturing company where she installs a component part for one of the company's products. She's paid $16 per hour for regular time, and time and a half for all work in excess of 40 hours per week. Becky's employer offers fringe benefits that cost the company $3 for each hour of employee time (both regular and overtime). During a given week, Becky works 42 hours but is idle for 3 hours due to material shortages. The company treats all fringe benefits relating to direct labor as added direct labor cost and the remainder as part of manufacturing overhead. The allocation of Becky's wages and fringe benefits for the week between direct labor cost and manufacturing overhead would be which of the following?
A. Direct Labor: $624 / Manufacturing Overhead: $190
B. Direct Labor: $672 / Manufacturing Overhead: $142
C. Direct Labor: $741 / Manufacturing Overhead: $73
D. Direct Labor: $688 / Manufacturing Overhead: $126
Use the following information to answer this question.
The following cost data pertain to the operations of Brentwood Store, Inc., for the month of December.
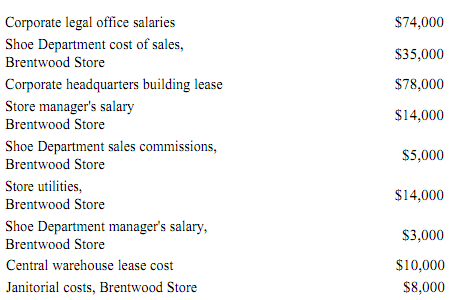
The Brentwood Store is just one of many stores owned and operated by the company. The Shoe Department is one of many departments at the Brentwood Store. The central warehouse serves all of the company's stores.
7. What is the total amount of the costs listed above that are direct costs of the Shoe Department?
A. $40,000
B. $35,000
C. $79,000
D. $43,000
8. Freeman Company uses a predetermined overhead rate based on direct-labor hours to apply manufacturing overhead to jobs. At the beginning of the year, the company estimated manufacturing overhead would be $150,000 and direct-labor hours would be 10,000. The actual figures for the year were $186,000 for manufacturing overhead and 12,000 direct-labor hours. The cost records for the year will show
A. underapplied overhead of $6,000.
B. overapplied overhead of $6,000.
C. underapplied overhead of $30,000.
D. overapplied overhead of $30,000.
9. Dewey Company uses the weighted-average method in its process-costing system. The first processing department, the Welding Department, started the month with 15,000 units in its beginning work-in-process inventory that were 20% complete with respect to conversion costs. The conversion cost in this beginning work-in-process inventory was $19,200. An additional 86,000 units were started into production during the month. There were 13,000 units in the ending work-in-process inventory of the Welding Department that were 60% complete with respect to conversion costs. A total of $575,360 in conversion costs were incurred in the department during the month.
The cost per equivalent unit for conversion costs is closest to
A. $6.206.
B. $6.400.
C. $5.812.
D. $6.690.
Use the following information to answer this question.
The following data (in thousands of dollars) have been taken from the accounting records of Karlana Corporation for the just-completed year.

10. The net operating income for the year (in thousands of dollars) was
A. $410.
B. $180.
C. $110.
D. $40.
Use the following information to answer this question.
Abis Corporation uses the weighted-average method in its process-costing system. This month, the beginning inventory in the first processing department consisted of 800 units. The costs and percentage completion of these units in beginning inventory were
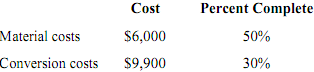
A total of 9,200 units were started, and 8,200 units were transferred to the second processing department during the month. The following costs were incurred in the first processing department during the month:
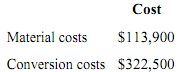
The ending inventory was 80% complete with respect to materials and 20% complete with respect to conversion costs.
Note: Your answers may differ from those offered below due to rounding error. In all cases, select the answer that's the closest to the answer you computed. To reduce rounding error, carry out all computations to at least three decimal places.
11. The cost per equivalent unit for materials for the month in the first processing department is closest to
A. $11.99.
B. $12.44.
C. $11.82.
D. $11.39.
12. Which situation always results in underapplied overhead?
A. Actual overhead is less than applied overhead.
B. Estimated overhead is less than actual overhead.
C. Actual overhead is greater than applied overhead.
D. Estimated overhead is greater than actual overhead.
Use the following information to answer this question.
The Lee Company uses a job-order costing system. The following data were recorded for June:
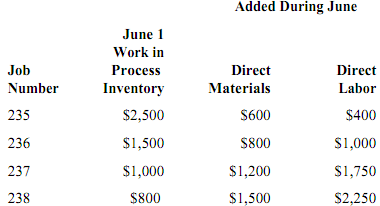
Overhead is charged to production at 80% of direct materials cost. Jobs 235, 237, and 238 were completed during June and transferred to finished goods. Jobs 235 and 238 have been delivered to customers.
13. Lee Company's cost of goods sold for June was
A. $14,640.
B. $15,520.
C. $10,170.
D. $9,730.
14. Melillo Corporation has provided data concerning the company's manufacturing overhead account for the month of October. Prior to the closing of the overapplied or underapplied balance to cost of goods sold, the total of the debits to the manufacturing overhead account was $67,000, and the total of the credits to the account was $57,000.
Which statement is true?
A. Manufacturing overhead for the month was overapplied by $10,000.
B. Manufacturing overhead transferred from finished goods to cost of goods sold during the month was $57,000.
C. Actual manufacturing overhead for the month was $67,000.
D. Manufacturing overhead applied to work in process for the month was $67,000.
15. Malaviya Corporation uses the FIFO method in its process-costing system. Operating data for the Casting Department for the month of September appear below:

According to the company's records, the conversion cost in the beginning work-in-process inventory was $63,104 at the beginning of September. Additional conversion costs of $654,240 were incurred in the department during the month. What would be the cost per equivalent unit for conversion costs for September? (Round off to three decimal places.)
A. $8.060
B. $9.087
C. $9.280
D. $9.400
Use the following information to answer this question.
Sanker Inc. has provided the following data for the month of August. There were no beginning inventories; consequently, the direct materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead applied listed below are all for the current month.
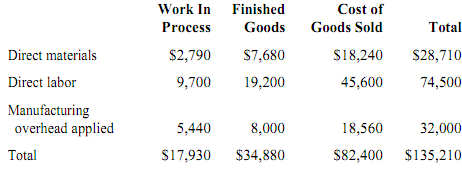
Manufacturing overhead for the month was overapplied by $5,000. The company allocates any underapplied or overapplied overhead among work in process, finished goods, and cost of goods sold at the end of the month on the basis of the overhead applied during the month in those accounts.
16. The work-in-process inventory at the end of August after allocation of any underapplied or overapplied overhead for the month is closest toA. $18,780.
B. $17,267.
C. $17,080.
D. $18,593.
Use the following information to answer this question.
Abis Corporation uses the weighted-average method in its process-costing system. This month, the beginning inventory in the first processing department consisted of 800 units. The costs and percentage completion of these units in beginning inventory were
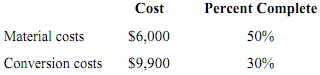
A total of 9,200 units were started, and 8,200 units were transferred to the second processing department during the month. The following costs were incurred in the first processing department during the month:
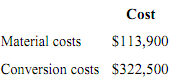
The ending inventory was 80% complete with respect to materials and 20% complete with respect to conversion costs.
Note: Your answers may differ from those offered below due to rounding error. In all cases, select the answer that's the closest to the answer you computed. To reduce rounding error, carry out all computations to at least three decimal places.
17. What are the equivalent units for conversion costs for the month in the first processing department?
18. The management of Baggerly Corporation would like to investigate the possibility of basing its predetermined overhead rate on activity at capacity. The company's controller has provided an example to illustrate how this new system would work. In this example, the allocation base is machine hours, and the estimated amount of the allocation base for the upcoming year is 81,000 machine hours. In addition, capacity is 95,000 machine hours, and the actual level of activity for the year is 84,900 machine hours.
All of the manufacturing overhead is fixed and is $6,617,700 per year. For simplicity, it's assumed that this is the estimated manufacturing overhead for the year as well as the manufacturing overhead at capacity. It's further assumed that this is also the actual amount of manufacturing overhead for the year. If the company bases its predetermined overhead rate on capacity, by how much was manufacturing
overhead underapplied or overapplied?
A. $703,566 underapplied
B. $318,630 overapplied
C. $318,630 underapplied
D. $703,566 overapplied
Use the following information to answer this question.
The following cost data pertain to the operations of Brentwood Stores., for the month of December.
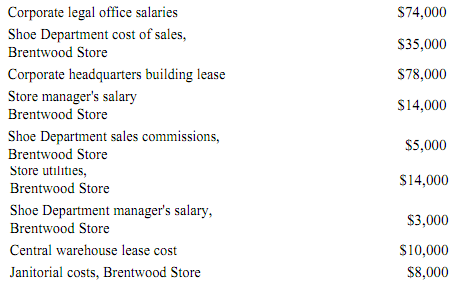
The Brentwood Store is just one of many stores owned and operated by the company. The Shoe Department is one of many departments at the Brentwood Store. The central warehouse serves all of the company's stores.
19. What is the total amount of the costs listed above that are not direct costs of the Brentwood Store?
A. $162,000
B. $43,000
C. $36,000
D. $78,000
Use the following information to answer this question.
The following data (in thousands of dollars) have been taken from the accounting records of Karlana Corporation for the just-completed year.

20. The cost of goods sold for the year (in thousands of dollars) was
A. $540.
B. $670.
C. $500.
D. $650.