Reference no: EM132579361
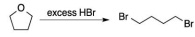
Question 1. Using the curved-arrow formalism, provide a mechanism for the following reaction. Show every stet detail and be clear about the origin and destination of each arrow
Question 2. Identify the better leaving group in each of the following pairs and provide a brief justification for each.
(a) NH3 vs. S NH2
(b) H2O vs. H2S
Question 3. Provide the starting material (substrate) and reagents (nucleophile/base and solvent) needed to prepare each of the following molecules by the indicated mechanism
Question 4. Consider the following reaction:
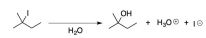
(a) Provide the rate law for the reaction.
(b) Using curved-arrow formalism, provide a mechanism for the reaction.
Question 5. Identify which of the following alkenes is more thermodynamically stable. Provide an explanation for your selection.
Question 6. Will a SN2 reaction performed in a polar protic solvent with an anionic nucleophile proceed at a faster rate, slower rate, or at the same rate than one performed in a polar aprotic solvent? Provide a brief justification for your selection
Question 7. Provide a brief justification for each of the following statements.
(a) (CH3)3CCH2Br, a primary alkyl halide, undergoes SN2 reactions very slowly
(b) (CH3)3CBr reacts at the same rate with both F- and H2O in substitution reactions.
C) A strong base is not necessarily a good nucleophile
Question 8. Consider E2 elimination from the following two substrates: Draw the major product that results from E2 elimination at each of the substrates.
Question 9. For each of the following reactions, provide the structure (including stereochemistry) of the major organic product. If no products are expected, indicate that the reaction does not proceed (NR).
Question 10. Provide the structure of an organic molecule that is most consistent with the given analytical and spectroscopic data. Show as much of your reasoning as possible.