Reference no: EM13226509
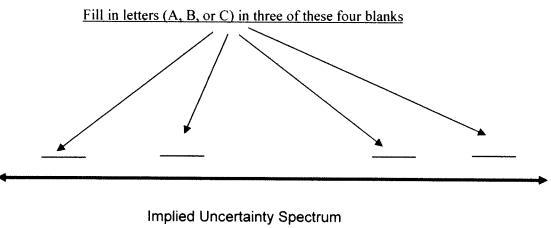
Problem 1: Where on the Implied Uncertainty Spectrum do the following products fall? (fill the letters A, B, or C in three out of four blanks in the figure below)
(A) 75-Watt light bulb
(B) A basic laptop
(C) A cell (mobile) phone that is also a handheld organizer and can be used to surf the web and send emails.
Problem 2
Classify the following typical situations as being a sign of responsiveness or efficiency:
a) A company keeps low levels of safety inventory.
b) Inbound transportation for a particular product is always in full truck loads.
c) The fraction of production orders not completed in time is over 30%.
d) A manufacturer that requires suppliers to have short lead times to supply components.
e) A highly utilized facility.
f) A computer processor that must be ordered 3 months in advance.
Problem 3: During the strategic design phase of a supply chain network, the number and location of production plants must be decided. The production and transportation cost per unit from plant i to market] is c,, and the tariffs at market j are t,. There are 6 markets and 4 potential plant locations. The demand at market] is D, and the selling price per unit is si. The production capacity for plant i is K„ and the fixed cost for opening a plant at location i is F,. The board of directors had decided that the company must at least open 2 plants but no more than 3. The CEO has decided that if a plant is opened at site number 1, then the company cannot open a plant at site number 3. Formulate a mathematical Linear/Integer Programming model to decide the optimal plant locations to maximize profit assuming that you cannot have more than one plant at a specific site (i.e., no multiple plants at the same site). Make sure that you clearly define all necessary decision variables, and state your objective function and constraints. (Don't solve, just formulate a model).
Problem 4:
For a responsive supply chain that has achieved its strategic fit, answer the following:
a) What can you conclude about the uncertainty of its product demand?
b) As the product goes through its life cycle phases, should the supply chain design stay the same strategy or should it change? Justify your answer.
Problem 5: What are the top two supply chain drivers that contributed the most to the success of Seven-Eleven Japan? Explain your answer.
Problem 6 :
Give a practical and real-life example to show that the selection of a distribution network is a strategic decision.
Problem 7: Consider two products: A and B. Product A has a transportation cost per unit that is a large fraction of unit cost and Product B has transportation cost as a small fraction of unit cost. In which of the two cases would you prefer a distribution network with fewer facilities? Why?
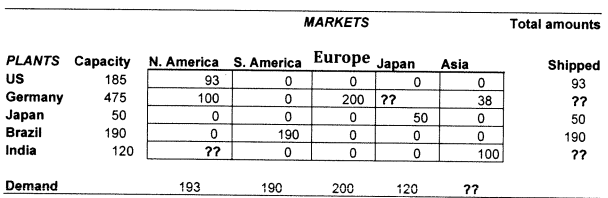
Problem 8: A company has five worldwide plants. Their locations, capacities, and demand in their markets are shown in the table below in thousands of units. It turns out that the optimal amounts to ship are as shown below assuming that the demand must be met. Show your calculations when you answer the followings:
a) What is the optimal amount to ship from India to North America?
b) What is the optimal amount to ship from Germany to Japan?
c) What is the total amount to ship from India?
d) What is the total amount to ship from Germany?
e) What is the total amount to receive in Asia?
If the company has 10 thousand units of additional capacity that can be used. Which plant(s) would you assign the additional capacity to and why?
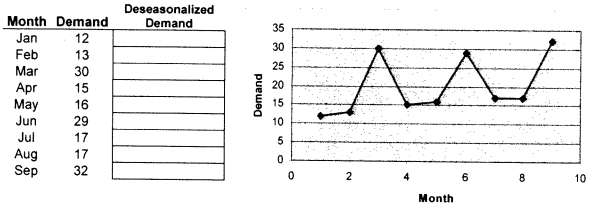
Problem 9: The demand for a product is given in the table below and depicted in the figure next to it. Deseasonalize the demand and show your calculations. Please fill in the values in allocated column below.