Reference no: EM13118396
Topic: Monopolistic Competition.
1. Consider the village of Fanjeaux - a beautiful, bucolic, historic (but remote) village in the province of Languedoc Roussillon, France. The Village Council has decided there will be only one gasoline station in the entire village. That is, only one gasoline station will be allowed to sell gasoline and this one gasoline station will have a monopoly.
However, this one gasoline station will have to pay the Village Council a royalty fee every year equal to 50 percent of its profits.
You are considering applying to the Village Council for the license to operate the single gasoline station. You estimate that your profit maximizing quantity of gasoline will be 100,000 liters per year; that you will charge 5 Euros (the currency used in France) per liter for gasoline; and that your average cost per liter of gasoline (including all fixed cost, variable cost and opportunity cost but not including the 50 percent royalty) is 2 Euros.
A. Given the above information, how much will your firm pay in royalties to the Village Council every year?
B. After your firm pays the royalty fee what will be its economic profits?
C. What is the maximum dollar amount your firm would be willing to pay in royalty fees to the Village Council every year for the monopoly right to sell gasoline in Fanjeaux?
Now suppose sometime after granting your firm the monopoly right to sell gasoline the Village Council eliminates the monopoly restriction on gasoline stations as well as the 10 percent royalty, and allows free entry into the village for gasoline stations. According to an expert in the market for gasoline, "Each new gasoline station will cause the price of a liter of gasoline to decrease by 0.50 Euros (1/2 of a Euro) and will cause the marginal cost of selling a liter of gasoline to increase by 0.25 Euros (1/4 of a Euro)."
D. What will be the equilibrium number of gasoline stations in Fanjeaux?
2. Suppose Poeing and ZirBus operate the only two companies that make large commercial aircraft. At present they compete intensely with each other. Each firm produces twenty five (25) large commercial aircraft per year for sale to the various airlines; charges the airlines a price of $20 million per aircraft; and has a constant average total cost per aircraft of $15 million.
One day by sheer chance the Chief Executives of Poeing and ZirBus find themselves seated next to each other at a movie. In the darkness of the movie theater one of them says, "You know, if we 'cooperated' with each other rather than 'competed'we both could make more profit. We could charge $25 million per aircraft by cutting the number of aircraft each of us makes from 25 to 20." The other replies, "Yes we could."
However, at the same time they both think to themselves, "If Poeing/ZirBus raises their price to$25 million then I'll cut my price back to $20 million. I'll then sell 45 aircraft per year and the other company will be left with only 5 aircraft to sell per year."
A. What are Poeing's and ZirBus's economic profits when they compete with each other?
B. What would be Goeing's and SirBus's economic profits if they cooperated? That is, if they formed a cartel/duopoly.
C. What would bePoeing's economic profit if it undercut ZirBus?
D. What would be ZirBus's economic profit if it undercut Poeing?
E. What do you think will be the equilibrium outcome? Will they continue to compete or will they cooperate?You may use a game tree to illustrate your answer and assume Poeing chooses first.
(Topic: Quantities, Prices and Profits in monopoly and perfectly competitive markets)
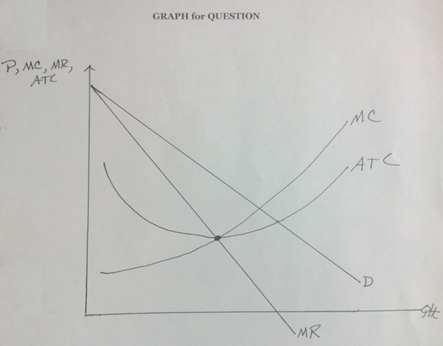
3. The Duck siblings, Huey, Duey, and Luey, own the only restaurant in town, The Foul Fowl. They have a monopoly. However, they each have different goals for the restaurant:
Huey, the compassionate one, wants to serve as many meals as possible without losing money- that is without incurring an economic loss. He is happy with zero economic profit.
Duey, the social climber, wants the restaurant to bring in as much revenue as possible. He wants the maximum revenue even if it means the restaurant incurs economic loss.
Luey, the greedy one, wants to make the maximum economic profit.
The graph shows the Demand schedule for meals at the Foul Fowl, the Marginal Revenue schedule, the Average Total Cost of providing a meal as well as the Marginal Cost.
Using the graph show the quantity and price of meals that will achieve each of the partner's goals. Use the symbols QH and PH for Huey; QD and PD for Duey; and QLand PLfor Luey.