Reference no: EM13846621
1.What is the price elasticity of demand? How is the price elasticity of demand calculated?
2. Why is time such an important determinant in the elasticity of supply? Is time also important in determining price elasticity of demand? Explain.
3. What is marginal utility? Why is the term marginal important in utility analysis?
4. Describe and explain the three principal methods of financing that are used by corporations.
5. What is the random walk theory? Explain.
QUIZ:
1: A payment for the use of any resource over and above its opportunity cost is called
- accounting profit.
- economic profit.
- normal cost.
- economic rent.
Question 2: An individual would willingly give a concert for $2,000. If she is paid $5,000 for the concert, she is
- receiving $3,000 to cover her opportunity cost.
- not being paid her full opportunity cost.
- receiving $3,000 of economic rent.
- certainly being paid more than warranted by the level of demand.
Question 3: Which of the following is a disadvantage of the corporate form of business organization?
- Limited liability
- Limited financing
- Double taxation
- Unlimited liability
Question 4: Economic profit can be calculated as
- total revenue - explicit costs.
- total revenue - implicit costs.
- total revenue - explicit costs - implicit costs.
- total revenue - fixed costs.
Question 5: In a partnership, legal responsibility for all debts is
- shared by the partners.
- passed to the shareholders.
- paid by the principle owner.
- handled by the bondholders.
Question 6: Interest is paid to
- all holders of stock.
- individuals who own gold.
- owners of capital.
- borrowers of funds.
Question 7: The greater is the risk of non-repayment of a loan, the
- higher is the expected rate of interest.
- longer is the expected time to repay the loan.
- lower is the handling charges for the loan.
- lower is the expected rate of interest.
Question 8: Businesses demand funds because
- they prefer earlier consumption to later consumption.
- they have deficits to cover.
- they prefer to purchase capital goods in the current year.
- they make investments that they believe will increase productivity and profitability.
Question 9: When a firm uses profits to purchase new capital equipment, it is engaging in
- tax evasion.
- reinvestment.
- balance sheet accounting.
- the most risky way the firm can obtain investment funds.
Question 10: A share of stock in a corporation is
- a guarantee to a fixed amount of income from the corporation.
- a legal claim to a lump-sum payment at a specified point of time in the future.
- a legal claim to a dividend, regardless of the corporation's ability to pay its interest payments.
- a legal claim to a share of the company's future profits.
Question 11: A legal claim against a firm that usually entitles the owner of the claim to receive a fixed annual coupon payment, plus a lump-sum payment at some future date, is known as
- a bond.
- a share of common stock.
- a share of preferred stock.
- a reinvestment coupon.
Question 12: The three primary sources of corporate funds are
- banks, friends, and family.
- government, other corporations, and the central bank.
- investment banks, brokerages, and insurance companies.
- stocks, bonds, and reinvestment of profits.
Question 13: The theory that there is no predictable trends in securities prices is the
- opportunity cost of capital.
- random walk theory.
- capital reinvestment.
- present value.
Question 14: Which of the following is a TRUE statement about stock markets?
- Economists can make above-average profits in the stock market because of their specialized knowledge of economics.
- It is always better to buy growth stocks than the older and more stable blue-chip stocks.
- The stock market on average over time is random and totally unrelated to the performance of the economy.
- It is illegal for a friend of a corporate executive to make large profits in the stock market by using his inside information.
Question 15: Economists generally define the short run as being
- that period of time in which at least one of the firm's inputs, usually plant size, is fixed.
- that period of time in which all inputs are variable.
- any period of time less than one year.
- any period of time less than six months.
Question 16: Which of the following is TRUE about the long run?
- All resources are variable.
- All resources are fixed.
- At least one resource is fixed.
- None of the above.
Question 17: Mr. James' company produces candy bars. Which is NOT a variable input for this firm?
- Sugar
- Assembly line workers
- The big chocolate-stirring machines
- Packaging materials
Question 18: Suppose that one worker can produce 15 cookies, two workers can produce 35 cookies together, and three workers can produce 65 cookies together. What is the marginal product of the 2nd worker?
- 15 cookies
- 20 cookies
- 30 cookies
- 35 cookies
Question 19: Average physical product is calculated by dividing total product by the
- amount of variable and fixed inputs employed.
- quantity of the variable input.
- quantity of the fixed input.
- production function.
Question 20: The marginal productivity of labor will eventually decrease as more workers are employed because
- average product is increasing.
- total product is decreasing.
- the amount of capital will also be increasing.
- on the average each worker will have fewer inputs to work with.
Question 21: Suppose that a firm is currently producing 1,000 units of output. At this level of output, AVC is $1 per unit, and TFC is $500. What is the firm's TC?
Question 22: In economics, a fixed cost is a cost that
- is present only in the short run.
- goes up as the level of output goes up.
- goes down as the level of output goes up.
- does not vary with the level of output.
Question 23: At the output rate at which diminishing marginal product begins, a firm will experience
- constant average total costs.
- increasing average fixed costs.
- increasing marginal costs.
- decreasing average variable costs.
Question 24: If the price of labor is constant and a firm experiences diminishing marginal product, then its
- marginal costs increase.
- marginal costs decrease.
- fixed costs increase.
- total costs decrease.
Question 25: In economics, the planning horizon is defined as
- 10 years for every firm.
- the longest time period over which the firm can make decisions.
- the period of time for which technology is fixed.
- the long run, during which all inputs are variable.
Question 26: Which of the following is NOT one of the reasons a firm might be expected to experience economies of scale?
- specialization
- the dimensional factor
- improved productive equipment
- depreciation
Question 27: Due to extremely large fixed costs, an electricity generating plant probably experiences which of the following returns to size?
- diseconomies of scale
- diminishing marginal product
- constant returns to scale
- economies of scale
Question 28: If a firm gets so large that management of employees and other resources becomes a costly problem, it will be experiencing
- diseconomies of scale.
- diminishing marginal product.
- constant returns to scale.
- economies of scale.
Question 29: Minimum efficient scale is defined as
- the lowest output level at which long-run average costs are at their minimum.
- the amount of labor that maximizes the marginal product of labor.
- the point at which marginal cost, average variable cost, and average fixed cost are all equal.
- the point at which economies of scale are at their maximum.
Question30. Refer to the above figure. The curve reflects
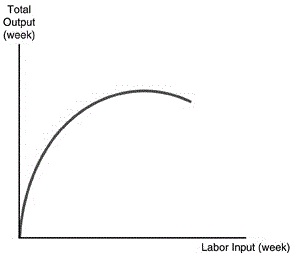
- the law of diminishing marginal product in labor.
- the law of increasing marginal product in labor.
- the law of diminishing marginal product in capital.
- the law of increasing marginal product in capital.