Reference no: EM1317099
CASE : Sanders cycle company job order costing
Sanders Cycle Company is a family-owned bicycle manufacturing company located in Stow, Ohio. Until recently,it had maintained slow but steady growth in producing and marketing its only product, the Tourist bicycle. In 2012, however, demand for this product line had stalled at 9,000 units per year due to heavy price reductions by competitors. Exploring for new business opportunities, Bryan Sanders, the owner, added a high-end racing bike, the Racer, to the product mix in 2013.
The company uses a job order costing system to record Racer's product costs. Table 1 shows the jobs in Work-in-Process Inventory (WIP) on November 30, 2013.
Table 1
|
Job No.
|
# bikes
|
Accumulated Cost
|
|
R025
|
150
|
$ 169,500.00
|
|
R026
|
250
|
206,060.00
|
|
R027
|
200
|
129,000.00
|
|
|
|
$ 504,560.00
|
On November 30, 2013, two jobs were still in the Finished Goods (FG) Inventory. These jobs were expected to be shipped to customers during the first week of December.
Table 2
|
Job. No.
|
# Units
|
Unit Cost
|
Accumulated Cost
|
|
R023
|
150
|
$1,325.00
|
$ 198,750.00
|
|
R024
|
200
|
1,410.00
|
282,000.00
|
|
|
|
|
$ 480,750.00
|
Figure 1 provides the flowchart of the production process of Racer bicycles. A narrative describing the production process is provided below.
Figure 1: Racer's Production Process
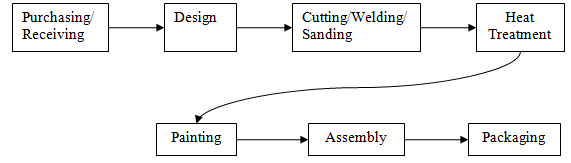
Purchasing/Receiving
The primary materials used in the Racer's production process consist of lightweight aluminum tubing for bicycle frames and assembled components (e.g., gear assemblies, pedals, wheels, etc.). The company's accounting system releases purchase orders on-line as needed, and the company receives material deliveries on a just-in-time basis.
Design
Customers purchasing the Racer work with firm technicians to custom design the bicycle frame using the company's CAD (computer-aided design) program
Cutting/Welding/Sanding
Workers use a laser to precision cut all tubing based on the customer-driven CAD program. Workers then weld the precision cut pieces to form the bicycle frames and sand the joints to prepare the frames for painting. Highly skilled craftsmen hand-weld the Racer frames due to the thin walls of the aluminum tubing. After sanding, workers hang the frames on an overhead conveyor that transports them through the next two processes.
Heat Treatment
All bicycle frames undergo a high temperature heat-treating process to strengthen the tubing walls that are weakened during the welding process. The thin-walled aluminum used in the Racer requires 3 hours of heat treatment.
Painting
After heat treatment, all frames pass through an electrostatic painting process in which each frame receives an electrical charge that enhances paint adherence. Customers had a choice of red or blue for the Racer.
Assembly
Workers remove the bicycles from the overhead conveyor and partially assemble them at the factory. Workers then self-inspect each finished bicycle for quality.
Packaging
Workers pack each bicycle in a box to be loaded on a truck transferring the products to the finished goods warehouse.
Manufacturing overhead are indirect costs to the product lines. Overheads are applied to each job using activity-based costing (ABC). The company has sixoverhead activity pools: (1) material handling, (2) CAD assistance, (3) labor-related, (4) heat treatment,(5) painting, and (6) quality control. The budgeted activity costs and activity driver units for Racer in 2013 were as follows.
Table 3
|
Activity Cost Pool
|
Expected Cost
|
Activity Driver
|
Cost Driver Unit
|
|
Material handling
|
$ 360,000
|
Number of parts issued
|
180,000
|
|
CAD assistance
|
140,000
|
Number of jobs (orders)
|
40
|
|
Labor-related
|
612,000
|
Number of direct labor hours
|
48,000
|
|
Heat treatment
|
648,000
|
Number of treatment hours
|
12,000
|
|
Painting
|
645,000
|
Number of bikes painted
|
4,000
|
|
Quality control
|
75,000
|
Number of bikes inspected
|
4,000
|
|
|
$2,480,000
|
|
|
Material handling: This cost pool is for all costs associated with ordering, receiving, and moving materials to production. The number of parts in each Raceris 45.
CAD assistance: The costs in this category consist primarily of salaries for the technicians that assisted customers in designing their customized Racer frames. CAD assistance cost is applied to each job at the beginning of the production process.
Labor-related: This cost pool consists of overhead itemssuch as utilities, equipment depreciation, butane, and indirect materialsincurred to support the time consuming activities of cutting, welding, sanding, assembling, and packaging.
Heat treatement: This cost pool includes utilities and depreciation of the furnace.Each frame unit requires 3 hours of heat treatment.
Painting: This cost pool includes the cost of painting frames and depreciation of painting equipment. Painting cost is incurred equally per bicycle.
Quality control: This pool consists of the training cost of factory workers and the salary of factory supervisors and quality control inspectors.
The company uses a Manufacturing Overhead (MOH) account to accumulate actual overhead costs and to record overhead costs applied to jobs and Work-in Process Inventory. The MOH account balance is closed to the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) account once a year at the end of each calendar year. Through the first 11 months of the year (January to November), the total overhead applied to all Racer jobs amounted to $2,186,350 and the total actual overhead costs allocated to Racer jobs amounted to $2,210,540. At the end of each month, overhead costs are applied to each job based on the progress made during the month. If the job is finished during the month, the overhead is applied when the job is finished.
The company maintains two direct material inventory accounts for Racer: Aluminum Tubing and Assembled Components, and an indirect material inventory account. On November 30, 2013, the balances in the Aluminum Tubing and Assembled Components accounts were $56,400 and $94,800, respectively. Additions to the direct materialinventory accounts and requisitions from jobs worked during December included the following.
Table 4
|
.
|
AluminumTubing
|
Assembled Components
|
Total
|
|
Purchases
|
$112,000
|
$226,000
|
$ 338,000
|
|
Requisitions:
|
|
|
|
|
R025
|
mce_markernbsp; 0
|
mce_markernbsp; 0
|
mce_markernbsp; 0
|
|
R026
|
0
|
68,200
|
68,200
|
|
R027
|
0
|
56,500
|
56,500
|
|
R028 (300 bikes)
|
45,000
|
76,400
|
121,400
|
|
R029 (400 bikes)
|
57,600
|
0
|
57,600
|
|
|
$ 102,600
|
$ 201,100
|
$ 303,700
|
The balance in the Indirect Material Inventory account on November 30, 2013 was $14,300. Total indirect material purchase during December was $23,600. Indirect material requisitions from all jobs worked in December amounted to $25,150.
During December, the factory payroll for the Racer production consisted of the following:
Table 5
|
Job No.
|
Direct Labor Hours
|
Factory Payroll Cost
|
|
R025
|
480
|
mce_markernbsp; 9,600
|
|
R026
|
950
|
19,000
|
|
R027
|
1,230
|
24,600
|
|
R028
|
2,080
|
41,600
|
|
R029
|
1,260
|
25,200
|
|
Supervision and quality control
|
|
23,400
|
|
Other indirect labor
|
|
29,200
|
|
|
|
$172,600
|
Other operating data for December were summarized as follows.
Table 6
|
Job No.
|
Number of parts issued
|
CAD assistance cost applied to job in Dec.?
|
Heat treatment hours
|
Number of bikes painted
|
Number of bikes inspected
|
|
R025
|
0
|
No
|
0
|
0
|
150
|
|
R026
|
11,000
|
No
|
0
|
250
|
250
|
|
R027
|
8,800
|
No
|
600
|
200
|
200
|
|
R028
|
13,500
|
Yes
|
900
|
300
|
0
|
|
R029
|
400
|
Yes
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
Jobs R025, R026, and R027 were completed during December. Three jobs, R023, R024, and R026 were shipped to customers during December.
Required:
I. Prepare journal entries, with supporting calculations if necessary, to record the following events during December.
1. Purchased direct materials (aluminum tubing and assembled components) and indirect materials on account.
2. Issued aluminum tubing and assembled components to production to fill job requisitions.
3. Issued indirect materials to production.
4. Incurred direct labor and indirect labor costs for jobs worked during the month.
5. Applied manufacturing overhead using the ABC cost pools and cost drivers to jobs worked during the month. (Hint: First determine the overhead activity rates using the budgeted overhead costs and cost driver information.)
6. Recognized December's depreciation of trucks used to move materials from the storage area to the manufacturing plant and to move finished goods from the plant to the finished goods warehouse, $61,900.
7. Accrued December's property taxes for the plant, $18,000. The taxes are scheduled to be paid in March.
8. Recorded December's depreciation of the company's office building, $12,500.
9. Recorded completed jobs during December.
10. Shipped jobs to customers and recorded cost of goods sold and sales revenue. All jobs are priced at 140 percent of their cost of goods sold.
11. Received bills for utilities, equipment maintenance, insurance, and other overhead items for the manufacturing plant for December, $67,000.
12. Recognized December's depreciation of manufacturing assets (property, plant, and equipment), $102,400.
13. Received December's freight bills for shipping finished goods to customers, $22,450.
14. Recorded December's rent expense for the material storage area, $25,000. The rent has been prepaid in October 2013for a 12-month period.
15. Closed the balance of the MOH account to the COGS account on December 31.
II. Prepare job cost reports for all jobs worked during December. Use the following format.
|
Job No.
|
Beg. Inv., Dec. 1
|
Added DM Cost
|
Added DL Cost
|
MOH Applied
|
Total Job Cost,
Dec 31
|
Job Status, Dec 31
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(Note: Job status = WIP, FG, or COGS)
III. Prepare T-accounts for Aluminum Tubing Inventory, Assembled Components Inventory, Indirect Materials Inventory, Manufacturing Overhead, Work-in-Process Inventory, and Finished Goods Inventory. For each T-account, show the balance on December 1, all relevant entries occurred during December (with supporting calculations, if necessary), and the balance on December 31.