Reference no: EM132661601
HI5016 International Trade and Enterprise - Holmes Institute
Learning Outcome 1: Acquire a broad understanding of the changing international trade and investment pattern among nations.
Learning Outcome 2: Analyse how major models and theories explain international trade and how nations benefit from international trade
Learning Outcome 3: Comprehend the international factor movements, trade policy instruments, the arguments for protectionism and; the role of Regional Trade Agreements and the WTO in promotion of international trade, investment and economic growth among nations.
Learning Outcome 4: Synthesise the theoretical and practical knowledge of international economics, a well-developed understanding of the language of international trade and the tools of trade policy used by policy makers in a nation.
Question 1: World Trade Overview and Gravity Model
In the 19th Century Britain was trading with countries from distant locations such as North America, Latin America, Africa and Asia. Today, Britain mostly trades with European countries. Examine the causes of the British changing trade pattern with reference to the Gravity Model.
Question 2: Resources and Trade: Heckscher-Ohlin (H-O) Model
How does the Ricardian model differ from the H-O theory in explaining international trade patterns among nations.
Question 3: Economies of Scale, Imperfect Competition and International Trade
Trade need not be the result of comparative advantage but it can be a result of economies of scale. Discuss.
Question 4: International Factor Movements
Explain the effects of migration of labour between two nations. Use the figure below and the marginal product of labour concept to explain your answer.
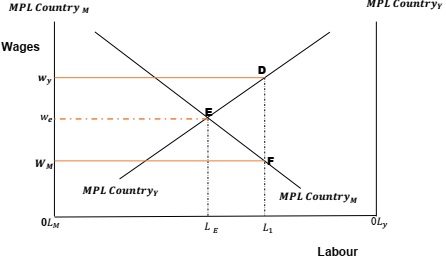
Question 5: Trade Policy in Newly Industrialized/Developing Countries
Infant Industry protection is a key solution for the growth of industrialization of developing countries. Discuss your answer by using the graph below and any other graph(s) that you can deem appropriate.
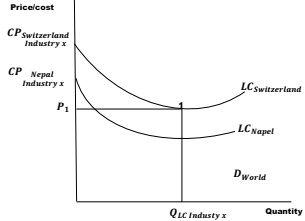
Question 6: Controversies in Trade Policy
After the Seattle 1999 World Trade Organization Ministerial Conference fiasco, in the next 2 years, large anti-globalization demonstrations rocked the International Monetary Fund and Work Bank in Washington. What was the anti-globalization movement goal- and was it right? Explain you answer and where appropriate use figures.