Reference no: EM13973737
1. The individual read sizes generated by next-generation sequencing (NGS) are typically between 100 - 1000 bp in length, depending on the specific system used. However, NGS is able to provide full-genome sequences for complex organisms. It is able to do this via producing ______________ from the individual reads.
-ddNTPs
-cDNA
-emulsified droplets
-contigs
-phosphodiester bonds
2. The constitutive promoter that you placed upstream of your gene is expressing too much of the gene. Which of the following can you use to have it express less?
-Make the promoter weaker by changing the sequences of the -10 and -35 regions to their reverse complements
-Make the promoter stronger by changing the sequences of the -10 and -35 regions to more closely match the consensus sequences
-Make the promoter weaker by changing the sequences of the -10 and -35 regions to more closely match the consensus sequences
-Make the promoter stronger by changing the sequences of the -10 and -35 regions to less closely match the consensus sequences
-Make the promoter weaker by changing the sequences of the -10 and -35 regions to less closely match the consensus sequences
3. You're writing a grant proposal that involves transferring foreign DNA into five different systems. For which of the following would you use the term "transform" for this introduction of foreign DNA?
-Escherichia coli
-Saccharomyces cerevisiae
-Cavendish banana plants
-Drosophila melanogaster
-Human cell lines
4. Before a eukaryotic gene can be properly expressed in a prokaryotic system, which of the following must be removed to leave only the coding sequence?
-Amplicons
-Electrons
-Exons
-Introns
-Decepticons
5. RFLP analysis is useful for identifying spatiotemporal migration patterns in outbreak investigations because the natural evolution rate of the organisms can cause _____________ to occur, which can destroy existing or create new ____________.
-codon bias;
-co-repressor molecules; inducible gene promoters
-mutations; restriction enzyme sites
-RNA interference (RNAi); gene silencing
-transformations; antibiotic resistance genes
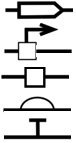
6. In an SBOL Visual representation of the lac operon, which of the following would represent lacO?
7. The 5' overhang on your vector is GATC. Which of the following restriction enzymes should you use to cut your insert so it is compatible?
-AluI
-BamHI
-EcoRI
-HindIII
-NotI
8. Which of the following would not eliminate the inducible nature of the lac promoter?
-Eliminating the lacO1 operator site
-Eliminating the lacO3 operator site
-Eliminating the lacI gene which encodes the lac repressor
-Eliminating the lacZ gene which encodes β-galactosidase
-Eliminating the ability of the lacI monomers to form a tetramer
9. In order to perform a successful transformation, for which of the following would you most likely have to use electroporation or chemical competence?
-Bacillus subtilis
-Escherichia coli
-Haemophilusinfluenzae
-Neisseria spp.
-Streptococcus pneumoniae
10. Which of the following would be the easiest method to identify if a bacterial clone's antibiotic resistance gene has been disrupted?
-Blue-white screening
-Functional complementation
-Library screening
-Replica plating
-TA cloning
11. You've used synthetic biology to design a new biological system that could help with the bioremediation of oil spills. Altogether, the genetic networks you designed total 150 kbp. In order to transform your synthetic network into Escherichia coli, which of the following vector systems should you use?
-Bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC)
-Bacteriophage λ
-Cosmid
-Plasmid
-Yeast artificial chromosome (YAC)
12. A suicide vector is not maintained as a plasmid in the target host but instead transforms the host by transferring its insert into the host genome (typically the chromosome). This transfer occurs via what mechanism?
-Baculovirus
-Co-immunoprecipitation
-Homologous recombination
-Origin of replication
-Sticky ends
13. Which of the following is not required to perform two-dimensional gel electrophoresis (2DGE)?
-Breaking the peptide bonds between amino acids
-Denaturing the higher-order structure of the proteins
-Isoelectric focusing
-Separation based on pI and molecular mass
-Use of a detergent, such as sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS)
14. The DNA melting curve for the PCR primer 5'- ATGCCCGAATTGCCTAGTAG -3' is shown in blue. Which of the following is the sequence for the PCR primer represented in red?
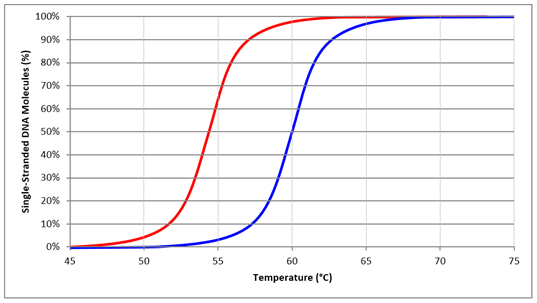
-5'- ATGCCCTAGTAGCCGAATTG -3'
-5'- CTACTAGGCAATTCGGGCAT -3'
-5'- TGAACCGTATGCCCTGCGAG -3'
-5'- CGGTACATGGCCATCATTAA -3'
-5'- ATGAGTACTTAGCCAGTGAA -3'
15. Pluripotent embryonic stem cells can be induced to differentiate into which of the following types of cells?
-Epithelial cells
-Fibroblasts
-Hepatocytes
-Lymphocytes
-All of the above
16. Which of the following techniques is not based on the basic principle of hybridization between complementary nucleotides?
-DNA microarrays
-Northern blotting
-RNA microarrays
-FISH
-Western blotting
17. Which of the following techniques relies on the fluorescent emission of one molecule being absorbed by another, which in turn produces a second fluorescent emission?
-Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP)
-Fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET)
-Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR)
-X-ray crystallography
-Yeast two-hybrid system
18. During PCR, an annealing temperature much lower than the Tm of the primers would most likely result in which of the following problems?
- Lack of denaturation
- Secondary structure formation of the primers
- No amplification
- Nonspecific amplification
-Insufficient extension
19. The following sequences were obtained by Sanger sequencing. What is the length of the properly generated contig?
TTAGATGCATAGAAATGA
CAGCCCTGGCACATGAAA
ATGAAATGGACATGTAGA
AAATGAGTGATCCAGCCC
-32bp
-48bp
-54bp
-60bp
-72bp
20. Which of the following is not necessarily a desired feature of a molecular diagnostic assay?
-Cost effectiveness
-Efficiency
-Nucleic acid detection
-Sensitivity
-Specificity