Reference no: EM13376077
Part A
1. Give the role & significance of O.R. in business & industry for scientific decisions.
2. "The primary contribution of the game theory has been its concept rather than its formal application to solving real life problems." Do you agree? Discuss.
3. What is queuing theory? Describe the different types of costs involved in a queuing system. In what areas of management can queuing theory be applied successfully? Give examples.
4. What do you mean by Simulation? Explain Monte Carlo Simulation in present business decision making.
5. Explain the terms: (a) Basic feasible solution; (b) Non-degenerate basic feasible solution; (c) Optimal solution and (d) Pivot column
Part B
6. Explain in brief with examples: (i) North West Corner rule (ii) Vogel's Approximation Method.
7. Show that assignment problems are particular cases of transportation problem. Can an assignment problem ever be a non degenerate transportation problem? Explain.
8. " Basic Problem in queuing theory is to strike an economic balance between the service cost and the waiting cost." Elucidate this statement by taking an example.
Case Study
M/s Gupta chemicals Ltd. Markets its product through five area distributors. The company has three plants the particulars of which are given below:
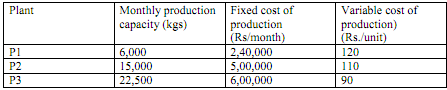
The selling price excluding freight is Rs. 250 per kg and the company has commitments to supple the following quantities to the distributors:
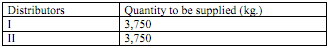
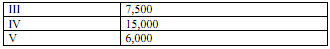
The transportation cost, rupees per unit (borne by the manufacturer), for supply for plants to distributor are as given below:
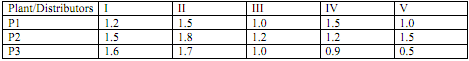
Determine the optimal tie-up between the plants and the distributors and the maximum profit company can make.
Part C
1. Every corner of the feasible region is defined by
(a) the intersection of 2 constraints lines
(b) Some subset of constraint lines and non negativity condition
(c) Neither of the above
2. G.J. Breveries Ltd. Have two bottling plants, one located at ‘G' and the other at ‘J'. Each plant produces three drinks - whisky, beer and brandy names A, B and C respectively. The number of bottles produced per day are as follows:
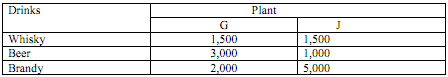
A market survey indicated that during the month of July, there will be a demand of 20,000 bottles of whisky, 40,000 bottles of beer and 44,000 bottles of brandy. The operating costs per day of plants at G & J are 600 and 400 monetary units. For how many days each plant be run in July so as to minimize the production cost, while still meeting the market demand?
(a) x1= 10, x2= 4, Max Z= 8,800
(b) x1= 12, x2= 4, Max Z= 8,800
(c) x1= 10, x2= 4, Max Z= 4,400
(d) x1= 12, x2= 2, Max Z= 2,200
3. Five machines are available to do five different jobs. From past records, the time (in hrs.) that each machine takes to do each job is known & given in the following table:
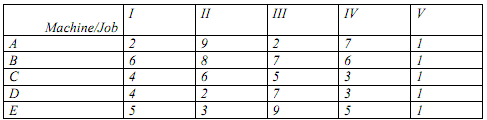
Find the assignment of machines to jobs that will minimize the total time taken.
(a) 10 hours
(b) 12 hours
(c) 13 hours
(d) 22 hours
4.In performing a simulation it is advisable to
(a) Use the results of earlier decisions to suggest the next decision to try
(b) Use the same number of trials for each decisions
(c) Simulate all possible decisions
(d) None of the above
Download:- OR.pdf