Reference no: EM13371855
Part-1 Firm Perspective
1. For the below three markets forms answer the following questions:
i) Perfectly competitive market
ii) Monopolistic competition
iii) Oligopoly
a) What are the main characteristics of each type of market form? Explain each one.
b) What is a real-life example which is similar to each market form from your country? In your answer explain why it is similar.
c) What is the long-run equilibrium in each market form? Why? Explain your answer with reference to relevant graphs.
d) Which market form do you think provides the best outcome for consumers? Why?
e) Which market form do you think provides the best outcomes for producers? Why?
Part 2: Macroeconomic Perspective
The following is taken from the European Economics Forecast Winter 2013 for Italy.
ITALY
Economic recession bottoming out in mid-2013
The protracted recession to end in mid-2013
The recession extended throughout 2012, completing six consecutive quarters of contraction in economic activity. As a result, in 2012 as a whole, real GDP is estimated to have declined by 2.2%.
Domestic demand fell significantly, as high uncertainty, tight financing conditions and the impact of fiscal consolidation (reduction in government spending) hit consumption and investment. This led to a collapse in imports, while exports increased on the back of sustained demand from non-EU trade partners. Indicators point to further contraction in economic activity in the first quarter of 2013, though at a slowing pace. Investment is set to decline - also due to still tight financing conditions for the private sector - while consumers continue to refrain from spending on the back of long declining real disposable income. By contrast, sustained demand from non-EU trade partners continues to support exports. As a result, domestic demand, and in particular investment in equipment, is set to resume growth in the second half of 2013.
However, the negative carry-over from 2012 implies that real GDP in 2013 as a whole is still projected to decline by 1%. Once again, net exports are set to provide a positive contribution to growth, as imports contract further. In 2014, the projected normalisation in financing conditions and reduced uncertainty are set to sustain activity. As a result, private consumption is expected to increase slightly more than disposable income due to improving confidence, while investment in equipment picks up.
As both imports and exports accelerate, net exports are no longer expected to contribute to growth. Real GDP is forecast to increase by 0.8%. The trade balance continues improving over the forecast horizon and in 2013 the current account is set to turn into surplus for the first time since 2001.
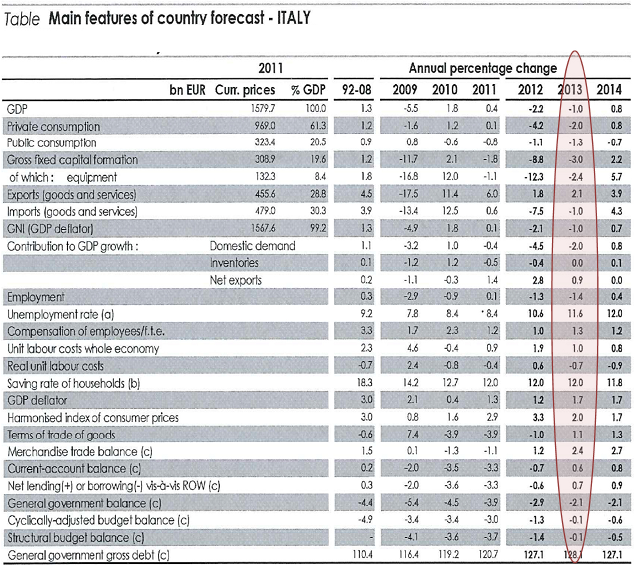
1. Based on the article and table above describe what is happening to all the components of real GDP in Italy in 2013 and how this affects overall GDP growth in 2013. Use theory and the information above to justify your answer.
2. Suppose the Italian economy is in the state described by the following table.
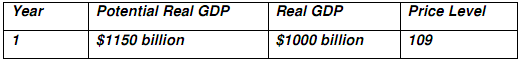
a) Represent this economy using the AD/AS model and explain the model.
b) What problem will occur in the economy if no fiscal policy is pursued? What fiscal policy tools could be used to combat the problem?
c) What will happen to the Italian economy in the long-run if no fiscal or monetary policy is pursed? Represent this on your graph and critically comment on whether you think this is a good outcome.