Reference no: EM13308167
1. Optimal Use of a Single Input. Julian Smyth is manages production at Taffy Apple Inc., a company that produces a variety of taffy/fruit candies. Over the last several months, he has varied then number of employees on his caramel apple production line, and found the following relationship.
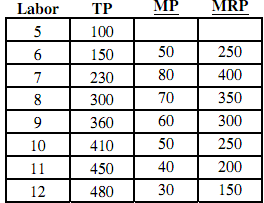
a. In the column labeled MP, calculate the marginal product of labor. (Note, make your first entry in row 6, as the change between 5 and 6 units of labor)
b. Suppose the apples sell for $5 (per dozen) box. Calculate the Marginal Revenue Product (MRP)
c. If labor costs $225 per day, how many laborers should the firm hire?
2. Optimal Use of a Single Input. A graphical representation.
a. In the coordinate axes provided below, illustrate the general relationship between MRP and the Price of Labor. Identify the equilibrium quantity of labor to hire. (Note, your graph need not use the numbers in problem 3. Just be certain to include ranges that illustrate gains from specialization and the law of diminishing returns in your graph.
b. Suppose that the candy workers union agrees to way concessions, that make the price of labor fall. In the coordinate axes below illustrate the effect on the equilibrium quantity of labor
c. Finally, suppose that the price of caramel apples increases. Illustrate the effect of this change on the equilibrium quantity of labor employed.
3. Optimal use of multiple inputs. In his shop, Julian Valenti retrofits sunroofs into automobiles. The process can use a combination of skilled labor and unskilled labor. Given his current mix of employees, the marginal product of the last unit of skilled labor is 3 sunroofs per day, and the marginal product of the last unit of unskilled labor is 1 sunroof per day. Current market rates for skilled and unskilled labor are $40 and $10, respectively. Is Julian using a least cost combination of inputs? If not, which of type of labor should he use relatively more?
4. Returns to Scale. Jake's Free Runoff Bottled Water Company Produces with the Long Run Production Function
Q = (KL)2/3
a. Currently K = 4 and L = 4. If Jake's doubles inputs to K=8 and L=8, will it realize increasing, constant or decreasing returns to scale (circle one)?
b. As a result, does Jake's enjoy economies of scale, diseconomies of scale, or does Jake's appear t be operating at Efficient Scale?
|
Find the maximum force exerted on the block from the spring
: An oscillator consists of a block of mass 0.600 kg connected to a spring. Find the maximum force exerted on the block from the spring
|
|
Model to explain the variability in the median school year
: Use the multiple regression model to explain the variability in the median school year, using a minimum of seven independent variables. Using the same model, thoroughly assess your model's diagnostics. Identify all relevant assessment dimensions, bri..
|
|
Write assembly-language program that counts all even numbers
: Write a HCS12 assembly-language program that counts all even numbers from a 10-variable, byte-sized array and moves the odd numbers to a new array.
|
|
Write a c program for that writes the value to memory
: Write a C program for a HCS12 microcontroller that writes the value, 0x78, to Memory Location VAR1 and then calls a delay function. The delay function should generate a delay of 0.25 milliseconds.
|
|
Operating at efficient scale
: Does Jake's enjoy economies of scale, diseconomies of scale, or does Jake's appear t be operating at Efficient Scale?
|
|
Compute the biologically equivalent dose given to the tumor
: A beam of particles is directed at a 0.014-kg tumor. There are 1.9 Ã- 1010 particles per second reaching the tumor, Find the biologically equivalent dose given to the tumor in 22 s
|
|
What is the persons absorbed dose in rads
: Over a year's time, a person receives a biologically equivalent dose of 24 mrem (millirems) from cosmic rays, What is the person's absorbed dose in rads
|
|
Obtain the inductance of the solenoid
: A 305 turn solenoid has a radius of 7.00 cm and a length of 24.0 cm. Find the inductance of the solenoid
|
|
Calculate the pressure at the bottom of the test tube
: An open test tube at 293 K is filled at the bottom with 12.1 cm of Hg and 5.6 cm of water is placed above the mercury. Calculate the pressure at the bottom of the test tube if the atmospheric pressure is 756 mm Hg.
|