Reference no: EM132306117 , Length: 900 Words
Assignment -
AIM - To improve the understanding of the working of oscillators and appreciate the importance of the Barkhausen criterion for obtaining sustained oscillation.
INTRODUCTION - Oscillators are electronic circuits that generate periodic signals (such as sine wave or other alternating waves) without the need of input signal. In another word, an oscillator converts the direct current from a power supply to an alternating current signal. The oscillator is the key circuit in any signal generators, which are widely used in many electronic systems. Oscillation can be produced as a result of positive feedback. In order to maintain a sustained oscillation in an electronic circuit, the Barkhausen criterion has to be met. The purpose of this coursework is to help students enhance their understanding of the working of oscillators through experiment. The experimental activities involve construction and testing of Wien bridge oscillators and investigate their waveform quality and stability against the Barkhausen criterion.
WIEN BRIDGE OSCILLATOR
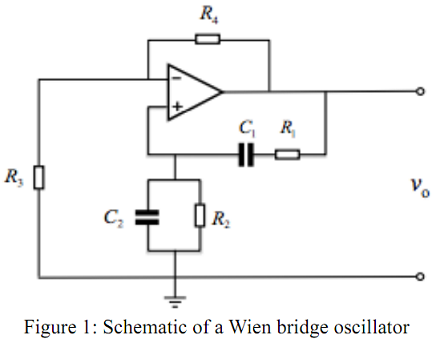
A Wien bridge oscillator is one of the widely used oscillators that generate sinusoidal signals. Figure 1 shows the circuit diagram of a basic Wien bridge oscillator. It consists of a noninverting op-amp and a positive feedback. For detailed understanding of the operating principle and the theory of the circuit, please refer to the relevant part of EN2083 lecture notes.
EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES
The experiment consists of three tasks. You are required to build and test the circuits as described below. You are encouraged to work together in a pair, but not more than two persons in a group. In order to complete all experiment activities successfully within limited laboratory time, you are advised to prepare for experiment in advance, including theoretical background, circuit design and familiarise with the detailed experimental procedures. During the experiment, please make sure that you record and collect all key data or results for your report.
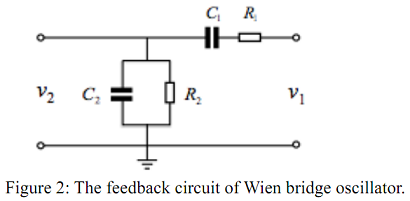
Task 1: This task focuses on understanding the characteristics of the "feedback" part of Wien bridge oscillator. Construct the feedback circuit shown in Figure 2 on a breadboard using the following component values: R1 = R2 = 8.1 kΩ and C1 = C2 = 18 nF. Apply a sinusoidal signal to the input, v1, and observe the amplitude and phase difference of the output voltage, v2 for a number of frequencies including 500Hz, 800Hz, 1100Hz, 1400Hz, and 2000Hz. You can explore more frequencies as you wish and pay attention to accurate measurement of the amplitude corresponding to 0o phase difference.
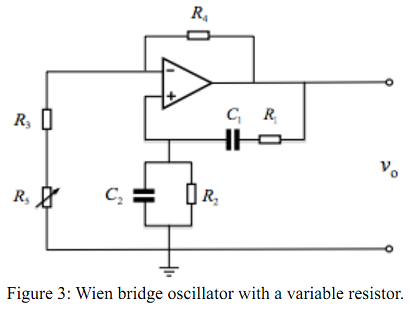
Task 2: Based on the circuit constructed in Task 1 (Figure 2), add the "non-inverting op-amp" part to form the complete circuit of a Wien bridge oscillator as shown in Figure 1, using a 741 op-amp with R3 = 2.2 kΩ and R4 = 5.1 kΩ. Observe the output signal using an oscilloscope and record your observation. Then, add a 500Ω variable resistor, R5, between R3 and the ground as shown in Figure 3. Observe the change in the output waveform with changing the resistance of the variable resistor R5. Also, use the FFT feature of the oscilloscope to characterise the purity of sinusoidal waves and pay particular attention to the best case and worse case scenarios (Note: you need to select appropriate scales for clear observation).
Task 3: The performance of Wien bridge oscillators can be improved with automatic gain control. This can be achieved by using a modified circuit shown in Figure 4, where two diodes, D1 and D2, and a resistor, R6, are added to control the gain of non-inverting op-amp within a desirable range (see Appendix C for details of how to define the gain range).
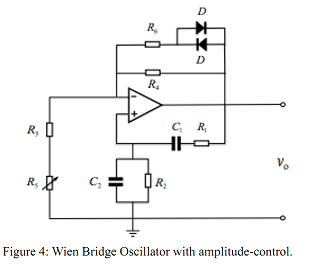
Based on the circuit you have already built on a breadboard in Task 2 (i.e., Figure 3), modify the circuit to obtain Figure 4 by adding two diodes (IN4148) and a resistor R6 = 15 kΩ. Observe the output waveforms (when changing the value of R5) and compare them with what you have observed in Task 2 and pay particular attention to the improvement.
|
How did the roosevelt corollary change america role
: How did the Roosevelt Corollary change America's role in the world? Assess the war's economic impact, including the expansion of factories due to wartime.
|
|
Sustainable development in the hospitality industry
: What are some of the unique challenges in sustainable development in the hospitality industry?
|
|
What were the causes of the american revolution
: What were the causes of the American Revolution? How did the British colonists evolve from good citizens to revolutionaries and back something as unique.
|
|
Disadvantages of using computer technology in decision
: Provide and explain examples of the advantages and disadvantages of using computer technology in decision-making
|
|
Observe the amplitude and phase difference
: Observe the amplitude and phase difference of the output voltage, v2 for a number of frequencies including 500Hz, 800Hz, 1100Hz, 1400Hz, and 2000Hz
|
|
Computer fraud and security measures in electronic commerce
: Understand the risks inherent in computer-based systems/ERP, including e- commerce, the role of ethics and the various internal control processes that need to
|
|
What were the main problems with articles of confederation
: What were the main problems with the Articles of Confederation that led to the Constitutional Convention of 1787? How did the national government under.
|
|
Countries of the european union has the highest birthrate
: What is your assessment of the attractiveness of the organic food industry ? Which countries of the European Union has the highest birthrate?
|
|
Compare the impacts of world war ii and the vietnam war
: In this essay, compare and contrastthe impacts of World War II and the Vietnam War on the American home front. In your answer, be sure to explain how each.
|