Reference no: EM132587436
NHM2420 Project, Quality and Production Management - University of Huddersfield
Section A
Answer All Questions
Question 1
i) There are 5 steps involved when defining a project, which of the following is the first?
A) Establish project priorities
B) Define the project scope
C) Verify the budget available
D) Assign team members to work on the project
E) Determine the required completion date
ii) The _________ is used to assist in making project trade-offs between schedule, budget, and performance objectives.
A) Responsibility matrix
B) Work breakdown structure
C) Project priority matrix
D) Work package
E) Criterion matrix
iii) The tendency for the project deliverables to expand over time-usually by changing requirements, specifications, and priorities-is called:
A) Scope erosion
B) Scope creep
C) Project bloat
D) Scope enhancement
E) Project add-ons
iv) Which of the following would best represent direct project costs?
A) Only labour
B) Only materials
C) Only equipment
D) Both labour and materials
E) Labour, materials and equipment
v) Reasons why estimating time and cost are important include all of the following EXCEPT
A) To schedule work
B) To determine how long the project should take and cost
C) To develop cash flow needs
D) To determine how well the project is progressing
E) To help establish a project selection process
vi) James is building a project network that involves testing a prototype. He must design the prototype (activity 1), build the prototype (activity 2), and test the prototype (activity 3). Activity one is the predecessor for activity 2 and activity 2 is the predecessor for activity 3. If the prototype fails testing, Bill must redesign the prototype; therefore, activity 3 is a predecessor for activity 1. This is an example of:
A) Conditional statements
B) Looping
C) Having more than one start node
D) Good network development
E) Natural network flow
vii) Which of the following will correctly calculate the total slack in an activity?
A) LS - ES
B) LF - EF
C) LS - LF
D) LF - ES
E) Either LS - ES or LF - EF
viii) Jessica just received the following information on her project:
PV =200, EV=300, AC=250, BAC=1500, EAC=1208.
In terms of cost at completion:
A) The project will currently finish under budget
B) The project will currently finish over budget
C) The project will currently finish on budget
D) The project will currently finish behind schedule
E) There is insufficient information to draw conclusions
ix) You are performing earned value technique on your project. After budget approval, an additional and unexpected cost item has been identified, which made the project more expensive some weeks ago. The item has meanwhile been paid by the project team, and it is expected that for the remaining duration of the project, costs will be as budgeted.
In this case, which is the best formula to calculate EaC (Estimate at Completion)?
A) EaC = BaC - CV
B) EaC = BaC / CPI
C) EaC = AC + BtC / CV
D) EaC = BaC / SPI
E) You cannot calculate EaC
x) Given the information in the following lag exercises, compute the early, late, and slack times for the project network. Which activities on the critical path have only the start or finish of the activity on the critical path?
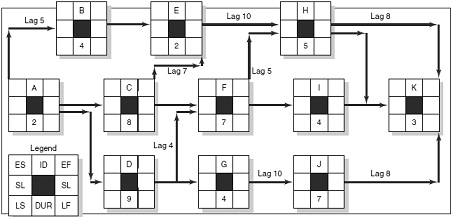
Question 2
(i) For the Failure or Hazard Rate, λ(t), reliability curve, indicate the three phases and discuss what the manufacturer of the product should understand about each phase and how the information can be used.
(ii) State five of the methods that can be used in Condition Based Maintenance.
(iii) Explain the differences between "Quality Improvement Teams" and "Quality Circles".
(iv) Using four diagrams illustrate the following:
1. Accurate and precise.
2. Accurate but not precise.
3. Precise but not accurate.
4. Neither precise or accurate.
(v) Provide the ISO9001 definition of Quality.
Section B
Answer Two Questions
Question 3
Use the information contained below in Figure Q2 to compress one time unit per move using the least cost method. Reduce the schedule until you reach the crash point of the network. For each move identify what activity(s) was crashed, the adjusted total cost, and explain your choice if you have to choose between activities that cost the same.
If the indirect costs for each duration are £1,500 for 17 weeks, £1,450 for 16 weeks, £1,400 for 15 weeks, £1,350 for 14 weeks, £1,300 for 13 weeks, £1,250 for 12 weeks, £1,200 for 11 weeks, and £1,150 for 10 weeks, what is the optimum cost-time schedule for the project? What is the cost?
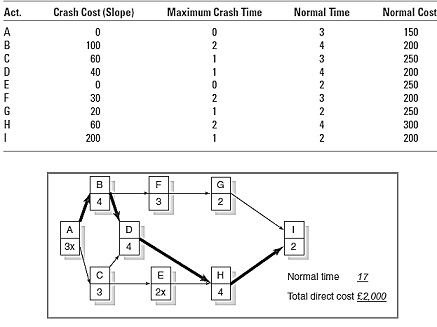
Figure Q3 -Crash cost and Network diagram
Question 4
i) How a cost-duration graph can be used by the project manager?
Draw the cost-duration graph and explain.
ii) What are the differences between bottom-up and top-down estimating approaches?
Under what conditions would you prefer one over the other?
iii) Given the time-phased work packages and network, complete the following baseline budget form (in Figure Q4) for the project.
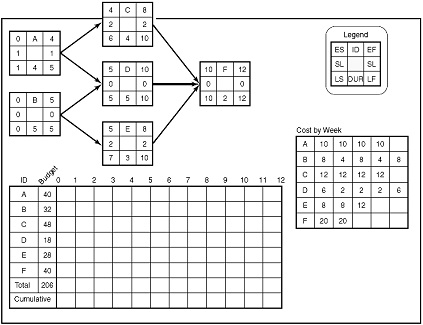
Question 5
An organisation has decided to embark on a Quality Improvement Programme. As an initial review concludes that there are problems with customer complaints, reducing market share, high levels of equipment downtime and high levels of scrap and rework.
Describe and discuss (with the aid of diagrams and/or charts) a suitable project plan for the reduction of total quality costs. Your plan should indicate how you can achieve short, medium and long term quality cost savings.
Question 6
The manufacturer of power supplies has decided to use Statistical Process Control (SPC), to determine if the process used in the manufacture of the power supplies is capable of meeting the customer's Acceptable Quality Level (AQL), i.e. fewer than 1% should operate outside the specified tolerance of 14 ± 0.25volts.
The manufacturer calculates process capabilities to ensure that the above requirements are met, taking a random sample of 50 power supplies from each batch of 1000 and subjecting them to a test operation. The latest random sample gave the following results:
|
14.20
|
14.00
|
14.10
|
14.00
|
14.10
|
|
13.95
|
14.10
|
13.95
|
14.15
|
14.05
|
|
14.00
|
14.15
|
14.05
|
14.05
|
14.00
|
|
14.10
|
14.05
|
14.00
|
14.10
|
14.05
|
|
14.00
|
13.95
|
14.05
|
14.00
|
13.95
|
|
14.05
|
14.05
|
14.10
|
13.95
|
14.15
|
|
14.00
|
13.90
|
14.05
|
14.20
|
14.00
|
|
14.10
|
14.15
|
14.00
|
13.90
|
14.10
|
|
13.90
|
14.00
|
13.85
|
14.10
|
14.05
|
|
14.15
|
14.10
|
14.05
|
14.00
|
13.95
|
a) Complete a process capability study using the capability chart provided.
b) How many power supplies would you predict are defective in the batch from which the above sample was taken?
c) Do the power supplies meet the customer's quality requirements?