Reference no: EM1375688
1. In each of the following types of growth, how is the rate of growth (dN/dt) influenced by the population size (N)?
Linear:
Exponential:
Logistic:
2. Note the following data concerning two species of paramecia. The abiotic factors (growth medium, temperature, etc) are identical in all flasks.
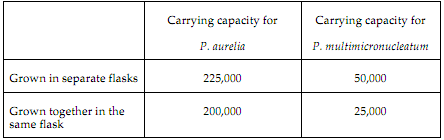
Is there evidence of competition between the two species of paramecia? Explain how you know.
If competition is occurring, does one species have a competitive advantage other the other? Explain how you know.
3. Note the following simple ecosystem.
Organisms:
Carnivorous fish (Secondary consumers)
Herbivorous fish (Primary consumers)
Photosynthetic algae (Producers)
Bacteria (These organisms break down the bodies of dead organisms. Decomposers use oxygen to aid decomposition.)
Three nutrients to consider (there are others, but three are important for understanding this question):
Nitrogen
Phosphorous (in the form of phosphate)
Oxygen
The ambitious owner of a "pay as you fish" lake who has a dim understanding of elemental cycles decides to increase the output of carnivorous fish in the lake (which are larger and more fun to catch) by adding phosphate to the lake water. The owner did this after learning that insufficient phosphates often limit growth. For a while, there were more algae and the herbivorous fish that feed on them and the carnivorous fish that feed on the herbivorous ones. For a while, everyone was happy.
However, the owner had not fully investigated the entire nutritional requirements of the algae. As a result disaster struck, the algae died, and then the primary and secondary consumers started to die, from a lack of oxygen.
Please draw a chart that shows the numbers of algae, herbivorous and carnivorous fish over time and explain what happened to the producers and consumers in the lake. Also, draw a similar chart of the three nutrients.
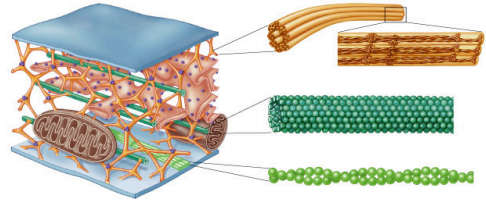
Cytoskeletal components
1. Label the figure below with the following items:
a) microfilament
b) microtubule
c) intermediate filament
2. For each component name (and/or describe) the protein subunits that it consists of.
3. For each component name the motor proteins that interact with it.
Motor proteins and disease
Associate each one of these symptoms with a defective motor protein, and explain how the defect in that protein is related to the disease.
1. Low levels of secreted proteins in the blood and inside the intestines.
2. Male infertility.
3. Low muscle tone and excessive fatigue after exercise.
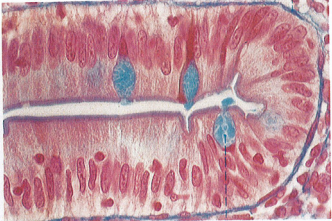
Epithelial cells and the basal lamina
1. Label the picture below with the following items:
a) the lumen of the intestines
b) the row of epithelial cells
c) the nuclei of the epithelial cells
d) the basal lamina
Membrane structure
1. Draw an accurate picture of a membrane surrounding a cell. You don't have to worry about the inside of the cell or the details of the bilayer, but your drawing should reflect the relative thinness of the membrane and the fact that it's flexible.
The experiment that was done to determine that the membrane of red blood cells is a lipid bilayer was described in lecture.
2. Write down all the individual steps in this experiment in detail. Hint, imagine you were actually doing this experiment, like in lab, and write down each step that you'd have to do. There should be at least six steps (be sure to include one or more analysis steps).
3. Diagram the trough apparatus used to make a monolayer of phospholipids.
4. What result would you have expected if the membrane were a monolayer of phospholipids?
5. Why are red blood cells a good choice for this experiment, as opposed to a cell that has a less regular shape.
6. Red blood cells are unusual eukaryotic cells that have lost their nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. How is the absence of nucleus and organelles an advantage for the experiment?
7. The axon of neurons (nerve cells) is the long part that carries an electrical signal (say the signal to move a finger) from one part of the body to another. The axon of many neurons is surrounded by several layers of membrane to improve the insulation around each axon. Based on the RBC experiment, design an experiment to determine how many membrane layers the average axon is surrounded by. Hint, certain parts of the spinal cord, which are almost entirely axons, can be dissected out.