Reference no: EM132304134
Question 1. Let A→ be a unit vector along the axis of rotation of a purely rotating body and B→ be a unit vector along the velocity of a particle P of the body away from the axis. The value of A→.B→ is
(a)1 (b)-1 (c) 0 (d) None of these.
Question 2. A body is uniformly rotating about an axis fixed in an inertial frame of reference; Let A→ be a unit vector along the axis of rotation and B→ be the unit vector along the resultant force on a particle P of the body away from the axis The value of A→ . B→ is
(a) 1 (b) -1 (c) 0 (d) none of these.
Question 3.
A particle moves with a constant velocity parallel to the X-axis. Its angular momentum with respect to the origin
(a) is zero (b) remains constant (c) goes on increasing (d) goes on decreasing. .
Question 4. A body is in pure rotation. The linear speed v of a particle, the distance r of the particle from the axis and the angular velocity ω of the body are related as ω = v/r. Thus
(a) ω ∝ 1/r (b) ω ∝ r (c) ω = 0 (d) ω is independent of r.
Question 5. Figure (10-Q3) shows a small wheel fixed coaxially on a bigger one of double the radius. The system rotates about the common axis. The strings supporting A and B do not slip on the wheels. If x and y be the distances travelled by A and B in the same time interval, then
(a) x = 2 y (b) x = y (c) y = 2 x (d) none of these.
Question 6. A body is rotating uniformly about a vertical axis fixed in an inertial frame. The resultant force on a particle of the body not on the axis is
(a) vertical (b) horizontal and skew with the axis (c) horizontal and intersecting the axis (d) none of these.
Question 7. A body is rotating nonuniformly about a vertical axis fixed in an inertial frame. The resultant force on a particle of the body not on the axis is
(a) vertical (b) horizontal and skew with the axis (c) horizontal and intersecting the axis (d) none of these.
Question 8. Let F→ be a force acting on a particle having position vector r→. Let Τ→ be the torque of this force about the Origin, then
(a) r→.Τ→ = 0 and F→.Τ→ =0 (b) r→.Τ→ = 0 but F→.Τ→ ≠ 0 (c) r→.Τ→ ≠ 0 but F→.Τ→ = 0 (d) r→.Τ→ ≠ 0 but F→.r→ = 0
Question 9. One end of a uniform rod of mass in and length l is clamped. The rod lies on a smooth horizontal surface and rotates on it about the clamped end at a uniform angular velocity ω. The force exerted by the clamp on the rod has a horizontal component
(a) mω2l (b) zero (c) mg (d) 1/2 mω2l
Question 10. A uniform rod is kept vertically on a horizontal smooth surface at a point O. If it is rotated slightly and released, it falls down on the horizontal surface. The lower end will remain
(a) at O. (b) at a distance less than l/2 from O (c)at a distance l/2 from O (d) at a distance larger than l/2 from O.
Question 11. A circular disc A of radius r is made from an iron plate of thickness t and another circular disc B of radius 4r is made from an iron plate of thickness t/4. The relation between the moments of inertia IA and IB is
(a) IA > IB (b) IA = IB (c) IA < IB (d) depends on the actual values of t and r.
Question 12. Equal torques act on the discs A and B of the previous problem, initially both being at rest. At a later instant, the linear speeds of a point on the rim of A and another point on the rim of B are vA and uB respectively. We have
(a) vA > vB (b) vA = vB (c) vA < vB (d) the relation depends on the actual magnitude of the torques.
Question 13. A closed cylindrical tube containing some water (not filling the entire tube) lies in a horizontal plane. If the tube is rotated about a perpendicular bisector, the moment of inertia of water about the axis
(a) increases (b) decreases (c) remains constant (d) increases if the rotation is clockwise and decreases if it is anticlockwise.
Question 14. The moment of inertia of a uniform semicircular wire of mass M and radius r about a line perpendicular to the plane of the wire through the centre is
(a) Mr2 (b) 1/2Mr2 (c) 1/4Mr2 (d) 2/5 Mr2
Question 15. Let I1 and I2 be the moments of inertia of two bodies of identical geometrical shape, the first made of aluminium and the second of iron.
(a) I1 < I2 (b) I1 = I2 (C) I1 > I2 (d) relation between 1, and 12 depends on the actual shapes of the bodies.
Question 16. A body having its centre of mass at the origin has three of its particles at (a,0,0), (0,a,0), (0,0,a), The moments of inertia of the body about the X and Y axes are 0.20 kg-m2 each. The moment of inertia about the Z-axis
(a) is 0.20 kg-m2 (b) is 0.40 kg-m2 (c) is 0.20 √2 kg-m2 (d) cannot be deduced with this information.
Question 17. A cubical block of mass M and edge a slides down a rough inclined plane of inclination θ with a uniform velocity. The torque of the normal force on the block about its centre has a magnitude
(a) zero (b) Mga (e) Mga sinθ (d) 1/2 Mga sinθ.
Question 18. A thin circular ring of mass M and radius r is rotating about its axis with an angular speed ω. Two particles having mass m each are now attached at diametrically opposite points. The angular speed of the ring will become
(a) ωM/M + m (b) ωM/M + 2m (c) ω(M -2m)/(M+2m) (d)ω(M + 2m)/M
Question 19. A person sitting firmly over a rotating stool has his arms stretched. If he folds his arms, his angular momentum about the axis of rotation
(a) increases (b) decreases (c) remains unchanged (d) doubles.
Question 20. The centre of a wheel rolling on a plane surface moves with a speed v0. A particle on the rim of the wheel at the same level as the centre will be moving at speed
(a) zero (b) vo (c) √2 v0 (d) 2 v0
Question 21. A wheel of radius 20 cm is pushed to move it on a rough horizontal surface. It is found to move through a distance of 60 cm on the road during the time it completes one revolution about the centre. Assume that the linear and the angular accelerations are uniform. The frictional force acting on the wheel by the surface is
(a) along the velocity of the wheel (b) opposite to the velocity of the wheel (c) perpendicular to the velocity of the wheel (d) zero.
Question 22. The angular velocity of the engine (and hence of the wheel) of a scooter is proportional to the petrol input per second. The scooter is moving on a frictionless road with uniform velocity. If the petrol input is increased by 10%, the linearavoet occity of' the scooter is increases) by
(a) 50% (b) 10% (c) 20% (d) 0%
Question 23. A solid sphere, a hollow sphere and a disc, all having same mass and radius, are placed at the top of a smooth incline and released. Least time will be taken in reaching the bottom by
(a) the solid sphere (b) the hollow sphere (c) the disc (d) all will take same time
Question 24. A solid sphere, a hollow sphere and a disc, all having, same mass and radius, are placed at the top of an incliend plan and released. The friction coefficients between the objects and the incline are same and not sufficient allow pure rolling. Least time will be taken in reaching the bottom by
(a) the solid sphere
(b) the hollow sphere
(c) the disc
(d) all will take same time
Question 25. In the previous question, the smallest kinetic energy at the bottom of the incline will be achieved by
(a) the solid sphere (b)the hollow sphere (c) the disc (d) all will achieve same kinetic energy,
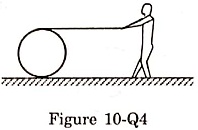
Question 26. A string of negligible thickness is wrapped several times around a cylinder kept on a rough horizontal surface. A man standing at a distance/from the cylinder holds one end of the string and pulls the cylinder towards him (figure 10-Q4). There is no slipping anywhere. The length of the string passed through the hand of the man while the cylinder reaches his hands is
(a) l (b) 2l (c) 3l (d) 4l.
OBJECTIVE II
1. The axis of rotation of a purely rotating body
(a) must pass through the centre of mass
(b) may pass through the centre of mass
(c) must pass through a particle of the body
(d) may pass through a particle of the body.
2. Consider the following two equations
(A) L = Iω (B) dL/dt = Τ
In noninertial frames
(a) both A and B are true (b) A is true but B is false (c) B is true but A is false (d) both A and B are false.
3. A particle moves on a straight line with a uniform velocity. Its angular momentum
(a) is always zero
(b) is zero about a point on the straight line
(c) is not zero about a point away from the straight line
(d) about any given point remains constant.
4. If there is no external force acting on a nonrigid body, which of the following quantities must remain constant?
(a) angular momentum (b) linear momentum c) kinetic energy (d) moment of inertia.
5. Let IA and IB be moments of inertia of a body about two axes A and B respectively. The axis A passes through the centre of mass of the body but B does not.
(a) IA < IB (b) If IA < IB the axes are parallel (c) If the axes are parallel, IA < IB (d) If the axes are not parallel, IA ≥ IB.
6. A sphere is rotating about a diameter.
(a) The particles on the surface of the sphere do not have any linear acceleration.
(b) The particles on the diameter mentioned above do not have any linear acceleration.
(c) Different particles on the surface have different angular speeds.
(d) All the particles on the surface have same linear speed.
7. The density of a rod gradually decreases from one end to the other. It is pivoted at an end so that it can move about a vertical axis through the pivot. A horizontal force F applied on the free end in a direction P to the rod. The quantities, that do not 'depend on which end of the rod is pivoted, are
(a) angular acceleration
(b) angular velocity when the rod completes one rotation
(c) angular momentum when the rod completes one rotation
(d) torque of the applied force.
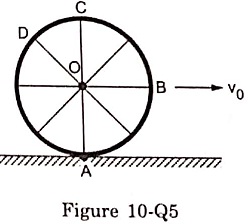
8. Consider a wheel of a bicycle rolling on a level road at a linear speed vo (figure 10-Q5).
(a) the speed of the particle A is zero
(b) the speed of B, C and D are all equal to vo
(c) the speed of C is 2 v0
(d) the speed of B is greater than the speed of O.
9. Two uniform solid spheres having unequal masses and unequal radii are released from rest from the same height on a rough incline. If the spheres roll without slipping,
(a) the heavier sphere reaches the bottom first
(b) the bigger sphere reaches the bottom first
(c) the two spheres reach the bottom together
(d) the information given is not sufficient to tell which it sphere will reach the bottom first.
10. A hollow sphere and a solid sphere having same mass and same radii are rolled down a rough inclined plane.
(a) The hollow sphere reaches the bottom first.
(b) The solid sphere reaches the bottom with greater speed.
(c) The solid sphere reaches the bottom with greater kinetic energy,
(d) The two spheres will reach the bottom with same linear momentum.
11. A sphere cannot roll on
(a) a smooth horizontal surface
(b) a smooth inclined surface
(c) a rough horizontal surface
(d) a rough inclined surface.
12. In rear-wheel drive cars, the engine rotates the rear wheels and the front wheels rotate only because the car moves. If such a car accelerates on a horizontal road, the friction
(a) on the rear wheels is in the forward direction
(b) on the front wheels is in the backward direction
(c) on the rear wheels has larger magnitude than the friction on the front wheels
(d) on the car is in the backward direction.
13. A sphere can roll on a surface inclined at an angle θ if the friction coefficient is more than 2/7 g tanθ Suppose the friction coefficient is 1/7g tanθ. If a sphere is released from rest on the incline,
(a) it will stay at rest
(b) it will make pure translational motion
(c) it will translate and rotate about the centre
(d) the angular momentum of the sphere about its centre will remain constant.
14. A sphere is rolled on a rough horizontal surface. It gradually slows down and stops. The force of friction tries to
(a) decrease the linear velocity
(b) increase the angular velocity
(c) increase the linear momentum
(d) decrease the angular velocity.
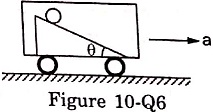
15. Figure (10-Q6) shows a smooth inclined plane fixed in a car accelerating on a horizontal road. The angle of incline 8 is related to the acceleration a of the car as a = g tanθ. If the sphere is set in pure rolling on the incline,
(a) it will continue pure rolling
(b) it will slip down the plane
(c) its linear velocity will increase
(d) its linear velocity will slowly decrease.