Reference no: EM132524645
MITS4004 IT Networking and Communication - Victorian Institute of Technology
Learning outcome 1: Identify the operation of the protocols that are used inside the Internet and use the seven-layer model to classify networking topology, protocol and security needs.
Learning outcome 2: Evaluate LAN technology issues, including routing and flow control. Explain the difference between switches and routers. Build and troubleshoot Ethernet, Wi-Fi and Leased line networks. Connect networks with routers.
Learning outcome 3: Critically analyse specific processes and functions that apply to a layered network model, with specific reference to TCP/IP; Subnet a network using multi-level subnetting and provide a subnetted IP design based on a given topology or business profile;
Learning outcome 4: Evaluate the business implications of the proposed network application through the use of a network performance simulator or Analyzer and recommend alternates that would improve on the network performance.
Problem 1: Understand IP Addressing scheme
IPv4 addressing
Using the IP address and subnet mask shown write out the network address:
|
IP network
|
|
|
150.201.21.19
255.255.0.0
|
|
|
101.10.18.2
255.255.0.0
|
|
|
10.10.10.10
255.255.255.0
|
|
|
203.20.35.215
255.255.255.0
|
|
|
117.15.2.51
255.255.0.0
|
|
IPv4 subnetting
Write the correct default subnet mask for each of the following addresses:
|
IP Network address
|
|
|
223.69.230.250
|
|
|
77.251.200.51
|
|
|
12.0.0.0
|
|
|
223.0.0.0
|
|
|
191.123.0.0
|
|
|
192.1686.1.0
|
|
Subnet the following sub-network into 4 equal size subnets
Problem 2: Building a Network
Use the Cisco Packet Tracer simulation tool to build and test a small data network provided below. Configure router, switch and end devices. While configuring, you must
• change router name to R1-Student ID (Example: R1- 44912)
• change end devices name to PC1-Student ID and PC3-Student ID (use group members Student ID)
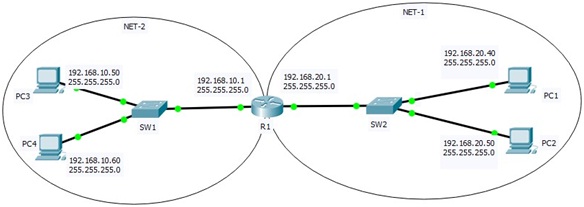
What to submit in Problem 2?
• Screenshots of detailed configuration you have made for all the devices.
• Screenshots as an evidence of successful connection between NET-1 (PC3) and NET 2 (PC1) (using ping to verify the connectivity).
Problem 3: Wireshark Lab: ICMP v7.0
In this task, you will explore several aspects of the ICMP protocol using WIRESHARK. Wireshark is a free and open-source packet analyzer. It is used for network troubleshooting, analysis, software and communications protocol development, and education.
• ICMP messages generating by the Ping program;
1. ICMP and Ping
Let's begin our ICMP adventure by capturing the packets generated by the Ping program. The Ping program is simple tool that allows anyone (for example, a network administrator) to verify if a host is live or not. The Ping program in the source host sends a packet to the target IP address; if the target is live, the Ping program in the target host responds by sending a packet back to the source host. As you might have guessed (given that this lab is about ICMP), both Ping packets are ICMP packets.
Do the following1:
• Let's begin this adventure by opening the Windows Command Prompt application. You can
also use the MacOS or Linux terminal.
• Start up the Wireshark packet sniffer and begin Wireshark packet capture.
• The ping command is in c:\windows\system32, so type either "ping -n 10 hostname" in the MS-DOS command line (without quotation marks), where hostname is a host on another continent.
• MacOS/Linux ping -c 10
• Try ping multiple times some of the packets will get lost that is ok.
• When the Ping program terminates, stop the packet capture in Wireshark.
What to submit in Problem 3?
• You should hand in a screen shot of the Command Prompt/Terminal window similar to
Figure 1 above. Annotate the ScreenShot2 to explain your answer. To print a packet, use File-
>Print, choose Selected packet only, choose Packet summary line, and select the minimum amount of packet detail that you need to answer the question.
You should answer the following questions:
1. What is the IP address of your host? What is the IP address of the destination host?
2. Examine one of the ping request packets sent by your host. What are the ICMP type and code numbers? What other fields does this ICMP packet have? How many bytes are the checksum, sequence number and identifier fields?
3. Examine the corresponding ping reply packet. What are the ICMP type and code numbers? What other fields does this ICMP packet have? How many bytes is the checksum field?
4. Wireshark is a software that analyses packets sent throughout a network. In your opinion, why analysing a network in a real time is necessary?
The report should be prepared in Microsoft word and uploaded on to the LMS. The report should be a properly constructed as an academic report. The report should include references in IEEE style.
Attachment:- IT Networking and Communication.rar