Reference no: EM13925033
1.Which of the following is an activity-based cost driver?
All of these answers are correct.
Number of machine setups
Machine hours
Material cost
2.Which of the following costs is likely to be driven by machine usage?
Factory insurance
Factory rent
Factory utilities
Depreciation on factory building
3.What is the principal reason that direct labor hours is no longer an effective base for allocating indirect costs in many modern manufacturing companies?
Changes in generally accepted accounting principles
Workers are not as productive as they were in the past
Movement from full-time to part-time workers
Automation
4.Costs incurred to avoid nonconforming products are:
failure costs.
appraisal costs.
prevention costs.
voluntary costs.
5.Benitez Company makes wicker and wooden slat picnic baskets. It requires approximately 1 hour of labor to make one basket of either type. Wicker baskets are produced in batches of 100 units and require 0.5 machine hours per basket. Wooden slat baskets are produced in batches of 50 units and require 0.75 machine hours per basket. Setup is required for each batch. During the most recent accounting period, the company made 8,000 wicker baskets and 2,000 wooden slat baskets. Setup costs amounted to $24,000 for the baskets produced during the period. If activity-based costing is used to allocate overhead costs to the two products, the amount of setup cost assigned to the wicker baskets will be:
$19,200.
$12,000.
$17,455.
$16,000.
6. The Farber Company recorded the following costs of quality during the current period:

Which choice below represents the correct amount of prevention and appraisal costs?
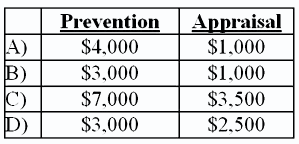
Choice A
Choice C
Choice D
Choice B
7.
The Tangier Company is considering eliminating the following product line:
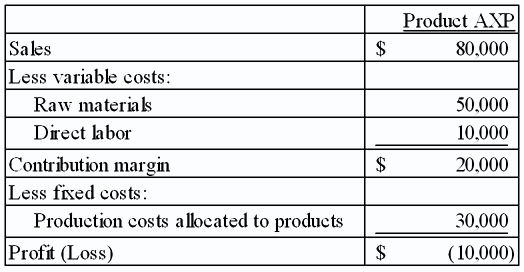
7.What amount of cost is avoidable if Tangier outsources production of this product?
$60,000
$20,000
$50,000
$90,000
8.Which type of cost drivers is most appropriate for most automated processes?
Direct labor-based drivers
All of these answers are correct.
Activity-based drivers
Volume-based drivers
9.Valspar Company produces several lines of laundry hampers. The factory is highly automated and uses an activity-based costing system to allocate overhead costs to its various products. During the upcoming period, the company expects to produce 72,000 units. The costs and cost drivers associated with four activity cost pools are given below:
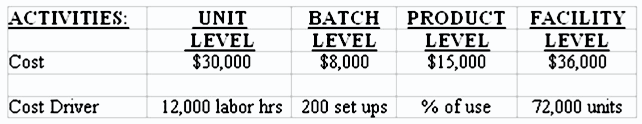
Production of 20,000 units of its popular foldable hamper required 3,000 labor hours, 75 setups, and consumed one-third of the product sustaining activities. What amount of unit-level costs will be allocated to the product?
$2,500
$6,000
$5,000
$7,500
10.Which of the following is an internal failure cost?
rev: 03_12_2014_QC_46491
Warranty replacement costs
Costs to rework defective units
Depreciation on testing equipment
Engineering and design costs
11.Roscoe Company produces a variety of garden tools in a highly automated manufacturing facility. The costs and cost drivers associated with four activity cost pools are given below:
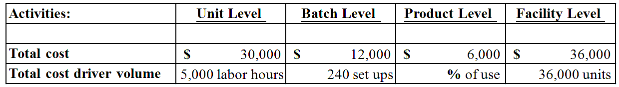
Production of 10,000 units of a hand-held tiller required 1,000 labor hours, 80 setups, and consumed 25% of the product sustaining activities. Assuming the company uses activity-based costing, how much total overhead will be allocated to this tool?
$21,500
$84,000
$11,500
$26,000
12.A product-level activity center would likely include all of the following costs except:
materials handling costs.
engineering development costs.
packaging design costs.
legal fees to obtain and protect patents.
13.Keene Company allocates overhead on the basis of direct labor hours. It allocates overhead costs of $8,000 to two different jobs as follows:
Job 1: (10 hours) = $4,000; Job 2: (10 hours) = $4,000
The production process for Job 2 was then automated. Now Job 2 requires only two hours of direct labor but four hours of mechanical processing. As a result, total overhead increased to $12,000. How much overhead cost will be assigned to Job 1 after automation?
$6,000
$10,000
$4,000
$2,000
14.Which of the following activity costs should usually be ignored when making a decision regarding whether to eliminate a product?
Unit-level costs
Facility-level costs
Product-level costs
Batch-level costs