Reference no: EM13922909
A Computing bond price and recording issuance LO P1
Hartford Research issues bonds dated January 1, 2013, that pay interest semiannually on June 30 and December 31. The bonds have a $26,000 par value and an annual contract rate of 12%, and they mature in 10 years. (Table B.1, Table B.2, Table B.3, and Table B.4) (Use appropriate factor(s) from the tables provided. Round all table values to 4 decimal places, and use the rounded table values in calculations.)
Table B4 -
Record the issue of bonds with a par value of $26,000 cash on January 1, 2013. Assume that the market rate of interest at the date of issue is 14%.Record the issue of bonds with a par value of $26,000 cash on January 1, 2013. Assume that the market rate of interest at the date of issue is 14%.
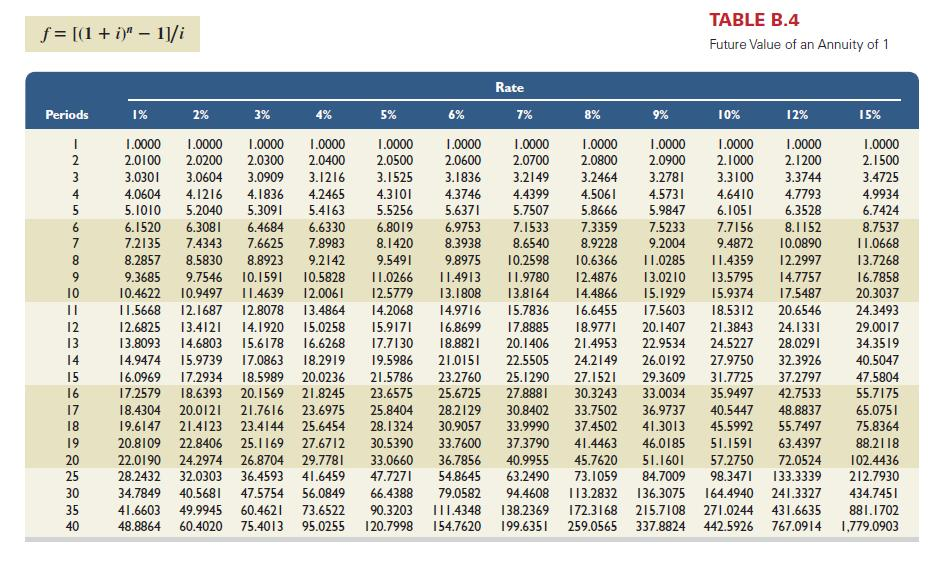 Record the issue of bonds with a par value of $26,000 cash on January 1, 2013. Assume that the market rate of interest at the date of issue is 14%.
Record the issue of bonds with a par value of $26,000 cash on January 1, 2013. Assume that the market rate of interest at the date of issue is 14%.
|
Decline and erratic trend in cash flows from operations
: John Young is a new assistant controller at Richmond Electronics, a large regional consumer electronics chain. Before John's recruitment, he was aware of Richmond's long trend of moderate profitability. The reports on his desk confirm the slight, but..
|
|
Subcontracting can handle a maximum
: Subcontracting can handle a maximum of 10 units per month. Beginning inventory is zero. Develop a plan that minimizes total cost. No back orders are allowed. Regular capacity Regular production.
|
|
Use a combination of overtime inventory
: Use a combination of overtime inventory, and subcontracting to handle variations in demand. Use overtime up to 750 cases per period and inventory to handle variations indemand.
|
|
Develop an aggregate plan using each of the following
: Develop an aggregate plan using each of the following guidelines and compute the total cost for each plan. You will need extra output in April and August to accommodate demand in the following months.
|
|
Market rate of interest
: Record the issue of bonds with a par value of $26,000 cash on January 1, 2013. Assume that the market rate of interest at the date of issue is 14%.
|
|
Develop a chase plan that matches the forecast
: Develop a chase plan that matches the forecast and compute the total cost of your plan. Over time is $ 60 per hundred bolts. Regular production can be less than regular capacity.
|
|
Compare the costs to a level plan that uses inventory
: Compare the costs to a level plan that uses inventory to absorb fluctuations. Inventory carrying cost is $ 2 per engine per month. Backlog cost is $ 90 per engine per month. There should not be a backlog in the lastmonth.
|
|
Modify your plan from part a to accommodate that new
: Suppose now that backlogs are not allowed. Modify your plan from part a to accommodate that new condition as economically as possible. The limits on overtime and subcontracting remain the same.
|
|
Use subcontracting to make up any needed output
: Use steady regular output of 400 units per month, use overtime as needed for up to 40 units per month, and use subcontracting to make up any needed output to match the forecast.
|