Reference no: EM133030325
LSGI 2224 Geo-Referencing Systems - The Hong Kong Polytechnic University
Question 1. 3D Coordinate conformal transformation is frequently used in geodesy and land surveying. The geodetic datum transformation from Hong Kong geodetic coordinates system (ITRF96) to Macao geodetic coordinates system (ITRF2005) have the attached rigorous formula:
Answer the following questions with detailed step-by-step derivations/calculations
(a) Assume that you have developed the following formula for Macao to Hong Kong geodetic coordinates system transformation:
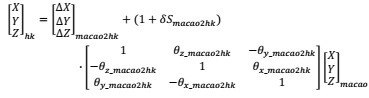
(b) Simplify your Bursa-Wolf transformation model into the following format through matrix operation.
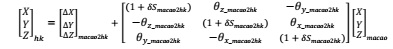
(c) Numerically calculate the δSmacao2hk so that (1 + δShk2macao)-1 in equation (2) can be written as (1 + δSmacao2hk). Express the δSmacao2hk in the unit of ppm, same as δShk2macao.
(d) Using the following approximation rule,
cos(θ??) ≈ 1
sin(θy) ≈ θy (radians)
sin(θz) sin(θ??) ≈ 0
Simplify the rotation matrix [Rx[θ??_hk2maco]-1 [Ry[θy_hk2maco]-1 [Rz[θz_hk2maco]-1 in equation so that it will eventually read like:
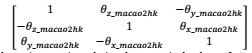
Write the simplified rotation matrix and give the numerical values of θx_macao2hk, θy_macao2hk, and θz_macao2hk.
(e) Numerically calculate 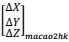 .Simplify the
.Simplify the
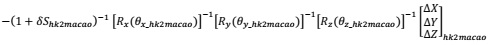 in equation (2) so that it can be simplified as
in equation (2) so that it can be simplified as
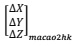 .
.
(f) Write your final 3D coordinate transformation formula for Macao to Hong Kong geodetic coordinates system transformation in the format:
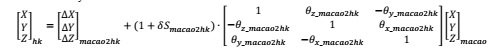
(g) There is one point  , calculate its corresponding coordinates
, calculate its corresponding coordinates 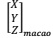
(h) There is one point 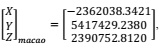 calculate its corresponding coordinates
calculate its corresponding coordinates 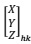 using the formula you obtain in (f).
using the formula you obtain in (f).
Question 2. The following are the formulas to convert the cartesian coordinates into geodetic coordinates. There are one points
e2 = f(2-f)
N = a/√(1-e2sinΦ)
p = √(X2 + Y2)
tan(λ) = Y/X
tan(Φ) = z + Ne2sin(Φ)/p
h = p/cos(Φ) - N
There is one point in Hong Kong with cartesian coordinate in the WGS84 ECEF as: X=-2411011.8949 meters, Y=5380267.2632 meters, Z=2425129.0941 meters.
(a) For the WGS84 ellipsoid, the size and shape parameters are given as semi-major axis a= 6378137.0 m; inverse of flattening=298.257223563, respectively. Calculate the geodetic coordinates (latitude, in the format of 22°56′23.984565′′ N; longitude, in the format of 114°25′25.124234′′E; and height, in the format of 111.1234 meter) of this point on the WGS 84 ellipsoid.
(b) For the International Hayford (1910) ellipsoid, which is also used in Hong Kong, the size and shape parameters are given as semi-major axis a= 6378388.0 m; inverse of flattening=297.0, respectively. Assume that the origin and orientation of the International Hayford (1910) ellipsoid are same as those of the WGS84 ellipsoid. Calculate the geodetic coordinates (latitude, in the format of 22°56′23.984565′′ N; longitude, in the format of 114°25′25.124234′′E; and height, in the format of 111.1234 meter) of this point on the International Hayford (1910) ellipsoid.
Attachment:- Geo-Referencing Systems.rar