Reference no: EM13708403
Question 1 :
A company changes stoping methods and discovers that the new method gives a substantially higher dilution rate and yet the profit margin is higher. Show by simple calculation how this can come about.
Question 2 :
Three basic methods of underground coal mining exist, name the three methods. Briefly compare and contrast the three methods, use sketches where ever possible and discuss the following:
a) Panel/pillar dimensions
b) Production methods
c) equipment
Question 3 :
Discuss the points you would consider when selecting a production method or methods for a particular ore body. Indicate which points you consider to be the most important.
Question 4 :
An ore body is mined by shrinkage stoping from a vertical shaft. Draw one or more simple sections to show the following details:
• Ore/waste pass systems
• Stope development
• Extraction level or levels
• Sub-levels
• Slot raises
Question 5 :
In multiple level room and pillar operations what potential problems exist due to the various levels interacting with each other. What methods are available to limit the effects of this interaction?
Question 6 :
In blockel caving what are the important criteria in planning the layout of development and supervising extraction?
Question 7:
What are the implications in the mining and treatment of sulphide ore, which tends to oxidise readily? What methods could be used to mine such ores?
Question 8 :
Illustrate a modern longwall coalface including the face and a short section of the gates. Note show all equipment and label the diagram clearly.
Question 9 :
Compare and contrast room and pillar mining with longwall mining in terms of economics, safety, productivity and depth of cover.
Question 10 :
Describe a method of open stoping in detail. What are the advantages and disadvantages of open stoping over other methods of mining similar ore bodies?
Question 11 :
To be successful in Sub-level caving, careful controlled draw point mucking must be practiced. Discuss this from a point of view of:
a) An individual draw point
b) A group of closely spaced drawpoints
Question 12 :
Compare and contrast longwall advancing and retreating methods of coal mining.
Question 13 :
A retreat longwall coal mining system utilises twin accesses on both the intake and return sides of a panel whose face width is 300m. If the access drives are 5m wide and chain pillars are 20m wide between the accesses determine the extraction ratio for the following cases:
a) Panel under development
b) Panel under production
It may be assumed that rib pillars 40 m wide are left for support between panels. It can also be assumed that a barrier pillar of 40 m width is left to protect the main mine entries and that the panel length is 3km.
Question 14 :
Describe in detail one method of pillar extraction in room and pillar mining.
Question 15 :
What methods of mining can be applied to the mining of inclined ore bodies dipping in the range 30 to 60 degrees? Describe one such method in detail citing an example of its application.
Question 16 :
Backfill is becoming more widely applicable in underground mining. What methods of backfilling can be applied? Describe these in detail citing
examples of their use, advantages and disadvantages of the method.
Question 17 :
With the aid of sketches describe the mining sequence applied in a mechanised cut and fill mining operation.
Question 18 :
In relation to underground metalliferous mining define:
a) Recovery
b) Dilution
What methods of sampling are available to determine each of the above?
Question 19 :
Describe the Avoca system of Open Stoping
Question 20 :
Describe the components involved in a traditional drill and blast mining cycle and those involved in a continuous mechanised mining cycle. What advantages and disadvantages do both systems of mining have?
Question 21 :
The diagram below illustrates the amount of coal that is left intact after mining in pillars and the amount of coal that is extracted in the rooms. If a1 = 20m, a2 = 22.5 m, b1 = 5m and b2 = 4.5m determine the recovery ratio in a 2.5 m coal seam.
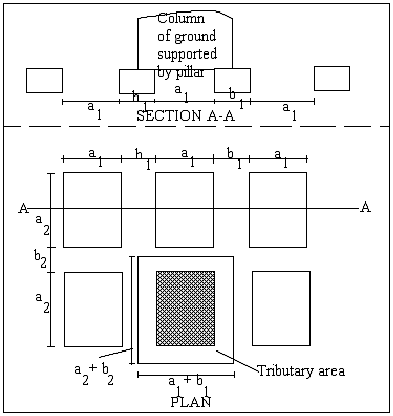
Question 22 :
What do the terms transverse and longitudinal mean with respect to the direction of mining within an orebody?
Question 23 :
Show with the aid of diagrams the development, production and filling phases for a typical open stoping mining setup. What advantages does filling of the stope give?
Question 24 :
Define the following:
a) Stope
b) Overhand mining
c) Underhand mining
d) Extraction ratio
e) Crown pillar
f) Sill pillar
g) Ore pass
h) Waste pass
i) Raise
j) Slot raise
k) Grade
Question 25 :
Define the following terms, diagrams may help:
a) Chain Pillar
b) Barrier Pillar
c) Crown Pillar
d) Sill Pillar
What other types of pillars are commonly used in mining?
Describe a method of pillar design suitable for the design of a room and pillar mining system. What are the main factors that influence the design of such pillars?
Question 26 :
Describe with the aid of sketches the layout of a typical South African longwall gold mining system. What particular advantages does this mining method have for mining at ultra-depths?
Question 27:
Describe a highwall mining technique in detail, if possible giving details of productivity levels that can be achieved.
Question 28:
Describe the longwall top caving mining method
Question 29:
What is square set stoping?.
Question 30:
In a typical block caving operation the following levels exist:
a) Undercut level
b) Draw or production level
c) Ventilation level
d) Transportation level
Describe the operations and requirements for each of these levels, citing examples wherever possible. What factors influence the spacing between these levels?
Question 31 :
Air blasting is not uncommon in block cave mines. Describe how a typical air blast can develop. How can air blasts be minimised and what engineering controls can be applied to ensure this?
Question 32 :
To ensure continuous production from a room and pillar type operation, determine the minimum number of headings required to be operating if the production is to be undertaken using:
a) Traditional drill and blast production methods
b) Continuous miners
What methods of ore transportation are applicable with the above?
Question 33 :
Define the terms over break and under break. What methods can be used to determine these in a typical production stope and what steps can be used to minimise both?