Reference no: EM133337495
Basics of Concurrency Control
Question 1. Deadlock prevention. In the lecture notes, there is an example illustrating Wait-die and wound-wait strategies for deadlock prevention:
• Assuming TS(T22) = 22, TS(T23) = 23, TS(T24) = 24. Data items X and Y are held by T23.
• Wait-die: If T22 requests write (X), it must wait. If T24 requests write(Y), it will be rolled back.
• Wound-wait: If T22 requests write (X), T23 is wound. If T24 requests write(Y), T24 will wait.
Provide a schedule involving three transactions T22, T23 and T24. Each transaction should access at least two data items. The schedule uses locking schedule but does not use 2PL. In order to prevent deadlock, timestamps are used and we assume TS(Ti) = I; for example TS(T22) = 22. Transactions with smaller timestamps are older. The schedule should be able to demonstrate the deadlock prevention strategies.
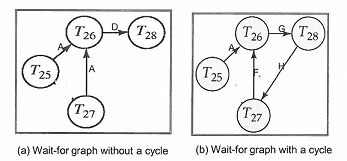
Question 2. Wait-for graph.
(a). For each of the two wait-for graph examples, show a concrete schedule (with read and write operations involving T25, T26, T27 and T28) which would produce that graph.
Question 3. Timestamp-based protocol. Verify (or point out problems of) the partial schedule shown in a slide (duplicated below) using timestamp-based protocol.
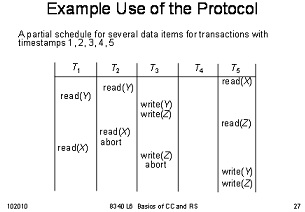
Assuming all the data items having initial timestamp 0, and initial timestamp for Ti = i (for example, TS(T1) = 1, TS(T2) = 2, etc.) For each read or write operation, you should plug in the data (i.e., timestamps involved) to verify each comparison needed for condition checking, and indicate whether any timestamp has changed due to this , operation; and if yes, what is the new value of the read or write timestamp of a particular data item.
Question 4. 2PL and timestamp schedules.
(a) Consider the following schedule. Is it a valid 2PL schedule? Is this schedule possible under timestamp protocol? Justify your answer. (Assuming the subscript of a transaction indicates the timestamp of the transaction.) For checking timestamp schedule, the same requirement of indicated in the previous question applies. [Note: R stands for read, W stands for write, L-S stands for shared lock, UL-S stands for unlock of shared lock, etc.].
|
T1
|
T2
|
|
L-S(A)
R(A)
L-S(B)
R(B)
UL(A)
UL(B)
|
L-X(B)
W(B)
UL(B)
|
(b) Consider the following schedule. Is it allowed in timestamp protocol? Is it possible under 2PL? Justify your answer.
|
T1
|
T2
|
T3
|
|
W(A)
W(B)
|
W(A)
W(B)
|
W(A)
|
(c) What kind of conclusion you can draw from (a) and (b)?