Reference no: EM131389965
Assignment: Intermediate Macro- Mathematical
This homework covers chapter 2 of the textbook and the related lecture notes. If there is a term you do not recognize in the homework, you should be able to find it in the book or in the other materials posted on Blackboard. Please have your homework ready to turn in at the beginning of class.
Reminder: You may work in groups for the homework assignments, but each person must turn in their answers in their own words and showing the relevant work. If you choose to work with others on the homework, make sure you completely understand how you arrived at each answer.
We can think about budget constraints for a discrete number of periods either separately or we can put them together into a lifetime budget constraint (LBC). For example, for a two-period model the (nominal) LBC could be written as:
P_1 c_1+(P_2 c_2)/(1+i)=Y_1+Y_2/(1+i)+(1+i) A_0
Where c_1 is consumption in period 1 and c_2 is consumption in period 2, P_1 is the nominal price of consumption in period 1, P_2 is the nominal price of consumption in period 2 (we often normalize this so that P_1=1 and then P_2 is the price of consumption in period 2 relative to the price in period 1), i is the nominal interest rate, Y_1 is nominal labor income in period 1, Y_2 is nominal labor income in period 2, and A_0 is the initial wealth of the household. Here's a timeline for this two-period model:
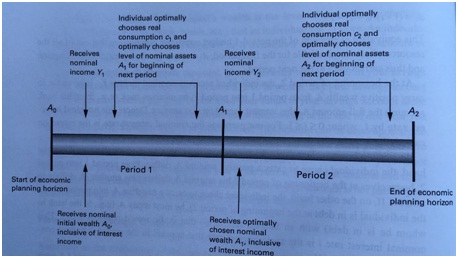
Using similar notation to the nominal LBC for the two period model above, write out the separate period 1 and period 2 budget constraints for this model. Hint: you will need to include an A1 and an A2as indicated in the timeline on the following page. Also, you can see if you're on the right track by combining them together to get the LBC given above.
We typically assume in these models that A0 and A1 can be either positive or negative.
How would you interpret a positive A? What about a negative A?
What do you think we typically assume about A2 in a two-period model? Why?
Now consider a three-period model that is analogous to the two-period model.
Write out the budget constraint for the 3rd period. Define any new notation you introduce, and briefly explain the logic you use in deriving your final expression.
Derive the LBC for the three-period economy. Define any new notation you introduce, and briefly explain the logic you use in deriving your final expression.
Provide a brief interpretation of the LBC you derive in part c.ii.
In reality, there are an "infinite" number of periods. Write down the LBC for an infinite period economy. (No need to be very mathematical - just use what you've learned in class and what you derived above)
The Permanent Income Hypothesis states that individuals consider their future lifetime earnings when making their current consumption decision. Discuss briefly how the multi-period models we are considering here (regardless of two-period, three-period, n-period, or infinite-period) are consistent with the Permanent Income Hypothesis.
An old (Keynesian) idea in macroeconomics is the "marginal propensity to consume," abbreviated MPC. Briefly, the MPC is the fraction of current-period income that is consumed in the current period. For example, if income in period one is 2 and consumption in period one is 1.8, the MPC=0.9.
Consider the standard two-period consumption-savings model in which the representative consumer has no control over his real labor income in period 1 and 2, denoted by y_1and y_2, respectively. Denote by r the real interest rate between period 1 and period 2, and assume the individual begins his life with zero initial assets (A_0=0). Make the additional assumption that in present-discounted-value terms, his real income in each of the two periods is the same - that is, y_1=y_2/(1+r). Using the LBC and the intertemporal optimality condition, derive for the following utility function the "period 1 MPC" - that is, derive what fraction of period-1 real income the consumer devotes to period-1 consumption. (In other words, derive the coefficient MPC in the expression c_1=MPC*y_1+constant). Hint:Set up the Lagrangian in order to solve.
u(c_1,c_2 )=√(c_1 )+√(c_2 )