Reference no: EM131697938
Workshop Assignment: The National Economy
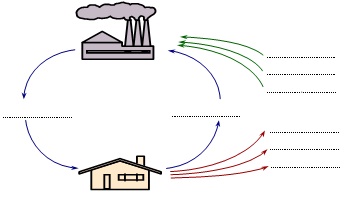
1. Position each of the following eight tenns in the US's circular flow of income diagram below:
Consumption (of domestically produced goods and services); Net saving; Net taxation; Government expenditure; Factor payments (national income); Expenditure on imports; Investment; Expenditure on exports.
Economists use specific letters to label each of these terms. The letters used are:
S, G, X, M, I, Cd, T, Y
Attach the correct letter to each of the terms you have written on the diagram.
2. Which of the following are changes in injections into, and which are than ges in withdrawals from the US's circular flow of income? In each case, identify whether the change is an increase or a decrease. In each case, assume that this is the only change. (Cross-out wrong words.)
(a) A council funds the building of new libraries. ....... Withdrawal/Injection Increase/Decrease
(b) The government raises tax-free thresholds. ....... Withdrawal/Injection Increase/Decrease
(c) The government reduces child benefit. ....... Withdrawal/Injection Increase/Decrease
(d) Fewer tourists visit the US ....... Withdrawal/Injection Increase/Decrease
(e) Finns, anticipating a rise in consumer demand, borrow more money in order to build up their stocks. ....... Withdrawal/Injection Increase/Decrease
(f) Consumers demand more goods that are domestically produced (but total consumption does not change). ....... Withdrawal/Injection Increase/Decrease
(g) People invest more money in banks and building societies. ....... Withdrawal/Injection Increase/Decrease
3. What will happen to the level of the US's national income if the following changes occur? (In each case assume other things remain unchanged.)
a. Firms are encouraged by lower interest rates to build new factories.
Rise /Fall /Impossible to tell without more information
b. Consumers abroad are deterred by a high price for the dollar from buying imports from the US.
Rise /Fall /Impossible to tell without more information
c. Both taxation and government expenditure are reduced.
Rise /Fall /Impossible to tell without more information
d. People decide to save a larger proportion of their income.
Rise / /Impossible to tell without more information
e. Our trading partners overseas begin to recover from recession.
Rise /Fall /Impossible to tell without more information
4. What wou Id b e the effect of each of the following events on actual and po tential economic growth? (Assume no other changes take place.)
(a) A reduction in the level of investment.
Actual growth: rise /fall /no effect
Potential growth: rise /fall /no effect
(b) People save a larger proportion of their income.
Actual growth: rise /fall /no effect
Potential growth: rise /fall /no effect
(c) A reduction in the working week.
Actual growth: rise /fall /no effect
Potential growth: rise /fall /no effect
(d) Increased expenditure on education and training.
Actual growth: rise /fall /no effect
Potential growth: rise /fall /no effect
(e) The discovery of new more efficient techniques which could benefit industry generally
Actual growth: rise /fall /no effect
Potential growth: rise /fall /no effect
(f) A reduction in interest rates. Actual growth: rise /fall /no effect
Potential growth: rise /fall /no effect
5. (a) Assuming that injections are constant at all levels of national income at $20 billion, complete the following table.
|
Income (v) ($bn)
|
40
|
80
|
120
|
160
|
200
|
240
|
280
|
|
Consumption () ($bn)
|
40
|
70
|
100
|
130
|
160
|
190
|
220
|
|
Injections (g) ($bn)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Withdrawals (t) ($bn)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Aggregate expenditure (b) ($bn)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(b) Calculate the marginal propensity to consume domestically produced goods (tnpcd).
(c) On the diagram below, label the line shown and then plot Cd , J and aggregate expenditure (E) against national income (Y).
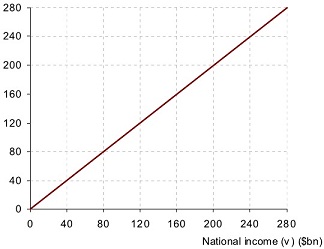
(d) What will be the equilibrium level of income (where E = Y)?
(e) What are withdrawals and injections at this level of income? W ....... J ......
(1) Plot the withdrawals line on the diagram.
You should now be a ble to see that there are two ways of findin g th e equilibrium level of national income.
Still referring to the table and diagram on the previous page, assume now that injections increase by $20 billion at all levels of national income.
(g) Plot the new injections line on the diagram.
(h) Plot the new total expenditure (E) line on the diagram.
(i) Mark the new equilibrium level of national income.
(j) How much has national income increased?
(k) How many times bigger is the rise in national income than the rise in injections?
6. (a) If the multiplier is 5 and the government decides to increase its expenditure by $10m, by how much will national income increase before equilibrium is restored?
(b) Explain why an increase in injections will lead to a multiplied rise in national income.
(c) The formula for the multiplier is 1 / (1-mpcd) or 1 / mpw (where the tnped is the marginal propensity to consume domestic goods and services (DCd/DY) and the mpw is the marginal propensity to withdraw (DW/DY).
Referring back to question 5 above, what are the values of the mpw and the mpcd?
(d) In question 5, what is the value of the multiplier?
(e) Assuming now that the multiplier is 5 (as in part (a) of this question), what are the values of the mpw and the mpcd?
7. The following table gives the aggregate demand and aggregate supply schedules in February 2008 for a particular country. (Ignore the AD2 and AS2 columns until question (d) below and AD3 until question (h).)
|
Price level
|
Aggregate demand ($ billions)
|
2
|
3
|
Aggregate supply ($ billions)
|
2
|
|
95
|
1000
|
___
|
___
|
950
|
___
|
|
100
|
970
|
___
|
___
|
970
|
___
|
|
105
|
950
|
___
|
___10
|
00
|
___
|
|
110
|
930
|
___
|
___10
|
30
|
___
|
|
115
|
915
|
___
|
___10
|
60
|
___
|
|
120
|
900
|
___
|
___11
|
00
|
___
|
(a) Draw the aggregate demand and aggregate supply curves on the following diagram, labelling them AD1 and AS1.
(b) What is the equilibrium level of national income?
(c) What is the equilibrium price level?
Assume that over the next 12 m onths aggregate de mand rises by $70 billion at all price levels and that aggregate supply rises by $20 billion at all price levels.
(d) Enter the new figures for aggregate demand and aggregate supply on the table in the columns AD2 and AS2.
(e) Draw the new aggregate demand and supply curves on the diagram, labelling them AD2 and AS2.
(f) What is the new equilibrium level of national income in February 2009?
(g) What is the rate of inflation in February 2009?
Assume that over the following 12 months aggregate demand rises by a further $50 billion at all price levels but that there is no increase in aggregate supply beyond AS2.
(h) Enter the new figures for aggregate demand on the table in the column AD3.
(i) Draw the new aggregate demand curve on the diagram, labelling it AD3.
(j) What is the new equilibrium level of national income in February 2010?