Reference no: EM13771967
1. Alkanes have the general formula,:
a. CnH2n-4.
b. CnH2n-2.
c. CnH2n.
d. CnH2n+2.
2. Alkenes have the general formula,:
a. CnH2n-4.
b. CnH2n-2.
c. CnH2n.
d. CnH2n+2.
3. Alkynes have the general formula,:
a. CnH2n-4.
b. CnH2n-2.
c. CnH2n.
d. CnH2n+2.
4. How many structural isomers are there of C4H10?
a. 4
b. 6
c. 2
d. 8
5. Which of these species is an aromatic compound?
a. C2H2
b. C6H12
c. C6H4Br2
d. C5H10
6. Which of these is the systematic name for the compound represented below?
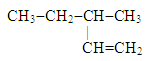
a. 2-ethylbutane
b. 3-methylpentene
c. 3-methyl-1-pentene
d. 3-methyl-1-hexene
7. The group of atoms that is responsible for the characteristic properties of a family of organic compounds is called a(n):
a. reaction center.
b. functional group.
c. binding site.
d. enzyme.
8. Which one of the following functional groups is found in alcohols?
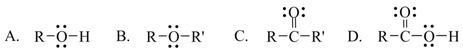
a. A
b. B
c. C
d. D
9. Which one of the following functional groups is found in carboxylic acids?
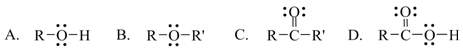
a. A
b. B
c. C
d. D
10. The reaction of an alcohol and a carboxylic acid yields a(n):
a. hydrocarbon.
b. ester.
c. ether.
d. aldehyde.
11. The reaction of Cl2 with CH4 to produce methyl chloride is an example of a(n):
a. free radical reaction.
b. addition reaction.
c. reduction reaction.
d. ester hydrolysis.
12. Which of these statements describes a condensation reaction?
a. Addition of H2O to a double bond
b. Linking an acid and an alcohol to make an ester and water
c. Addition of H2 to an alkene
d. Oxidation of ethanol to acetaldehyde
13. Bromination of benzene (C6H6), an aromatic compound,:
a. occurs by substitution rather than addition.
b. occurs by addition rather than substitution.
c. occurs more rapidly than bromination of a nonaromatic compound.
d. results in formation of 1,2,3,4,5,6-hexabromocyclohexane.
14. Which functional group, when present in a compound that is allowed to stand in air, poses a danger of slowly yielding explosive peroxides?
a. Ether
b. Alcohol
c. Carboxylic acid
d. Ketone
15. The molecule shown below is chiral; i.e., not superimposable on its mirror image.
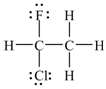
a. True
b. False
16. The term, "hybridization," refers to:
a. a change in the orbital configuration of electrons about an atom which has undergone bonding.
b. a way to describe elemental reactions.
c. changes in shapes of atoms.
d. a way to describe elements.
e. none of the choices apply.
17. When carbon atoms undergo bonding interactions,:
a. the hybridization of the atoms always changes.
b. the electronic state of the atoms change.
c. the reaction is always reversible.
d. none of the choices apply.
18. Enantiomers are:
a. sets of molecules with the same connectivity, atom to atom.
b. molecules with different orientation of substituents, about one or more atoms.
c. molecules which behave differently in biological systems.
d. non-super imposable mirror image isomers.
e. all of the choices apply.
19. Carbon chemistry is vastly diverse as compared to non-carbon chemistry because:
a. a large diversity of compounds are stable under normal conditions.
b. inorganic compounds cannot make large structures.
c. organic compounds do not make salts.
d. the chemistry of life is based on carbon.
e. a large diversity of compounds are stable under normal conditions and the chemistry of life is based on carbon.
20. It is not safe to carry out chemical experiments without:
a. proper ventilation.
b. chemical-resistant gloves.
c. someone else present in case of an emergency.
d. firm knowledge of what you're doing, and the consequences.
e. all of the choices apply.
21. A(n) __________ is composed of only hydrogen and carbon.
a. halocarbon
b. salt
c. hydrocarbon
d. organic compound
e. reagent
22. The products of the complete combustion of a hydrocarbon are:
a. water and carbon dioxide.
b. water, carbon dioxide, and carbon monoxide.
c. carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide.
d. ozone.
e. water and ozone.
23. Boiling points of alkanes with un-branched changes:
a. increase with decreasing chain length.
b. increase with increasing chain length.
c. increase with temperature.
d. decrease with size.
24. Alkanes and cycloalkanes are soluble in water.
a. True
b. False
c. Not possible to know
25. The name of a parent compound with alkanes comes from:
a. The shortest sub-unit.
b. The longest chain of carbon atoms.
c. The octane value.
d. The number of other atoms in the chain.
26. Reaction of bromine with a double bond:
a. decolorizes because of evaporation.
b. decolorizes because of reaction.
c. decolorizes because the bromine is no longer present.
d. causes the solution to fume.
e. decolorizes because of reaction and decolorizes because the bromine is no longer present.
Correct = e
Hint = Page 388
LO = 9A8
27. Formation of acetic acid from ethanol is:
a. a process which occurs only in a lab.
b. a process which occurs naturally in the human body.
c. a process which should be carried out only under proper supervision.
d. a process which is an oxidation.
e. a process which occurs naturally in the human body and a process which is an oxidation.
28. The Lewis dot structure of a carbon atom in a molecule must:
a. have 10 electrons around the carbon.
b. have 8 electrons around the carbon.
c. have 6 electrons around the carbon.
d. have 4 electrons around the carbon.
29. Which atom in the following list does not adhere to the Lewis electron dot rule?
a. H
b. Xe
c. N
d. O
e. F
30. Bonding between two carbon atoms is always:
a. covalent.
b. ionic.
c. non-polar.
d. polar.
e. distributed equally.