Reference no: EM13765917
Perfect Competition and Monopoly
Define the following terms:
Barriers to Entry:
Long-run Competitive Equilibrium:
Marginal Cost:
Marginal Revenue:
Market Power:
Market Share:
Market Structure:
Monopoly:
Normal Profit:
Short Answer Questions:
1. What are the six defining characteristics of a perfectly competitive market?
2. Explain the shutdown decision? (When do firms decide not to produce?)
3. Why do firms in a competitive market earn zero profits in the long run?
4. Why do firms in a competitive industry have a perfectly elastic (horizontal) demand curve?
5. Explain why a perfectly competitive firm will still earn a positive accounting profit even though they earn zero economic profit?
6. What factors are necessary for a monopoly to exist?
7. What gives the monopolist the ability to earn positive economic profits when the firm facing perfect competition can only earn zero economic profits in the long-run
1. Complete the table below and answer the corresponding questions.
|
P = MC
|
Output
|
Total
Revenue
|
Fixed
Costs
|
Vatiable
Costs
|
Total
Costs
|
Marginal
Coss
|
Average
Total
Costs
Profit
|
|
|
20
|
0
|
|
|
|
50
|
-
|
-
|
|
|
|
1
|
|
|
15
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2
|
|
|
|
75
|
|
|
|
|
|
3
|
|
|
|
|
5
|
|
|
|
|
4
|
|
|
|
|
2
|
|
|
|
|
5
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13
|
|
|
6
|
|
|
47
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7
|
|
|
|
112
|
|
|
|
|
|
8
|
|
|
|
|
25
|
|
|
|
|
9
|
|
|
|
|
|
18
|
|
|
|
10
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3
|
a. According to the table above, is this a perfectly competitive firm or a monopolist?
b. What is the profit maximizing level of output?
c. How much profit does this firm make at the profit maximizing level of output?
d. What is causing profit to decrease beyond the profit maximizing level of output?
2. Use the graphs below to answer the following questions
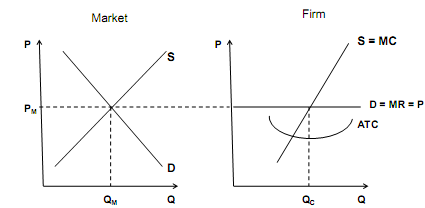
a. Is the firm pictured above experiencing positive or negative profits?
b. Draw and label the profit/loss rectangle on the graph of the firm.
c. Explain the process of returning to zero economic profits works.
d. Illustrate the process you explained in part c on the graphs above
3. Use the graphs below to answer the following questions
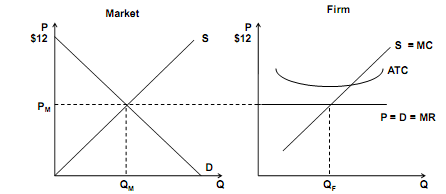
a. Is the firm pictured above experiencing positive or negative profits?
b. Draw and label the profit/loss rectangle on the graph of the firm.
c. Explain the process of returning to zero economic profits works.
d. Illustrate the process you explained in part c on the graphs above
4. Complete the table below and answer the corresponding questions.
|
P = MR
|
Output
|
Total
Revenue
|
Fixed
Cost
|
Variable
Cost
|
Total
Cost
|
Marginal
Cost
|
Average
Total Cost
|
Profit
|
|
50
|
0
|
|
|
|
150
|
|
|
|
|
|
1
|
|
|
35
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2
|
|
|
|
|
30
|
|
|
|
|
3
|
|
|
105
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
150
|
|
305
|
|
|
|
|
|
5
|
|
|
|
365
|
|
|
|
|
|
6
|
|
|
28C
|
|
|
|
|
a. What is the profit maximizing level of production?
b. What is the profit at the level of production in part a?
c. Explain why this firm would choose to produce the level in part a rather than shutting down and not producing even though they will be losing money?
5. Use the graph below to answer the following questions.
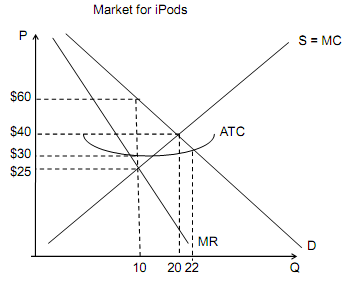
a. How many iPods would a perfectly competitive market produce?
b. What price would the perfectly competitive market charge?
c. How much profit would the perfectly competitive market make?
d. How many iPods would a monopolistic market produce?
e. What price would a monopolistic market charge?
f. How much profit will the monopolistic market make?