Reference no: EM131148592
Principles of Macroeconomics - BoP and Exchange Rates Practice Set
True-False Questions
1. The foreign exchange market is where the international trade of goods and services takes place.
2. An exchange rate is the number of units of one currency required to purchase one unit of another currency.
3. As a nation's income increases, its demand for imports increases, creating an increase in its demand for foreign currencies.
4. A currency depreciates if less of that currency is required to buy one unit of another currency.
5. The supply curve of a currency will shift to the right when interest rates in that country fall relative to interest rates in other countries.
6. If exports of merchandise are greater than imports of merchandise, then a favorable balance of trade exists.
7. One problem with a fixed exchange rate is that if the demand for imports continually increases, an excess demand for foreign currency will be generated at the fixed exchange rate that may deplete foreign currency reserves.
8. The balance of payments account is an itemized account of a country's exports and imports of merchandise.
9. Exports of goods and services and income receipts on investments from the rest of the world represent dollar inflows in the balance on current account.
10. An American taking a vacation in Skardu has the same effect on Pakistan's balance on current account as a Pakistani businessperson exporting goods and services to the United States
Multiple-Choice Questions
1. One effect of an appreciation of the U.S. dollar is that
a. it increases the demand for U.S. labor
b. Americans can buy imports more cheaply
c. American incomes decrease
d. foreigners will demand more U.S. exports
e. U.S. labor will become less productive
2. An increase in income in the Pakistan will
a. increase the demand for foreign currencies
b. cause Pakistan exports to increase
c. cause the value of the rupee measured in terms of dollar to increase
d. decrease the demand for dollar
e. shift the supply curve of rupees to the left
3. An example of dollar inflows on the balance on current account for USA is
a. the export of services
b. current transfers of dollars to U.S. students in Europe
c. increase in U.S. assets abroad
d. the payments on foreign investments in the United States
e. the import of services
4. The balance of trade is given by
a. income receipts minus income payments on investments
b. the balance of current transfers
c. merchandise exports plus service exports minus the sum of merchandise and service imports
d. merchandise exports minus merchandise imports
e. the balance on current account
5. If the U.S. dollar appreciates relative to the Japanese yen, then
a. more yen will be required to purchase one dollar
b. fewer yen will be required to purchase one dollar
c. the dollar has weakened relative to the yen
d. Japan's demand for U.S. goods will increase
e. the Japanese supply of yen will increase
6. The balance on current account includes all of the following items except
a. merchandise exports minus merchandise imports
b. exports of services minus imports of services
c. income receipts minus income payments on investments
d. changes in U.S. assets owned abroad and foreign assets owned in the U.S.
e. gifts given by individuals
7. Given a deficit on the balance of trade, the current account can still be in surplus if
a. there is a larger value for merchandise imports
b. exports of services are less than imports of services
c. current transfers of dollars out of the United States exceed current transfers of dollars into the United States
d. sales of U.S. assets to foreigners increase
e. exports of services are greater than imports of services by enough to offset the unfavorable trade balance
8. The impact of an Indonesian businessman purchasing a U.S. bond is to
a. increase the current account deficit in the United States
b. increase the balance on capital account in the United States
c. increase the U.S. government budget deficit
d. cause U.S. interest rates to rise
e. contribute to a balance of payments problem in the United States
9. The supply curve of U.S. dollars on the foreign exchange market reflects the
a. willingness of people in the United States to supply goods and services on the international market
b. willingness of foreigners to demand U.S. goods and services on the international market
c. willingness of people in the United States to demand foreign goods and services on the international
market
d. willingness of foreigners to demand U.S. dollars on the foreign exchange market
e. the net exports (exports minus imports) that U.S. producers sell on the international market
10. In an economy's balance of payments account,
a. the capital and current accounts must add to one
b. the current account is always greater than the capital account
c. both the balance on current account and the balance on capital account are zero
d. the capital plus current account balances must equal zero
e. capital outflows must equal capital inflows
11. Floating exchange rates refer to
a. the ability of exchange rates to even out when displaced by shocks to the foreign exchange market
b. new issues of foreign exchange offered on the market
c. an exchange rate determined by the demand for and supply of a nation's currency
d. an excess demand for a nation's currency that causes its devaluation
e. an excess supply of a nation's currency that causes its appreciation
12. If the current account for a country is in deficit, then there must be
a. a surplus in the government budget
b. low interest rates
c. high productivity
d. a capital account surplus
e. the presence of attractive investment opportunities
13. If Elrod is a student at the University of Toronto in Ontario, Canada, and his parents in Fresno, California, send him $75, the money is a
a. private current transfer, shown as a U.S. dollar outflow in the U.S. balance of payments account
b. private current transfer, shown as a Canadian dollar outflow in the Canadian balance of payments account
c. current account transfer, shown as a U.S. dollar inflow in the U.S. balance of payments account
d. capital account payment, shown as a U.S. dollar inflow in the U.S. balance of payments account
e. capital account payment, shown as a Canadian dollar outflow in the U.S. balance of payments account
14. A potential problem with free floating exchange rates is that
a. people who practice arbitrage may gain from the losses of others
b. uncertainty in exchange rate fluctuations may hinder international trade
c. exchange rates may never reach equilibrium
d. the currency markets may become monopolized
e. less-developed countries may issue too much currency
15. Some countries may not worry about an unfavorable balance on current account because
a. they know they can always borrow to cover the deficit
b. they import capital goods to build up export industries that will eventually eliminate the deficit
c. deficits are always a stimulant to economic growth, which is a higher priority
d. they can, if necessary, fix the exchange rate to wipe out the deficit
e. their capital account will be favorable since the balance of payments always ends up at zero
16.Consider the following hypothetical exchange rates: $1 = .50 British pounds; 1 Chinese yuan = $.10. We can conclude that 1 pound trades for:
a. 10 yuan
b. 5 yuan
c. 1 yuan
d. 20 yuan
17.If Nokia (a Finnish telephone manufacturer) purchases a production facility in the U.S., this will be recorded in the U.S. balance of payments as a:
a. debit in the current account
b. foreign currency outflow
c. credit in the capital and financial account
d. credit in the reserve account
18.Use the following diagram to answer the next question:
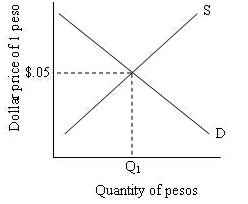
At the equilibrium exchange rate:
a. $1 will buy 20 pesos
b. $1 will buy 5 pesos
c. 95 pesos will buy one dollar
d. 5 pesos will buy one dollar
19.Use the following diagram to answer the next question:
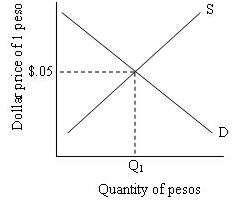
Suppose the U.S. increases its imports from Mexico. All else equal, this would:
a. shift the demand curve to the left, causing the dollar to depreciate
b. shift the demand curve to the right, causing the dollar to depreciate
c. shift the supply curve to the right, causing the dollar to appreciate
d. shift the supply curve to the left, causing the peso to appreciate
20.Suppose that Canada and Mexico allow their currencies to float. Other things equal, if the Canadian central bank raises Canadian interest rates relative to Mexican rates:
a. the Canadian dollar will appreciate relative to the Mexican peso
b. Mexico will be forced to accept policies leading to lower unemployment and higher prices
c. gold will flow into Canada
d. Mexico will be forced to sell official dollar reserves to maintain price stability
21.Which of the following is always entered as a negative number in the U.S. balance of payments?
a. Net transfers
b. Net investment income
c. Goods exports
d. U.S. purchases of assets abroad
22.If the exchange rate changes so that fewer Swiss francs are required to buy a Mexican peso, then:
a. the franc has appreciated relative to the peso
b. Mexicans will buy more Swiss goods and services
c. the franc has depreciated relative to the peso
d. gold will flow from Mexico to Switzerland
23.If a nation's balance on current account is positive and it has neither a deficit nor surplus in its overall balance of payments:
a. its imports exceed its exports
b. foreign purchases of its assets exceed its purchases of assets abroad
c. it has a trade deficit
d. it has a capital and financial account deficit
24. Country A has a trade surplus and a floating exchange rate. Financial capital can freely flow in and out of Country A If Country A uses an expansionary fiscal policy to stimulate its economy out of a recession, this policy will also result in
a. a decrease in A's trade surplus
b. a depreciation in A's currency
c. an increase in A's exports
d. both a and b are possible
Problems
1. Graph the supply and demand for the foreign exchange market, expressed in terms of pesos per dollar. Show the equilibrium price at 5 pesos per dollar. Suppose the demand for dollars increases so that the new exchange rate is 7 pesos per dollar. Has the peso appreciated or depreciated? Which currency has strengthened? Is this good or bad for the United States? For Mexico?
2. Indicate whether each of the following creates a demand for or a supply of European Euros in foreign exchange markets:
a. A U.S. airline firm purchases several Airbus planes assembled in France.
b. A German automobile firm decides to build an assembly plant in South Carolina.
c. A U.S. college student decides to spend a year studying at the Sorbonne in Paris.
d. An Italian manufacturer ships machinery from one Italian port to another on a Liberian freighter.
e. The U.S economy grows faster than the French economy.
f. A U.S government bond held by a Spanish citizen matures, and the loan amount is paid back to that person.
g. It is widely believed that the euro will depreciate in the near future.
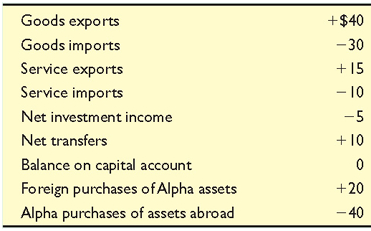
3. Alpha's balance of payments data for 2008 are shown below. All figures are in billions of dollars. What are the (a) balance on goods,(b) balance on goods and services, (c) balance on current account, and (d) balance on capital and financial account? Suppose Alpha needed to deposit $10 billion of official reserves into the capital and financial account to balance it against the current account. Does Alpha have a balance-of-payments deficit or surplus? Explain.