Reference no: EM13334141
GDP of China
Introduction
• China is the world's fastest-growing major economy, with growth rates averaging 10% over the past 30 years
• China is a global hub for manufacturing, and is both largest manufacturing economy in the world and the largest exporter of goods.
• China is also the world's fastest growing consumer market and second largest importer of goods.
Body
I. Background of China's economy.
1. Closed country before 1978.
2. Wars and culture revolutions
3. China, economically frail before 1978, has again become one of the world's major economic powers with the greatest potential
II. GDP of China from 2000 to present grows extremely fast since China joined WTO in 2001.
1. GDP = C + I + G + (Ex - Im)
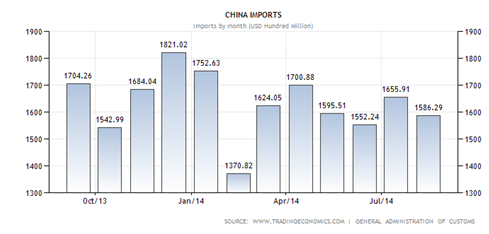
2. GDP chart from World Bank.
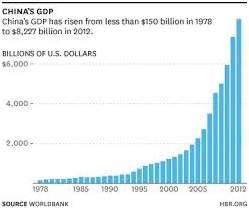
III. Consumption: total spending by consumers
1. The latest value for Final consumption expenditure, etc. (current US$) in China was $3,475,020,000,000 as of 2011.
2. In 2012, China's private consumer spending amounted to almost 36% of its GDP. Adding government outlays pushed up its total consumption to 49.5%.
3. China's level of consumer spending still remains far below America's. But it is growing much faster in percentage terms.
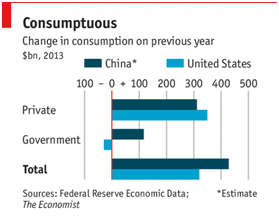
IV. Investment
1. Chinese production and consumption of coal increased for the 13th consecutive year in 2012. China is by far the world's largest producer and consumer of coal, accounting for 46% of global coal production and 49% of global coal consumption-almost as much as the rest of the world combined.
2. The top 10 coal-producing countries supplied 90% of the world's coal in 2012. China produced nearly four times as much coal as the second largest producer, the United States, which had a 12% share of global production. China has accounted for 69% of the 3.2 billion ton increase in global coal production over the past 10 years.
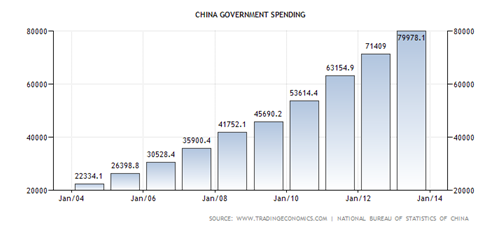
V. Government spending
1. Total government expenditures account for 24 percent of GDP, and reported public debt is 23 percent of gross domestic output.
2. The regulation explicitly prohibits government agencies from purchasing luxury items, goods or commodities above certain standards, as well as defines a frugal working style for the country's civil servants.
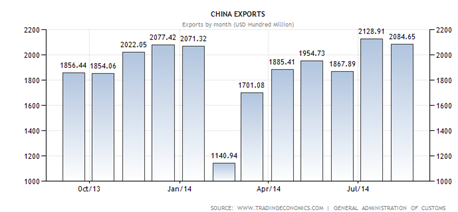
VI. Exports
1. Since its accession into the WTO in 2001, China‘s share in global trade has doubled - accounting for 10.38 percent of the world's merchandise trade exports and 9.43 percent of merchandise trade imports.
2. China is rapidly becoming their most important bilateral trade partner. In 2011, they were the largest exporting/importing partner for 32 and 34 countries respectively.
3. Primary exports - commodities: electrical and other machinery, including data processing equipment, apparel, radio telephone handsets, textiles, integrated circuit
4. Primary exports partners: US (17.2 of total exports), Hong Kong (15.8 percent), Japan (7.4 percent), South Korea (4.3 percent), Germany (3.4 percent)
5. Export growth has been a major component supporting China's rapid economic expansion. Exports of goods and services constitute 30% of GDP.
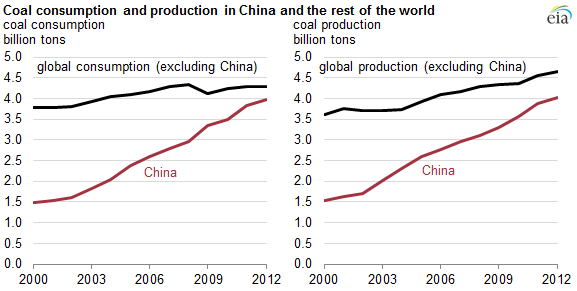
VII. Imports
1. Primary imports - commodities: electrical and other machinery, oil and mineral fuels, optical and medical equipment, metal ores, motor vehicles
2. Primary imports partners: Japan (9.8 percent of total imports), South Korea (9.3 percent), US (7.3 percent), Germany (5.1 percent), Australia (4.6 percent)
3. China's main imports are electromechanical products (43 percent of total imports).