Reference no: EM133354
QUESTION 1
(a) The use of satellites in RF communication system is a great deal fact in everyday life.
(i) Explain in detail INTELSAT and INSAT satellites?
(ii) Discriminate amid polar orbiting satellites and geostationary satellites.
(iii) By referring to artificial satellites orbiting the earth, state Kepler's third law.
(b) A satellite dish is in communication or messaging with a geostationary satellite above the earth surface. The angle over which the satellite dish can lie is 1430. For better communication, the dish is slanted at an angle of 100. Work out the height of the satellite from the earth surface.
(c)A satellite makes a north to south equatorial crossing at longitude 900W, finishing one revolution around the earth in 102 min. presumptuous that the orbit is circular and crosses accurately over the poles, estimate the following:
(i) The number of orbits per day.
(ii) By how much will the earth rotate eastward in the 102 min?
(iii) The position of the satellite at the time 0h 10 min after the equatorial crossing.
(d)A meteorite is a meteoroid (a solid piece of debris from such sources as asteroids or comets) originates in outer space that survives impact with the Earth's surface. Radar systems are used to monitor this dangerous phenomenon. In one such situation, a radar system of transceiver antenna gain of 4000, operating at a frequency of 10 GHz with a peak pulse power of 250 KW is used to track down a meteoroid.
If the power pulse inward bound at a range of 50 km is 10-11 W, what is the cross-sectional area of the target meteoroid?
(e)Using a block diagram, describe the subsystems involved of a 2G system architecture.
QUESTION 2
(a) The Gain over Temperature ratio (G/T) is a parameter (figure) of merit used when designing RF systems.
(i) Beginning from power received by a receiver system, derive equations for the input G/T and output G/T ratios.
(ii) Draw a label diagram of a typical dual-conversion receiver.
(b) A microwave link requires participating stations to have a least G/T ratio given by:
1 10 G / T 20.5 20 log ( f / 4)dBK where f is the frequency in GHz. Operation is at 4 GHz with a terminal consisting of an antenna followed by a waveguide of physical temperature 300 K with 0.6 dB loss and an amplifier with a 1.0 dB noise figure and 15 dB gain. The amplifier drives a mixer with a 7 dB noise figure and 30 dB gain. Following the mixer is an IF receiver with a 12 dB noise figure.
Compute the minimum antenna diameter required to meet the G/T specification.
Imagine that the antenna noise temperature is 15 K independent of diameter and that the aperture efficiency is 65 percent. All noise figures are standard with T0 = 290 K.
c) A geostationary satellite transmits a signal at 12 GHz with a 2 MHz bandwidth to an equatorial receiving station. Both antennas are parabolic reflectors with a diameter of 2m and a 60% aperture efficiency.
Including a 20 dB fading margin and rain attenuation corresponding to a 5 km path through rain at a rate of 50 mm/hr, determine the transmitter power required to ensure a received SNR of 10 dB for a receiver antenna temperature of 288 K and receiver noise factor F of 4.
You may assume perfect alignment of transmitting and receiving antennas and that external noise is negligible.
[k = Boltzmann's constant = 1.38x10-23 J/K, Rain attenuation in dB/km is given by:
B dB km ap / where a = 0.0215, b = 1.136 and p is the rain rate in mm/h].
QUESTION 3
(a) What is expected by the term ‘Third Order Intermodulation Products', and why are they so important in communications systems?
(b) Make a distinction between the linear dynamic range and the spurious free dynamic range.
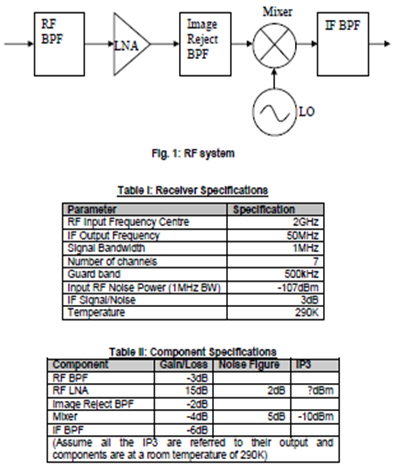
(c) Investigate the following sub-system (Fig. 1) and component specifications provided in the two tables (I & II) below and answer the following questions.
(i) Work out the overall noise figure, gain and output noise power?
(ii) What is the minimum acceptable signal level at the input to the RF BPF and the input signal to noise ratio?
(iii) The receiver is mobile and can move up to 1km nearer the transmitter from the minimum signal point. If all third order intermodulation distortion is to be maintained below the output noise level, calculate the minimum IP3 that is required for the receiver, and hence for the LNA.
(iv) Assuming that this is a single stage conversion receiver, what two choices are possible for the frequency range of the Local Oscillator, and over what frequency range would we have to specify the passband and topband of the image rejection filter in each case.

QUESTION 4
(a) Make clear the concept behind designing practical filters.
(b) Refer to Q4(a), devise & design a lowpass filter of length N=11 and cutoff frequency ωc = π/3, sing the rectangular window.
(c) Consider a butterworth filter of response given by Derive the filter transfer function by computing the system poles.