Reference no: EM131574552
Intermediate Microeconomics Homework: Price discrimination
Problem 1 - A university sports stadium sells tickets to two groups - students and the public. The stadium is a monopolist ticket-seller and can distinguish between members of the two groups, for instance by requiring student ID to enter the stadium with a student ticket. The demand curves for the two groups are DP(p) = max{120000-3000p,0} and DS(p) = max{20000-1250p, 0}for the public and students, respectively.
1. If the stadium charges separate prices to the two groups, what sort of price discrimination is this?
2. Suppose the stadium has no marginal cost of selling seats, but can sell seats only up tothe stadium's capacity. For each of the following capacities, compute the optimal ticket prices and quantities sold to each group:
a) 80000
b) 53000
c) 61500
(NB: It is not necessarily true that the stadium will want to sell out all seats.)
3. Now suppose the stadium incurs a marginal cost of $2 per seat sold, due to service and upkeep expenses.
a) If the stadium's capacity is 53000 seats, find the optimal ticket price and quantity sold to each group.
b) What is the smallest stadium capacity for which optimal ticket prices do not sell out the stadium?
4. Suppose members of the public gain the ability to cost lessly forge student IDs, so that members of either group can purchase and use either ticket type. The stadium's capacity is 53000 and there is no marginal cost of providing a seat.
a) What ticket prices will the stadium set and how many tickets will be sold to each group?
b) Calculate social welfare, producer surplus, and consumer surplus of each group before and after ID counterfeiting. Is more surplus generated before or after ID counterfeit-ing? Who wins and who loses from the introduction of counterfeiting?
Problem 2 - An amusement park serves customers with quasilinear utility and increasing, concave valuation for total number of rides in the park. There are two types of consumers; the low-type has value function
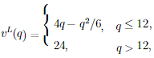
while the high-type has value function
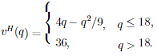
(The piecewise definition ensures that the value function is never decreasing; low type consumers have a satiation point at q = 12 rides while high types are satiated at q = 18 rides.) There are 10000 customers of each type. The park incurs no marginal cost by providing additional rides.
1. Construct the aggregate demand curve for rides.
2. If the amusement park charges no admission fee and a uniform price per ride, what is its optimal price and corresponding profits? What quantities are consumed by each type?
3. In a socially efficient allocation, how many rides would be consumed by each consumer type?
For the rest of the problem, the park recognizes that it can attain extra additional revenue through second-degree price discrimination. So rather than charging a uniform price per ride it sells bundles which charge an up-front tariff and then allow access to a set number of rides for a uniform price per ride. (For simplicity assume consumers can buy only one bundle and cannot top up with further rides.)
4. Is it ever optimal to offer a bundle with a non-zero marginal price per ride? Why or why not?
5. Suppose the park sells a single bundle offering the efficient number of rides for the low type. What is the maximum tariff it can charge if it wants to ensure both types buy the bundle?
6. Suppose the park sells a single bundle offering the efficient number of rides for the high type. What is the maximum tari? it can charge if it wants to ensure high types buy the bundle?
7. Suppose the park sells two bundles, each offering the efficient number of rides for one of the types. If the low-type bundle has associated tariff TL, what is the maximum tariff which can be charged for the high-type bundle if the park wants to ensure each type consumes their efficient number of rides?
8. What is the park's optimal menu of bundles? Your answer must describe how many bundles are offered and who purchases which bundle, and it must calculate the tariff, marginal price, and number of rides in each bundle. Does your solution feature quantity discounts or markups?
9. Calculate social welfare, producer surplus, and consumer surplus for each group under uniform pricing and optimal bundling. Which outcome is more efficient? Who wins and who loses from bundling?