Reference no: EM131305481
Problem 1.
Find the Maximum Likelihood (ML) test for a single observation x(0) to distinguish between H0 and H1 if
H0 : Px(0)(x(0)) = 1/2exp (-|x(0)|)
H1 : Px(0)(x(0)) = 1/2exp (-|x(0) - A|)
when A > 0. Find the error probability. Find the probability of deciding H1 when H1 is in fact true.
Problem 2.
For the previous problem, find the Neyman-Pearson (NP) test (to distinguish between H0 and H1) that achieves PFA = 0.1. What is PD? Does your test depend on the value of A? Explain.
Problem 3.
We make a single observation x(0) with
H0 : x(0) = ω(0)
H1 : x(0) = 6 + ω(0)
with
pω(0)(ω(0)) = 1/2exp (|ω(0)|)
This is an instance of a signal (6) in additive noise (ω(0)), and we wish to detect the signal while avoiding false alarms.
1. Find the log likelihood ratio as a function of x(0).
2. Determine the test that maximizes PD while PFA = 1/2e.
3. What is PD for your test?
Problem 4.
The PDFs of a single observation x(0) under H0 and H1 are shown below. Find PD as a function of PFA for the optimal Neyman-Pearson detector and sketch the ROC.
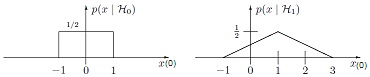
Problem 5.
You measure iid x(n), n = 0, 1, ....., N - 1.
H0: px(n)(x(n)) = exp(-x(n)), if x(n) > 0
0, otherwise.
and
H1: px(n)(x(n)) = 1/µ exp(-x(n)/µ), if x(n) > 0
0, otherwise.
1. Find the log likelihood ratio as a function of x(0).
2. Determine the test that maximizes PD while PFA.
3. What is PD for your test?
Example.
You know a single observation x(0) is distributed under two hypothesis as follows:
H0: px(0)(x(0)) = 1/2, if x ∈ {-1, 1}
0, otherwise.
and
H1: px(0)(x(0)) = 3/2x2 if x ∈ {-1, 1}
0, otherwise.
The probability of occurrence of H0 and H1 are Pr(H0) = 0.95 and Pr(H1) = 0.05.
1. Determine a detector based on x(0) to minimize the error probability.
2. Now suppose that the cost of deciding H0 when H1 is true is $475 and the cost of deciding H1 when H0 is true $48. Under these assumption about the cost, determine a decision rule based on x(0) that minimizes the expected cost.
3. For your decision rules in (1) and (2), calculate the probability of decisding H1 when H1 is in fact true.
|
Find confidence interval for population mean of all studdent
: Choose one of the following quantitative variables from the data set: Age, Weight, Cell Phone, Study, TV, Sleep, Pets, or Work. Find a 95% confidence interval for the population mean [variable] of all ABC students
|
|
What should the minimum rated a-hr of batteries
: what should the minimum rated A-hr of batteries be if they shouldn't be discharged more than 80 percent? Assume battery temperature is 25° C.
|
|
Describe persons involved in the greeting encounter
: Write down where, when, and for how long you conducted your observation ,Describe persons involved in the greeting encounter: age, gender, appearance, etc. ,Write down the words of the greeting exchange,Note people's facial expressions ,Describe body..
|
|
Do you agree with given analysis
: If that bond was bought for $870, the actual yield to maturity would be 9.2%. Do you agree with this analysis? Briefly explain.
|
|
Find the neyman-pearson test
: ENGI 4053 Statistical Signal Processing - Find the Maximum Likelihood (ML) test for a single observation and find the Neyman-Pearson (NP) test (to distinguish between H0 and H1) that achieves PFA = 0.1. What is PD? Does your test depend on the value ..
|
|
Draw the new shaded i-v curve for the module
: Suppose there is enough shading on the bottom cells to cause the lower diode to start conducting. Draw the new "shaded" I-V curve for the module.
|
|
Maturity on a coupon bond and the rate of return
: What is interest-rate risk? Why does a bond with a longer maturity have greater interest-rate risk than a bond with a shorter maturity?
|
|
Would these bonds be of interest only to investors
: Would these bonds be of interest only to investors who were young enough to expect to still be alive in 40 years, when the bonds will mature?
|
|
At what time will it stop running
: Once the pump starts running, it needs 8 V to keep spinning. At what time in the morning will the pump start running? At what time will it stop running?
|