Reference no: EM13178070
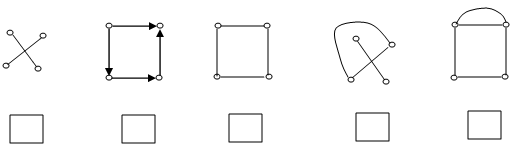
1) Correctly match each of the following listed sets of properties to one of the graphs below by inserting the letter for the properties that best describes the graph in the open square box under the graph.
(A) simple, connected (B) simple, not connected (C) digraph (D) not simple, connected (E) not simple, not connected
2) The adjoining graph consists of 6 nodes (or vertices) labeled A, B, C, D, E and F and 9 edges connecting pairs of nodes.
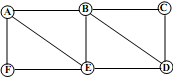
Does this graph contain an Euler path? If your answer is yes, provide an example of an Euler path for this graph. If your answer is no, explain why no Euler path exists.
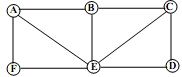
3) The adjoining graph consists of 6 nodes (or vertices) labeled A, B, C, D, E and F and 9 edges connecting pairs of nodes. Does this graph contain an Euler path? If your answer is yes, provide an example of an Euler path for this graph. If your answer is no, explain why no Euler path exists.
4). Consider the adjoining connected graph consisting of 8 nodes and 10 edges. Answer the following questions regarding this graph.
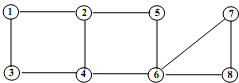
(a) Does this graph contain an Euler circuit? If your answer is yes, describe the circuit. If your answer is no, explain why there is no Euler circuit.
(b) Does this graph contain an Euler path? If your answer is yes, describe the path. If your answer is no, explain why there is no Euler path.
(c) Does this graph contain a Hamilton circuit? If your answer is yes, describe the circuit. If your answer is no, explain why there is no Hamilton circuit.
5). The adjoining diagram is a graph with six nodes (or vertices) labelled A, B, C, D, E and F. The lengths of the edges joining the nodes are shown on the graph.
(a) Find all Hamilton paths going from node A to node F.
(b) Find the lengths of each of the Hamilton paths from node A to node F.
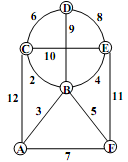
6). Consider the following three matrices. One is an adjacency matrix of a graph, one is the incidence matrix of a graph and the third is the incidence matrix of a digraph (but not in the order stated).
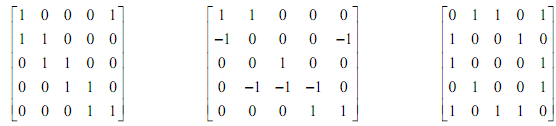
(a) Which matrix is the adjacency matrix? Give reasons for your choice. Draw the graph represented by this adjacency matrix.
(b) Which matrix is the incidence matrix? Give reasons for your choice. Draw the graph represented by this incidence matrix.
(c) Which matrix is the incidence matrix of a digraph? Give reasons for your choice. Draw the digraph represented by this incidence matrix.
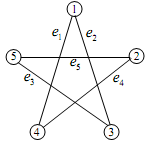
7). Find both the adjacency and incidence matrices for the following graph.
8) Find the incidence matrix from the following digraphs.
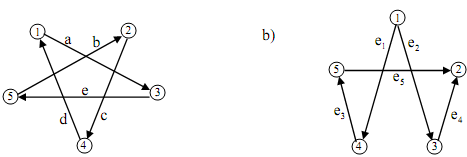 a
a