Reference no: EM131038805
1. Assuming that the inverse demand function for shale gas in period 1 is P1 = 90 - q1 and the demand function in period 2 is half of the demand of Period 1 (i.e. future generations prefer to consume renewable resources). The Marginal Cost in Period 1 and Period 2 are both constant and equal to MC=$5. Furthermore, assume that the discount rate is 5%, and the total amount of the shale gas is 50 tons.
(a) Find the Dynamic Efficient Allocation. Determine the current, future and total quantity of the depletable resource. Discuss.
(b) Compute the optimal prices and Marginal User Cost (MUC) in both periods.
(c) Construct a graph representing the dynamic efficient allocations in both periods.
(d) Would the static and dynamic efficiency criteria yield the same answers for this problem? Why or why not?
2. There are two persons stranded on a desert island. Their respective annual demand for coconuts are as follows:
Person 1: ??1 = 40 - ??1
Person 2: ??2 = 60 - ??2
There is one coconut tree, which generates 40 coconuts each month without any incurred cost.
(a) Suppose this coconut tree is the only one on the island. What is the efficient coconut consumption level for each person?
(b) Suppose that, besides this aforementioned coconut tree, there are other trees located on the top of a mountain. Climbing the mountain to get the coconuts has a cost: ?????? = 0.6??????????????????. What is the efficient coconut-consumption level for each person?
(Hint: What is the marginal cost of coconut supply combining both the easily accessible coconut tree and the mountain coconut trees when the coconut supply is beyond 40 units?)
(c) Suppose Person 1 owns the beach coconut tree, and Person 2 owns the mountain trees, but there is no coconut market. How much coconut would each person consume?
(d) What is the efficiency loss (social surplus loss) due to the non-existence of a coconut market?
3. Consider the case of an almond farmer. This farmer is a monopolist in the almond market. Since almond production uses significant amounts of water, it negatively affects the scarcity of available water resources. Recall that, when a firm is a monopolist, it reduces its production so that it can increase price; although it sells fewer units, the higher price more than makes up for the reduced volume.
Consumers lose, and total welfare is reduced, due to the higher price and lower quantity. A pollution externality, in contrast, implies production above the socially optimal quantity.
(a) Draw a supply-demand figure for a firm with the demand curve Q = 30 - 2 * P, and marginal cost curve MC = 3 (based on total costs C = 3 ∗ Q). If this were not a monopoly, what would be the equilibrium price and quantity? Calculate the firm's total revenue and producer surplus. Also calculate consumer surplus. Recall that the formula for net social benefits is "consumer surplus plus producer surplus minus damages." Calculate that value.
(b) Suppose that, instead, the firm decided to act like a monopolist and restrict output. It produces 12 units and charges $9 for each unit. Calculate the producer surplus, consumer surplus and net social benefits. Is there any deadweight loss? Are net benefits higher or lower? Is the firm better or worse off?
(c) Now let's consider the scenario where production has some related damages in the form of pollution. Suppose the firm is the source of marginal damages of $4/unit. For both (a) and (b), recalculate net benefits to account for the pollution damages.
(d) Find the social efficient equilibrium. Calculate the producer surplus, consumer surplus, damages, and net social benefits.
(e) If forced to be liable for any damages, what will the monopolist produce and charge for each unit? Calculate the producer surplus, consumer surplus, damages, and net social benefits.
(f) Compare the results for (c), (d), and (e). Rank them from the highest net benefits to the lowest.
(g) A regulator who can break up monopolies is examining this situation. Compare net benefits for the monopolist who pollutes [the recalculation for the monopolist in Part (c)] with the competitive firm that pollutes [the recalculation for the competitive firm in Part (c)]. Will the regulator improve net benefits by breaking up the monopoly?
(h) Now assuming monopoly production, compare net benefits for the monopolist who pollutes [the recalculation for the monopolist in (c)] with net benefits for the monopolist who pays the full costs of pollution in (e). Will a regulator increase net benefits by taxing pollution?
(i) Does correcting a market failure always improve welfare?
4. Ana and Bob fish for crab in the State of Alaska. The graph below depicts how the crab community's total revenue from crab fishing and the total costs of fishing depend on effort, measured by how many crab traps are set
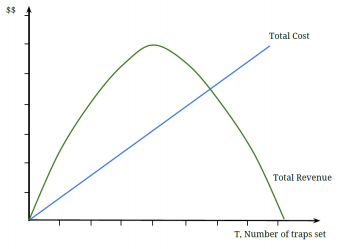
The total revenue from a crab trap is TR = 100T- 2T², with a marginal revenue of MR = 100- 4T, and the price of a crab trap is constant at $20.
(a) What is the efficient number of traps for the community to set? Identify this level of effort in the graph.
(b) Suppose that Bob, Ana and the rest of the community catch crabs without restriction or regulation, how many traps will be set? Identify this level of effort in the graph. Why is this level above/below the efficient level determined in part (a)?
(c) Bob and Ana are disgusted with their fellow fisherpeople, and decide to enforce the efficient outcome from part (a) by increasing the cost of effort and waging a crab war. They do this by cutting the lines to X% of the traps set (no matter how many traps are set). What percentage of the set traps do they have to cut to induce the efficient number of traps from part (a)? (Hint: Start by finding what total costs have to be so that the level of effort without regulation would be equal to the level in (a). )