Reference no: EM132331464
Question 1. The elasticity of demand for a firm's product is -2 and its advertising elasticity of demand is 0.12. a) Determine the firm's optimal advertising-to-sales ratio. b) If the firm's revenues are $70,000, what is its profit-maximizing level of advertising? c) Can Advertising be considered as an entry barrier? Why or why not?
Question 2. Refer to the figure below. A) If this firm is a price taker and the price of each unit of output is $30 in the short run. What is the quantity, the price, and total economic profits, at its profit maximizing equilibrium?
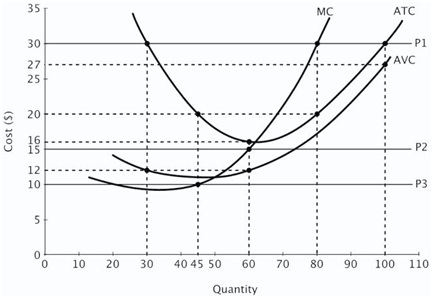
b). Explain the long run equilibrium if the industry is perfectly competitive and there is free entry and exit. Draw a graph.
Question 3). Suppose demand for Microsoft software in the US is: P = 200-Qus, and marginal revenue is MR = 200-2Qus where quantity is measured in millions. Demand for software in Canada is P = 100-2Qca and marginal revenue is MR=100-4Qca. The marginal and average cost of production for Microsoft is $50.
a) What price Microsoft should charge in Canada? In the US? How much will it sell if it aims for maximizing profits?
b) How much profit will Microsoft make if it charges different prices in the US and Canada?
c) Suppose it charges a uniform price of $100 in the two markets. Show that this strategy is inferior to international price discrimination. (Hint: When finding profits, ignore fixed costs or just concentrate on producer surplus).
Question 4). Suppose the domestic demand for honey is Qd = 1600-2P (where quantity is measured in tons) and the domestic supply is Qs= -500+P and there are many buyers and sellers such that the market is perfectly competitive.
A) Find the competitive market equilibrium price and quantity. What can we say about the efficiency of this equilibrium from a social standpoint?
B) If honey producers form a cooperative and form a monopoly, find the monopoly equilibrium price and quantity.
C) Compare the competitive equilibrium to the monopoly equilibrium in terms of price quantity and welfare. What is the social loss due to monopoly?
Question 5). In studying for his economics final, Sam is concerned about only two things: his grade and the amount of time he spends studying. A good grade will give him a benefit of 20; an average grade, a benefit of 5; and a poor grade, a benefit of 0. By studying a lot, Sam will incur a cost of 10; by studying a little, a cost of 6. Moreover, if Sam studies a lot and all other students study a little, he will get a good grade and they will get poor ones. But if they study a lot and he studies a little, they will get good grades and he will get a poor one. Finally, if he and all other studentsstudy the same amount of time, everyone will get average grades. Other students share Sam's preferences regarding grades and study time
a. Model this situation as a two-person prisoner's dilemma in which the strategies are to study a little and to study a lot, and the players are Sam and all other students. Include the payoffs in the matrix.
b. What is the equilibrium outcome in this game? From the students' perspective, is it the best outcome?