Reference no: EM13803205
1) Three blocks with masses m, and in. are connected by an inextensible string. The block with mass In is placed on a frictionless table. The string goes over a smooth massless pulley and the block with mass m, hangs down as shown in the figure. Now another block with mass m. is placed on top of the block with mass in. as shown in the figure. There is no friction between the two blocks on the table. If the system is released And
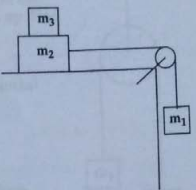
(a) the accelerations of the three blocks and
(b) the force of tension of the string.
2) Three blocks with masses rityrn.and m. are connected by two inextensible strings as shown in the figure. The blocks with masses m. and In are placed on a frictionless table. One string goes over a smooth massless pulley and the block with mass in. hangs down as shown. If the system is released find

(a) the accelerations of the three blocks and
(b) the force of tension of the strings.
(c) Now the string connecting the two blocks on the table is cut. Use your results from (a) and (b) to find the new accelerations of each block and the force of tension of the string connected to the hanging block.
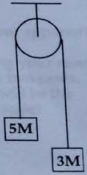
3) A system is made up of two blocks with masses 5M and 3M connected by an inextensible string and a fixed smooth massless pulley as shown in the figure. The string goes over the pulley and the two blocks hang on either side of the pulley. When the system is released from rest, Find
(a) the acceleration of each of the blocks, and
(b) the tension of the string.
(c) Use the result from example 4.4 to check your answer.
4) Consider an Atwood machine with three blocks and two strings as shown in the figure. When the system is released, assume the block with mass m. moves up. Find
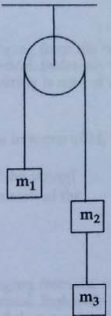
(a) the acceleration of each block, and
(b) the tensions of the two strings.
(c) If the bottom string breaks, what will be the accelerations of the three blocks?
Objects Inside Moving Systems
5) Cfrk parcel of mass NI is hanging down from a string attached to a hot air balloon. Find the tension of the string in the following situations.
(a) The balloon is moving up with constant speed V.
(b) The balloon is moving up with constant acceleration a (magnitude).
(c) The balloon is moving up with constant deceleration a (magnitude).
6) You are inside an elevator moving down. You find a bathroom scale next to you and decide to step on it. If your mass is NI, find the reading of the bathroom scale (your apparent weight) in the following situations.
(a) The elevator is accelerating with constant acceleration a (magnitude).
(b) The elevator is moving with constant speed V.
(c) The elevator is decelerating with constant deceleration a (magnitude)
(d) If your mass is 50 kg and the constant speed is 0.5 m/s, using your result from (b) find your apparent weight as shown by the bathroom scale.
(e) If your mass is 50 kg., and the magnitude of the acceleration/deceleration is 0.4 m/s., using your result from (a) and (c) find your apparent weights as shown by the bathroom scale in the above two cases.
(f) If the cable of the elevator suddenly breaks, and the elevator undergoes a free fall, what will be the reading of the bathroom scale (assume you didn't panic, but stood still on the bathroom scale).
7) Assume you are traveling in a bus and there is a pendulum of mass NI and length I. hanging from the roof of the bus. The bus is moving with constant velocity V and you notice that the string is vertical. Suddenly the driver steps on the gas pedal, and the car accelerates. You notice that the bob of the pendulum moves and the string is now at a constant angle 0 with the vertical.
(a) Find the acceleration of the car and the tension of the string. Your answer should be in terms of M, V, 0, L and g (as required).
(b) If 0 = 15° what is the acceleration of the car?
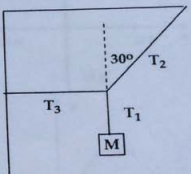
8) A block of mass NI is suspended from three strings as shown in the figure.
The string attached to the ceiling makes an angle 30° with the vertical. If the block is in equilibrium, find the tensions T1 T2, and T3 of the three strings.