Reference no: EM13618
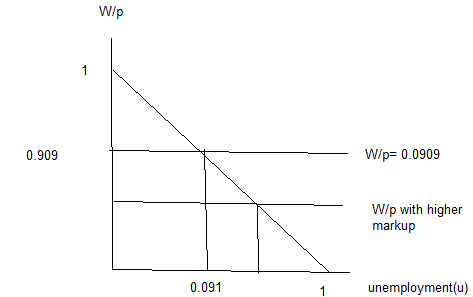
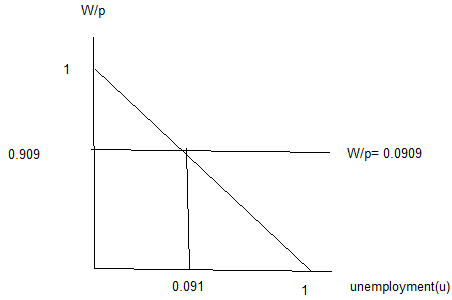
Suppose the firm mark up over the cost is 10% and the wage setting equation is W=P (1-u) where U is the unemployment rate.
a) Find out the real wage rate implied by the price setting equation.
The price setting equation is W/p = 1/(1+µ)
or P= (1+µ)W
where µ is the markup
P= 1.1W
W/p = 1/1.1 =0.909
b) Determine the natural rate of unemployment.
AS the markup is 10%, P= 1.1W
W/p= 1/1.1= .909
so u= 1-0.909= 0.091ot 9.1%
c) Plot the wage- setting and price setting equation or a property labelled graph and identity the nature rate of unemployment.
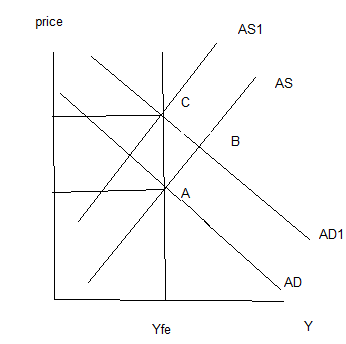
5- Carefully explain the neutrality of money on the medium run. Use an aggregate demand - Aggregate supply diagram to illustrate your answer.
Neutrality implies that money does not affect the real variables in the economy- unemployment, GDP, consumption, investment. It only affects inflation. In the long run any change in money supply is reflected by the same amount on inflation. So if money increases by 10% prices will also rise by 10%. This is the crux of the quantity theory of money and monetarism.
This is shown with AD AS diagram. We star at A where AD= AS, and economy is at long run equilibrium. Let money supply rise, so that demand for good rises. This causes AD to shit up and we are at B. The GDP rises along with prices. This inflation causes inflationary expectations to build up, causing workers to ask for wage rise. This translates into rise in input costs, which shifts AS upwards to AS1, and we reach a new equilibrium at C. Comparing A and C, we can see that the rise in money supply is reflected in price rise fully, with no effect on GDP as the economy attains equilibrium at natural unemployment rate.
6- Given the Phillips curve Πt= Πt' +0.24 -4ut
a) Plot the relationship when Πt the relation becomes πt= .24 -4ut
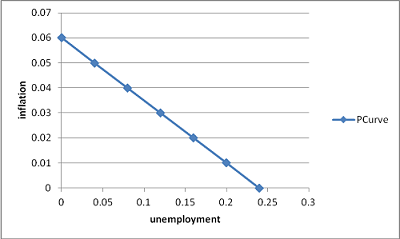
b) Find the natural rate of unemployment (NAIRO)
At NAIRU
expected inflation= actual inflation, so that
unemployment= NAIRU = .24/4 = .06 or 6%
c) What is likely to happen to the curve if wage indexation becomes more widespread? illustrate your answer on the graph?
When µ is higher, real wages are lower. This can be seen from the wage-setting equation- the unemployment rate must be higher for real wage to be lower. This causes increase in natural unemployment rate.