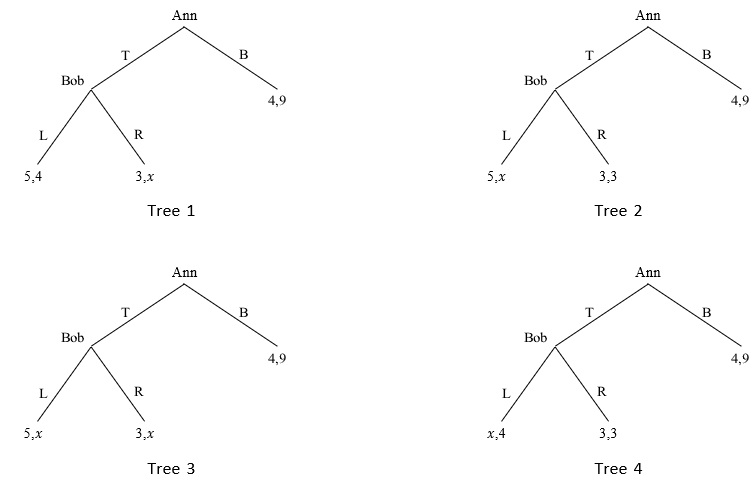
Reference no: EM133013790
Exercise 1
For each tree, find (a) all (pure strategy) Nash equilibria (NE), and (b) all (pure strategy) subgame- perfect Nash equilibria (SPNE). In every tree, payoffs are in alphabetical order. For each tree you gain up to 10 points (5 points for NE and 5 points for SPNE). Recall that to find NE on a tree, it is necessary to translate a tree into a matrix and find NE on the matrix. Hence, it is imperative that your answers are accompanied by correctly constructed matrices. Provide explanations.
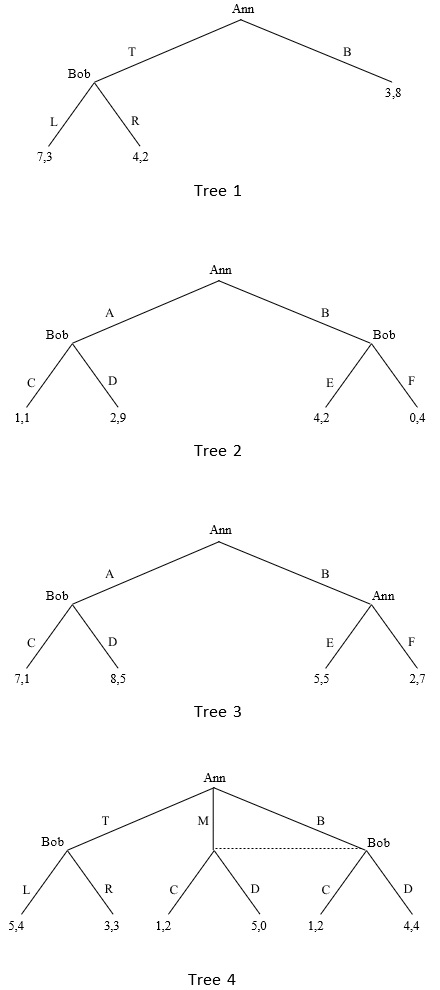
Exercise 2
Consider the following static game.
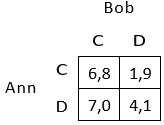
Note that (D, D) is the only Nash equilibrium. Imagine that the above static game is repeated infinitely many times. Assume that each player uses the grim trigger strategy. Assume that players have different discount factors, δA δB where δA is Ann's discount factor and δB is Bob's discount factor. Identify all values of δA and δB such that (C, C) is played at every round. Provide an explanation of the process you went through.
Exercise 3
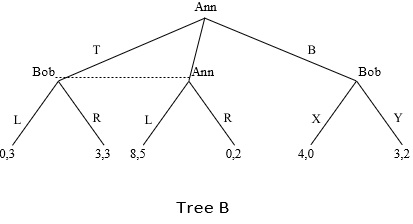
(a) Is there anything wrong with Tree A depicted below? In nothing is wrong, just indicate that this is the case. However, if something is wrong explain what it is and suggest how to fix Tree A.
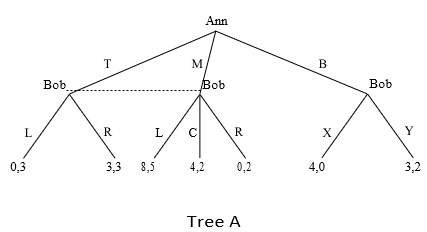
(b) Is there anything wrong with Tree B depicted below? In nothing is wrong, just indicate that this is the case. However, if something is wrong explain what it is and suggest how to fix Tree A.
Exercise 4
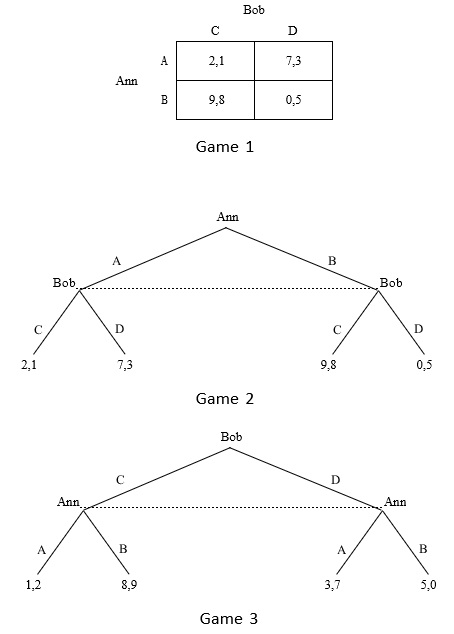
Other than Game 1 being depicted as a matrix while Games 2 and 3 depicted as trees, are there any other differences among the three games? Explain.
Note that in Game 1 and Game 2, payoffs are in the order (uAnn, uBob) - the first number is Ann's utility while the second number is Bob's utility. In Game 2, the payoffs are in the order (uBob, uAnn) - the first number is the utility of Bob while the second number is Ann's payoff.
Exercise 5
Consider Experiment 2 (Firm A spying on Firm B). Description of the experiment:
• Players: Firm A and Firm B.
• Firms A and B are involved in a fierce competition.
• Firm B is innovative while Firm A relies on industrial espionage.
• Currently, Firm B is running three top secret project: Alpha, Beta, and Gamma.
• Firm B's security system is imperfect.
o If Firm A spies on project Gamma, then Firm B knows about it.
o If Firm A spies on project Alpha or Beta, then Firm B knows that they are a victim of espionage but are not sure whether Firm A targets Alpha or Beta. Experiment 2
• Stage 1: Firm A decides which project to spy on: Alpha, Beta, or Gamma. Firm A has limited resources and can spy on only one project.
• Stage 2: Firm B learns whether Firm A spies on Gamma or not. If Firm A does not spy on Gamma, this means that Firm A spies on either Alpha or Beta, but Firm B does not know which specific project Firm A spies on.
• If Firm A spies on Gamma, then Firm B chooses between defending Gamma and not defending Gamma.
• If Firm A spies on Alpha or Beta, then Firm B chooses to defend either Alpha or Beta. Firm A is unable to defend more than one project at a time. Experiment 2 Values: Alpha = 5, Beta = 2, and Gamma = 3.
• If Firm A spies on a project that Firm B does not defend, then Firm A gets the whole value and Firm B gets nothing.
• If Firm A spies on a project that Firm B defends, then Firm A gets nothing, and Firm B gets the whole value.
(a) Depict the game in Experiment 2 as a tree. Provide an explanation of the process you went through.
(b) Find all Nash equilibria in a tree you constructed in (a). Explain.
(c) Find all subgame perfect Nash equilibria in a tree you constructed in (a). Explain.
In (b) and (c), focus on pure strategy equilibria.
Exercise 6
Your job is to invent and solve a finite dynamic game. Think about some interactive situation from your professional or personal life. The task is to describe this situation using the language of game theory (tree), and solve it (subgame perfect Nash equilibria).
It is important that what you propose is original. That is, what you analyze must be your own invention. Your task is to put on the hat of applied game theorist: you analyze some problem using the game-theoretic tools. You can think of your job as consisting of three steps.
Start with a story. Explain, in English, a problem you want to analyze. Your story should not be longer than 1 page. You can pick whatever topic you want.
The following restrictions apply: (i) The game is dynamic. (ii) There are at least two players. (iii) Each player has a finite number of strategies (at least two) so the game can be depicted as a tree.
(iv) The game is your own invention. If you copy or just modify a game that you found on the Internet or in a book or saw in class, then your grade for this exercise will be zero. Be creative! Your game can be with perfect or imperfect information - the choice is up to you.
Once the story is finished, create a tree that depicts your story. Explain how you constructed the tree. Finally, find all (pure-strategy) subgame perfect Nash equilibria (SPNE) in the tree you drew. Explain how you found SPNE.
Bonus Exercise
For each tree, find all values of x such that (B, L) is the only subgame-perfect Nash equilibrium. In each tree, payoffs are in the order (uAnn, uBob) - the first number is Ann's utility while the second number is Bob's utility. [Hint: This exercise might or might not be tricky.