Reference no: EM132493677
Part I
Multiple Choice Questions
1 The main difference between a free good and an economic good is that
A It is not available B It is not tradable
C No one desires any amount D It is not scarce
2 " Over the long term inflation is less a problem than unemployment" is an example of
A A positive statement B A statement that could never be true
C A statement that suffers from a logical error D A normative statement
3 Which of the following statements relates to the concept of efficiency?
A Being able to produce more of one good only by producing less of something else. B Using resources as effectively as possible
C The absence of waste D All of the above.
4 After Rayan received a raise in his income, he began buying more Ice Cream Cones and fewer Popsicles. For Rayan Popsicles is
A A joint product B A normal good
C A complementary good with Ice Cream D An inferior good
5 Which of the following will shift the supply curve for textbook to the left
A A decrease in the demand of substitutes in production B A decrease in taxes on textbook suppliers
C An increase in printing costs D A decrease in the number of buyers
6 If the marginal benefit(MB) of good (X) > the marginal cost (MC) of good (X) then
A It is better to produce or consume more of good(Y) B It is better to produce or consume less of good (X)
C It is better to produce or consume more of good (X) D It the allocatively efficiency
7 Which of the following best defines the subject of economics?
A the art of making money
B the study of choices that businesses make to maximize profit
C the science that studies unemployment, inflation, and economic stability D the study of choices made to cope with scarcity
8 When a textile firm decides to produce more cotton fabric and less synthetic fabric, it is most directly answering the ---------- question.
A How B Why
C For whom D What
9 Which factor of production earns profit
A Land B labor
C Capital D entrepreneurship
10 The production possibilities curve is the boundary between
A Those combinations of goods and services that can be produced and those that cannot B Those resources that are limited and those that are unlimited
C Those combinations of goods and services that can be produced and those that can be consumed. D Those wants that are limited and those that are unlimited
11 Using the production possibilities curve model, unemployment is described as producing at a point
A on the exact middle of the PPCcurve
B inside the PPC curve
C on either end of the PPC curve D outside the PPC curve
12 If demand is price elastic, it means
A 1% decrease in the price leads to an increase in the quantity demanded that exceeds 1 % B The price is very sensitive to any shift of the supply curve.
C 1% increase in the price leads to an increase in the quantity demanded that exceeds 1% D 1% decrease in the price leads to a decrease in the quantity demanded that is less than 1%.
13 The price elasticity of demand can range between
A Negative one and one B Negative infinity and infinity
C Zero and one D Zero and infinity.
14 A good with a vertical demand curve has a demand with
A Infinite elasticity. B Unit elasticity.
C Zero elasticity. D Varying elasticity
15 When the price of Nike soccer balls fell, Ronaldo purchased more Nike soccer balls and fewer Adidas soccer balls. Which of the following best explains Ronaldo's decision to buy more Nike soccer balls?
A The substitution effect B An increase in the demand for Nike soccer balls
C The income effect D The price effect
Part II
Problems solving
Question one
Following is a production possibilities table for two goods: Trucks and mobiles. The table is constructed using the usual assumptions.
|
Choices
|
Trucks (T)
|
Mobiles (M)
|
The opportunity cost for trucks
|
|
A
|
0
|
110
|
-
|
|
B
|
1
|
105
|
5
|
|
C
|
2
|
96
|
9
|
|
D
|
3
|
84
|
12
|
|
E
|
4
|
63
|
21
|
|
F
|
5
|
36
|
27
|
|
G
|
6
|
0
|
36
|
A. What is the opportunity cost of 3rd and 5th of trucks? Is the opportunity cost increasing or decreasing or fixed?
B. Using the figures in the above table to draw the production possibilities curve (PPC). Show all possible choices.
C. Determine if the following choices are attainable, unattainable, efficient, or inefficient and why?
D. If the economy started to use new technology in Mobiles production. What will happen to the production possibilities curve (PPC), show your answer graphically?
Question two
Given the following two equations:
Qd = 150 - 3P
Qs = 70 + 2P
A. Calculate the equilibrium price and the equilibrium quantity. Show all your work.(4 marks).
B. Using the two equations, complete the following table?
C. Draw a graph to shows the market state when P= 20. Show on this graph the equilibrium price and the equilibrium quantity.
D. If the consumer income increases by 20%, show graphically what will happen to the equilibrium price and quantity
Question three
In the above figure:
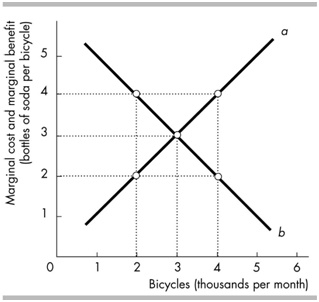
A. What does the curve (a) represent? (1 mark)
B. When 2000 bicycles are produced, how much is the marginal benefit? (2 marks)
C. What is the allocatively efficient level of output? (1mark)
D. If at the moment 4000 bicycles are produced per month, should more or fewer bicycles be produced? Explain. (1 mark)
Question four
The following is a straight-line demand curve that confronts a single firm.
Find TR, MR, PED, and the degree of PED between each two points
|
Price
|
Quantity demanded
|
TR
|
MR
|
PED
|
Degree
|
|
$6
|
1
|
6
|
-
|
-
|
|
|
5
|
2
|
10
|
-4
|
-1
|
|
|
4
|
3
|
12
|
2
|
-1
|
|
|
3
|
4
|
12
|
0
|
-1
|
|
|
2
|
5
|
10
|
-2
|
-1
|
|
|
1
|
6
|
6
|
-4
|
-1
|
|
Part III
Question one
Explain why both nations with high living standards and nations with low living standards face the problem of scarcity. If you won $1 million in a lottery, would you escape the scarcity problem?
Question two
From Opportunity cost point of view. Although attending college is expensive, time-consuming, and requires effort, but people decide to attend college. Explain why?
Question three
There is a shortage of college basketball and football tickets for some games, and a surplus occurs for other games. Why do shortages and surpluses exist for different games?
Question four
What is the main difference between the law of demand and the price elasticity of demand?
2-What is the meaning of perfectly inelastic demand and perfectly elastic demand? How would each be graphed?
Question five
A gasoline station very near a professional football stadium parks cars on its lot to make money on game days. Last year it charged $4.00 per car and parked 1000 cars. This year it raised the parking price to $5.00 and parked 850 cars. Did the station owner make a good economic decision in raising the parking prices from one year to the next? Explain.
Question six
What is the relation between price elasticity of demand (PED) and Revenue (TR and MR)? Why is it likely that a firm would sell at a price and quantity where its demand curve is price elastic?
Attachment:- Problems solving questions.rar