Reference no: EM133001801
Active class 8: Internet is Full of Network Protocols
The learning objective of this class is to learn the role of Network Address Translation (NAT) protocol, Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) and Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) which are (perhaps considered as) significant network layer protocols.
At the end of this activity, you should be able to:
1. Explain the functionalities of the mentioned protocols
2. Build a simple network and analyse the protocols.
Activity 1: Group Discussion.
It is predicted that we will have 50 billion IoT devices in our networks soon. Yes, just IoT devices! If you think about this, most devices need an IP address to communicate with the network. Discuss the following questions with your group members.
1. Do we have enough IP addresses to assign for each device that connect to the network?
2. Do we have any solution?
3. Explain a protocol that we can use along with IPv4 to conserve the global IP address space?
Activity 2: Who does assign an IP address when your computer connects to the network?
This is the role of DHCP. First, we are going to do a small role play to mimic DHCP. Each member of the group has a role to play. Assume your group is your local area network (LAN). For example, you could consider a LAN at home or at Campus or at your workplace.
1. One group member can act as a router with a DHCP server and other three members are host devices that try to connect to the network. These host devices could be a PC, a printer, and network storage device. A sample network is shown in the below figure.
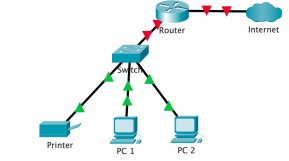
2. Assume the all the devices are physical connected as shown in the above figure. Now, your job is to set up the network and establish the connections with the router using DHCP. Each member needs to send/ respond with the correct message and message sequence to establish the connections and receive IP address for each host.
3. Draw a timing diagram to indicate the sequence of messages transferred between devices.
4. Next, we are going to implement a DHCP server in Cisco packet tracer and check the DHCP in action. Make use to take screenshots of the networks you build, analysis, and verifications. Open the packet tracer and implement the following network. You may need to use the same model of the devices shown in the diagram. Today, we are not going to use static IP configuration for the hosts as we are going to check the DHCP in action. Tips: You need to add a module with a fast ethernet port to the router, so that the router can support three LANs as shown in the below network diagram.
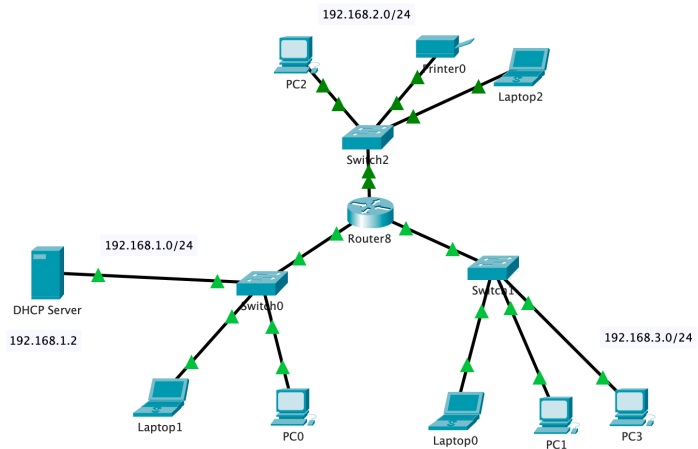
a. Set up the DHCP server by configuring network pools, default gateway, and IP address (use the subnets mentioned in the diagram).
b. Set up the router by configuring the interfaces and DHCP (use the subnets mentioned in the diagram).
c. Set up each host with DHCP to obtain IP configuration and verify the IP address and the default gateway configured.
d. Verify the connectivity between each host in the network.
Activity 3: ICMP
In this activity, we are going to use Cisco Packet tracer's simulation tool to explore ICMP. To do this, you are going to use the network that you have implemented in Activity 2.
1. Use the Simulation mode and send a simple packet from one host (Host A) from LAN1 to another host (Host B) in LAN2. In simulation tool, you can run the simulation step by step. When you go through each step, pay attention to the type of the message passed (highlighted in the below figure).
2. You may notice when Host A ping Host B, we use ICMP protocol. Double click on one entry as shown below to explore the ICMP message,
3. You should be able to view the packet details as follows.
4. Explain what information you can find in "outbound PDU details".
5. Have a closer look at the ICMP message format. Can you identify the type of ICMP message and specific information is in there (type and code)? You can refer to RFC792 for more help. https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/html/rfc792
6. Can you identify the changes in ICMP message when you use a traceroute from Host A to Host B compared to what you have witnessed in the above question? Note that you can use tracert command in each device (in command prompt) similar to the way that ping command is used.
Above and Beyond Tasks:
Those who are targeting for Credit and above can complete the following task as part of Task 4.1C and 5.2D to demonstrate your deeper understanding on network layer.
1. Analyze DHCP in Wireshark (you may want to disconnect your wireless connection and connect it again whilst capturing the packets). You can show the sequence of DHCP messages and the details of those messages.
2. Why are different inter-AS and intra-AS protocols used in the Internet? What are the examples of these two different types of routing protocols?
Attachment:- Network Protocols.rar