Reference no: EM131193943
Part - 1
1.1. Explain the formation of hybrid electron orbitals in carbon and their relation to the formation of sigma and pi bonds
1.2. Illustrate the formation of free radicals, from covalent bond homolysis, and the formation of carbonium ions from covalent bond heterolysis.
2.1. Use experimental analytical data to calculate the empirical and molecular formula of an unknown organic compound.
2.2. Derive possible structural formulae for an unknown organic compound from its molecular formulae.
2.3. Identify the probable structural formula/formulae of an unknown organic compound from experimental data relating to its chemical, physical and spectroscopic properties.
3.1. Classify organic compounds from their structural formulae.
3.2. Explain the characteristic properties of an homologous series of organic compounds.
3.3. Identify common functional groups in organic structures (eg: C=C, C≡C, halogeno, hydroxyl, ester, carbonyl, carboxyl, nitrile, nitro, amine and amide,).
3.4. Use the IUPAC systematic names to name simple aliphatic, aromatic and alicyclic compounds and their isomers
3.5. Write and name the molecular formulae and displayed structural formulae for a range of different types of organic compounds, and their structural isomers and stereoisomers.
3.6. Examine the structural formulae of unfamiliar organic compounds and draw conclusions about their classification, nomenclature, bonding and 3-dimensional shape.
4.1. Explain how the physical properties of organic compounds relate to their structure.
4.2. Analyse and interpret data relating to the physical properties of organic compounds.
4.3. Explain, with balanced equations, characteristic reactions of some of the organic functional groups.
4.4. Explain, with balanced equations, the mechanism of a named organic reaction (eg: electrophilic addition or substitution, nucleophilic addition or substitution, esterification, saponification).
4.5. Examine the displayed structural formulae of unfamiliar organic compounds and draw conclusions relating to their possible physical and chemical properties.
4.6. Compare and contrast the physical and chemical properties of isomers eg: structural isomers, cis and trans geometrical isomers, and enantiomers).
Q3 (a)Three compounds A, B and C have the molecular formula C4H8O. All three compounds give a yellow precipitate with 2,4-dinitrophenyl hydrazine (Brady's) reagent. B and C also give a red precipitate with Fehling's solution. Identify the functional groups and suggest possible structural formulae and names for compounds A, B and C. (AC 3.3 and AC 3.4)
Q3 (b)Compounds D, E and F have the molecular formula C4H10O. All three compounds react with PCl5 to form a gas which turns blue litmus paper red. Compound D is oxidised to an aldehyde; compound E is not readily oxidised; compound F has an optical isomer.
Identify the functional groups and suggest possible structural formulae and names for compounds D, E and F. (AC 3.5)
Q4.1 Solubility
Describe and explain what happens when:
(i) Hexane is added to water
(ii) Ethanol is added to water(AC 4.1)
Q4.2The table below gives the melting temperature and boiling temperature of different organic compounds.
|
Compound
|
Relative molecular mass
|
Melting temperature/oC
|
Boiling temperature/oC
|
Density at melting temp/g cm-3
|
|
Butane
|
58
|
-138
|
-0.5
|
0.579
|
|
2-Methylpropane
|
58
|
-160
|
-12
|
0.557
|
|
Ethanol
|
46
|
-117
|
78.5
|
0.789
|
Account for the differences in the melting temperature and boiling temperature of the following pairs of compounds:
(i) Butane and 2-Methylpropane
(ii) Butane and ethanol(AC 4.2)
Q4.3 Give brief explanations using equations for each of the following:
(i) In aqueous solution ethanoic acid is a weak acid.
(ii) In aqueous solution 1-aminoethane is a base. (AC 4.3)
Q4.4. Draw and name A, B, C, D and Ein the following equations, and classify each of the reactions by selecting from the following list (no explanations are required):
acid/base reaction,
condensation reaction,
electrophilic substitution reaction,
hydrolysis reaction,
nucleophilic substitution reaction,
redox reaction.
(i) 2-Bromo-3-methylbutane is mixed with aqueous sodium hydroxide solution:
H HHH
| | | |
H--C--C--C--C--H (l) + NaOH (aq) -------> (A) + NaBr (aq)
| | | |
H | Br H
|
H--C--H
|
H
(ii) Butan-1-ol is heated with an acidic solution of potassium dichromate (VI):
H HHH
| | | |
3 H--C--C--C--C--O--H (l) + Cr2O72- + 8H+ --------> 3 (B) + 2Cr3+ (aq) + 7H2O (l)
| | | |
H HHH
(iii) Butan-2-ol is heated with an acidic solution of potassium dichromate (VI):
H HHH
| | | |
3 H--C--C--C--C--H (l) + Cr2O72- + 8H+ --------> 3 (C) + 2Cr3+ (aq) + 7H2O (l)
| | | |
H H O H
|
H
(iv) Ethanal (an aldehyde) is mixed with a solution of 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine (2,4 DNPH)
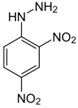
Ethanal + 2.4DNPH -----> (D) + H2O
(v) Methanoic acid is warmed with ethanol in the presence of sulphuric acid:
O H H
|| | |
H--C--O--H (l) + H--C--C--O--H (l) -------> (E) + H2O(l)
| |
H H
Q4.5 Atropine, an important drug used in the treatment of heart failure:
Atropine
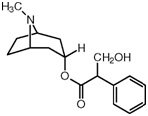
(i) Give the molecular formula of atropine.
(ii) Draw the structure on your answer sheet and label the following parts of the
molecule (no explanations are required):
(i) A primary alcohol group;
(ii) An ester group;
(iii) A tertiary amine group;
(iv) A part of the molecule which is planar in structure;
(v) A part of the molecule where the covalent bonds around the carbon atom are arranged tetrahedrally;
(vi) A carbon atom which is asymmetric.
(iii) Predict which part of the atropine molecule might attach itself to water molecules
Q4.6 Discuss the following types of isomerism which occur in organic chemistry
In each section you should describe what is meant by the type of isomerism and give the structural formulae of a pair of isomers.
(i) chain isomerism
(ii)position isomerism
(iii)optical isomerism
(iv) Give the structural formula and name of the stereoisomer formed by one of the compounds below and explain why the other compound does not have a stereoisomer.
CH3 COOH H COOH
\ / \ /
C = C C = C
/ \ / \
HOOC CH3 H H