Reference no: EM132458217
Question 1:
P1: Consider the process below (consider standard interactions only),
For each process:
- If occurs at tree level, draw all contributing Feynman diagrams.
- If it does not occur at tree level but can occur at one top level, draw one example Feynman diagram that contribute
- If it does not occur at all, explain which symmetry forbids it
(a): n → γγ
(b): vee- → vee-
(c): b → sγ
(d): e-u → vec
P2: Explain what the algebra 3⊗3¯ = 8⊕1 means when related to the bound state of quark and anti quark
P3: Explain how quark mixing arises in the standard model, and why there are no flavour changing neutral currents.
Question 2:
Imagine that the Standard model gauge symmetry were spontaneously broken by a Higgs triplet, H, rather than doublet, where H transforms under SU(3)C ⊗SU(2)L ⊗U(1)γ as follows:
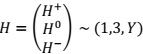
P1: show that this triplet must have zero hypercharge, Y=0
P2: assume H develops the vacuum expectation value :
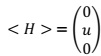
Examine the symmetry properties of this vacuum state under the generator of SU(2)L ⊗U(1)F to determine: which generator are broken? How many gauge bosons will acquire mass?
P3: rescalling that the gauge boson masses arise from the scalar kinetic term in the Lagrangian, (DµH)+(Dμ H), determine the masses of the bosons.
Useful information: Dµ = ∂µ + igTaWµa + ig'Y/2βµ, where the Ta the SU(2) generators. A convenient 3D representation of the SU(2) generators is :
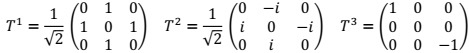
Question 3: All chiral anomalies vanish in the standard model. Then, imagine that we promote baryon number, B, to a local symmetry, ie, we gauge the U(1)B symmetry such that the standard model gauge group becomes SU(3)C ⊗SU(2)L ⊗U(1)F ⊗U(1)B
P1: Prove that baryon number is anomalous by demonstrating that at least one anomaly does not cancel
P2: now replace U(1)B with U(1)B-L where B - L = baryon number - lapton number.
Show that the particular anomaly you considered in (a) now cancels
(note: in order for the full set of anomalies to cancel in gauged B-L model, we must include RH neutrinos which transform as VR~(1,1,0) under SU(3)C ⊗SU(2)L ⊗U(1)F )
P3: Neutrino may have either Dirac or Majorana masses, with mass term given by
Dirac: mDV¯LVR
Majorana: mMV¯LVC
Where VLc = CVL¯T denotes the charge conjugate. For each of these mass terms, explain whether the B - L symmetry is conserved.
Question 4:
Quark flavour
P1: Was Cp violation in the B system observed in the following process?
If so, give one example
a) Mixing
b) Direct CP violation
c) Interference between mixing and decay
P1: Which decay modes can be used to measure the following properties of the unitarity triangle?
For each answer provide Feynman diagrams
(a) The 3 interior angles: Φ1(β), Φ2(α), Φ3(γ)
Give one decay mode for each angle
(b) The side lengths, specifically the CKM matrix element magnitudes measured in β
decays : |Vub|, |Vcb|, |Vtd|. Give one decay mode for each element
P3: Measurements of gluonic penguin decays can be used to search for new heavy particles beyond the standard model
(a) The leading one loop diagram for βo → ηuKo is gluonic penguin diagram. Draw a representative diagram with an internal top quark. Identify the CKM elements at each quark vertex.
(b) Explain why there is no tree level diagram
(c) What is the standard model weak phase dependence in a time dependent measurement of CP violation with this mode?
P4: In an experiment on η meason is produced with total energy E0 = 2000MeV in the lab frame. Estimate the width of η → γγ mass peak measured in a calorimeter that has an energy and angular resolution of σE/E = 5% and σθ = 0.05 radians, respectively (m = 547.51 MeV/c2).
Question 5: Neutrino and Dark matter
P1: The MINOS experiment studied the neutrino oscillations of a muon neutrino beam, and was located 735km from the Fermilab beamline. By comparing the energy spectrum of charged- current neutrino interactions in the near and far detectors, MINOS directly measured the oscillation probability as a function of Ev .
(a) what would be the energy threshold for a tau neutrino interaction via charged current with a nucleon, (e,g) vcn → τ-p ? if the muon neutrino with an energy of 2GeV oscillates into a tau neutrino, would it be detected?
(b) use the approximation that Δ31 ≈ Δ32 to express the muon neutrino survival probability as a function of Δm322, L, Ev, θ23 and θ13.
Hint: with Ev > 1 GeV, the contribution to the oscillation probability from the long wave length component associated with Δ12 can be neglected
P2: Dark matter scattering kinematics
(a) obtain an expression for the kinetic energy, ER, of a nucleus of mass MR recoiling in an elastic collision with a dark matter particle of mass MD and incident kinetic energy ED, in terms of the angle of emission relative to the incident direction
(ii) find the limiting values of recoil energy in terms of MD, ED and MR
(iii) calculate the maximum recoil energy of an Iodine nucleus, in collision with a dark matter particle of mass 10GeV travelling with a typical galatic velocity of 200 km/s. Assume that the dark matter is at rest in the rest frame of the galaxy.
Question 6:
P1. Deep inelastic scattering and the Higgs
(i) Deep inelastic scattering
(a) if quarks were spin-0 particles why would F1ep(x) / F2ep(x) be zero?
(b) what is the expected value of 0∫1 u(x) - u¯(x) for the proton?
(c) the figure below shows the raw measurements of the structure function F2(x) in low-energy electron-deuterium scattering. When combined with measurements from electron-proton scattering, it is found that 0∫1 F2eD(x)dx /0∫1F2eP(x)dx ≈ 0.84 . Write down the quark-parton model prediction for this ratio and determine the relative fraction of the momentum of the proton carried by down-/anti-down quarks compared to that carried by the up/anti-up quarks, fd/fu
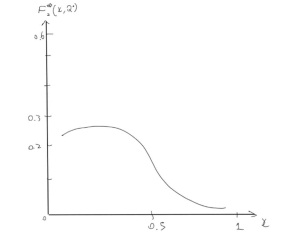
Y axis -> F2eD(x, Q2)
P2. detecting the Higgs at the LHC
(a) assuming a total Higgs production cross section of 20Pb an integrated luminosity of 140fb-1 , now many H → γγ and H → μ+ μ- μ+ μ- events are produced in the ATLAS experiment.
(b) How does one experimentally distinguish each particle in the following list from the other particles in the list in the ATLAS or CMS detectors? Here we consider only long lived particle.
- photons / electrons / muons / quark or gluon jet (mostly hadrons, (eg) P, K, π, n).