Reference no: EM133150540
Petroleum Production Engineering - Teesside University
Drilling Engineering
Write a report based around the production of petroleum that either you are familiar with, if you work in the industry, or that you can adequately research based on the resources available to you.
You are advised to initially submit a short plan to the module tutor indicating the range and depth of the area to be covered and to get the subject area approved before continuing with the preparation of the final report.
Topics to be considered where appropriate are:
- An overview of the theory underpinning petroleum production.
- An explanation of the appropriate control mechanisms.
- An overview of the fundamentals of petroleum production processes, systems, procedures and equipment.
- A discussion of the context of the chosen area of study to the concepts, meanings and objectives of petroleum production activities.
- Design aspects of the various petroleum production components.
- Mechanical design of various components.
Reservoir Engineering
Question 1. Fill in the blanks of the hydrocarbon classification shown below,
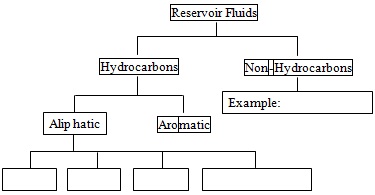
Question 2. Define saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons.
Question 3. Fill in the blanks or select the correct choice:
a. Asphaltene is the (heavy/light) fraction of the crude oil that .............. in light alkanes such as pentane, but is ......... in aromatic solvents such as ........ and
...........
b. Asphaltene and resin molecules have (polar/non-polar) molecular structure.
c. Resins (assist/decrease) the solubility of asphaltenes in the crude oil.
d. The term "sour gas" is used for natural gas samples containing significant amount of .............
Question 4. Draw a typical phase diagram of a pure substance and describe it briefly indicating the critical point.
Question 5. Draw a typical phase diagram of a two-component mixture and describe it briefly indicating the critical point.
Question 6. Describe the classification of reservoir fluids based on their phase diagrams (hint: there are five classes). Plot the phase diagram pointing out the initial and final pressure of the reservoir.
Question 7. Explain briefly what an equation of state (EoS) is.
Question 8. Explain what is meant by:
• Solution gas-oil ratio,
• Oil formation volume factor
• Oil Viscosity
Plot the diagram of these three oil properties against pressure.
Question 9. Consider a gas sample with the composition listed in bellow table:
|
Component
|
Mole fraction
|
|
C1
|
0.45
|
|
C2
|
0.15
|
|
C3
|
0.07
|
|
C4
|
0.03
|
|
C5
|
0.04
|
|
C6
|
0.06
|
|
C7+
|
0.01
|
|
H2S
|
0.01
|
|
CO2
|
0.02
|
|
Total
|
1
|
Calculate the:
• MW and specific gravity of this gas sample
• API gravity of this gas sample
• The pseudo-critical pressure and temperature of this gas based on Sutton's (1985) equations.
Ppc = 756.8 - 131.0γg - 3.6 γg2
Tpc = 169.2 + 349.5γg - 74.0 γg2
Question 10. Consider a gas sample with the following composition; calculate the pseudo-critical pressure and temperature of this gas.
|
Component, i
|
Mole fraction, yi
|
Pci (Psi)
|
Tci (°R)
|
|
C1
|
0.7
|
673
|
344
|
|
C2
|
0.18
|
709
|
550
|
|
C3
|
0.02
|
618
|
666
|
|
C4
|
0.03
|
551
|
766
|
|
C5
|
0.04
|
485
|
847
|
|
C6
|
0.01
|
434
|
915
|
|
C7+
|
0.02
|
361
|
1024
|
|
Total
|
1
|
|
|
Question 11.
(a) Define the gas compressibility factor (z-factor).
(b) Determine the gas compressibility factor for the gas in question 9 at 2500 psi 750°R. (Hint: use the chart developed by Standing and Katz (1954)), you can find this chart at the end of this booklet.
(c) Define the gas formation volume factor
(d) Determine the gas formation volume factor for a reservoir gas sample of part (b)
Question 12. Briefly describe the black oil and compositional reservoir simulation approaches and outline their difference.
EOR
Question 1. Name the primary recovery mechanisms; provide brief explanation for each recovery mechanism.
Question 2. Explain briefly what an artificial lift system is and why it is used.
Question 3. Define the following parameters:
• Recovery factor
• Single phase mobility
• Mobility ratio
Question 4. What is viscous fingering and how it can be mitigated?
Question 5. What are the two most common classes of polymers used in polymer injection processes? Provide an example of each class with brief explanations.
Question 6. Name the methods of enhanced oil recovery, and briefly explain the mechanisms involved in each method that improves the recovery of oil.
(Hint: there are three methods that need to be discussed).
Question 7. What parameter is measured in a slim-tube test? Explain the test procedure and plot the typical results of a slim-tube test.
Question 8.
(a) Define the interfacial tension.
(b) What is its unit in SI system of units?
(c) What is the typical value of the interfacial tension for an oil/brine system?
(d) How interfacial tension is controlled in oil/brine systems?
Question 9. Fill in the blanks, or select the correct choice:
• Surfactants are classified into three groups of (a) ........ , (b) ........ , and (c) .........
• In polymer flooding, the main objective of adding polymers to the aqueous fluid phase is to (increase/decrease) the ............ of the aqueous phase.
This (increases/decreases) the mobility ratio.
• Alkaline flooding is not a suitable method for (sandstone/carbonate) reservoirs, due to the existence of ...... in the rock which may chemically react with alkaline ions and result in formation damage.
Attachment:- Petroleum Production Engineering.rar