Reference no: EM13155706
Question 1:
In lectures we covered how to develop spreadsheets to value American and European call and put options using the binomial option pricing model.
Develop a spreadsheet to
- cope with up to 100 time steps in a binomial tree model
- be able to value either a call or a put
- be able to value either an American or a European style option
Allow the user to specify
- the type of option (call or put)
- the type of exercise rights (american or European)
- the spot price (price of the underlying asset)
- the exercise price
- the term to maturity
- the volatility
- the risk free rate
- the dividend yield
- the number of time steps to use
(a) Test your spreadsheet on some test data: describe what tests you think you should do and give details of the testing you did.
(b) Are you confident your spreadsheet is working satisfactorily? Could you extend it to do a 1,000,000 step tree in excel?
(c) Write some "user" documentation of the spreadsheet for another user to read. It should explain what type of inputs go in, where (i.e. what cells) to put them, what restrictions apply to those inputs, what cells in the spreadsheet should not be overwritten, and what types of calculations are done by the spreadsheet.
(d) Write some "audit documentation" for colleagues so that if someone else wanted to verify the correctness of the spreadsheet model, they could do so and understand how it works. This documentation should explain where the excel code came from, i.e. what mathematical
methods or formulae it implements, the source of that mathematical / financial theory (i.e. a reference) in addition to the content of the user documentation.
Question 2 Executive Share Option Scheme
An executive share option scheme has the following features
Upon joining a firm, the executive is granted a "forward start option". This is a call option over the stock of the firm. It has the following features:
- The option starts at time T1 after the executive starts with the firm
- When the option starts:
1. it has a maturity date of T2 years, and
2. an exercise price which is a multiple α times the stock price prevailing in the market at the date when the option starts
3. the option has European style exercise rights
4. the option payoff at time T2 is defined in terms of the stock price at times T1 and T2 and the formula for the payoff = 100,000 x max (sr2 - αST1 payoff which is 100000 times the payoff on a call option over 1 unit of the stock
Valuation formula for pricing the executive option:
Consider the start date of the option, and the value of the option at that time Let S1 be the value of the stock at time T1, so the strike price of the option is X=αS1
The value of the option at time T1 is C = 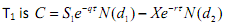
where 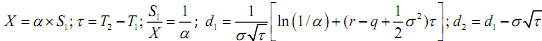
it follows that the value of the option as at the start date (T1) is
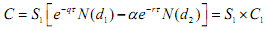
which is proportional to S1, the price of the stock at the time (T1) when the option starts
Note that the quantity in the square brackets is the value C1 of a call option on an asset with a spot price of $1.00 and a strike price of α, a term of T2-T1 etc. This is a constant, independent of S1.
Using the risk neutral valuation approach, we can value the option as at the valuation date (time 0) using the formula
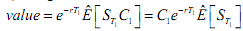
This is C1 times the discount factor times the risk neutral expectation of the value of the stock at time T1
But the risk neutral expectation E(ST1) of the stock price at time T1 is the forward price for dilivery at time T1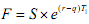
It follows that the value of this executive option
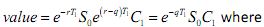
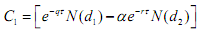 is the value of an option over a stock worth $1 with an exercise price of $α and a term of τ = T2- T1
is the value of an option over a stock worth $1 with an exercise price of $α and a term of τ = T2- T1
(i) The firm wants advice on the value of this part of the executive's remuneration package. Apply the formula (write a spreadsheet for this) derived above to compute the cost of such an option given the following data:
- The stock price is currently S = $10.00,
- the risk free interest rate is r = 6% pa (continuously compounded)
- the volatility of the stock is σ = 40% p.a.
- the stock pays a continuous dividend yield of y = 4% p.a.
- the option start date is T1 = 1 year from the valuation date
- the option maturity date is T2 = 3 years from the valuation date
- the term of the option as at the start date (T1) is T2 - T1 = 3 - 1 = 2
- on the option start date the strike price of this Call Option is set to α = 110% of the stock price as at that time, so it is an "out of the money option" when it starts. This means the share price must rise by at least 10% over the 2 year term of the option's existence in order for the option to be worthwhile exercising when it matures.
- the option is cash settled (no requirement to issue new shares at the option maturity date) give details of your working
(ii) what difference would it make to the cost of the option if the executive were able to change the firm's dividend policy so as to stop the firm from paying out any dividends during the term of the option (i.e. after the start date T1 of the option but not before).
Note that this means the q term (the dividend yield) in the factor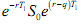 may be different from the q term in the factor
may be different from the q term in the factor 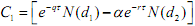 give details of your working
give details of your working
(iii) what difference would it make to the cost of the option if the executive were able to exercise the option early during the period between times T1 and T2? Using a 100 step binomial tree to answer this question
(iv) do a sensitivity analysis of the European type option value in (ii) using the following variables:
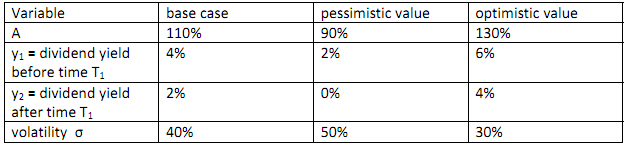
(v) do a sensitivity analysis of the American type option value in (iii) using the following variables:
Write a spreadsheet to do these calculations and produce a report setting out the results of the valuations and of the sensitivity analyses