Reference no: EM132360987
Question 1
A sample and hold (S&H) circuit is an analog device that is used to sample, i.e. take the voltage of a constantly changing analog signal and locks its value at a stable level for a particular least period of time called holding time. The S&H precedes the quantizer in analog-to-digital converters (ADCs).
S&H is usually integrated into sampling ADCs.
The datasheet of AD684 monolithic quad S&H circuit designed by Analog Devices include the data:
• 500 ns Hold Mode Settling
• 1 µs Maximum Acquisition Time to 0.01%
• Low Droop Rate: 0.01 µV/µs
• 75 ps Maximum Aperture Jitter
• Low Power Dissipation: 430 mW
• Works with 12-bit ADC
Assume that Fig. 3.11 is a model of the S&H circuit.
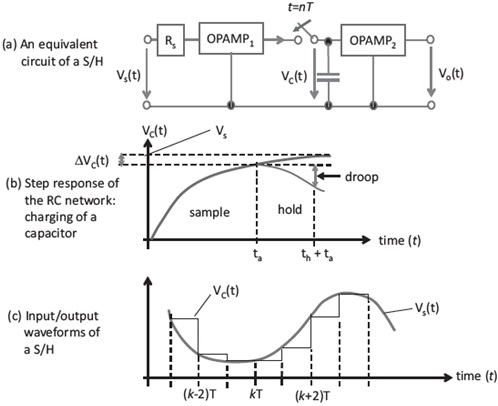
Characteristics of S-H circuit
a) Using the data given above, compute the required sampling period (Ts) and sampling rate (Fs) of the AD684 S&H.
b) Using the appropriate digitization theorem, analyse the frequency content of analog signals which can be digitized using the ADC employing the AD684 S&H.
c) Assuming that the maximum amplitude of the analog signal sampled by the AD684 S&H is Vs=60 nV, and that the capacitor is able to charge to this level during the acquisition time. Evaluate the voltage which is quantized by the quantizer in the ADC.
d) Evaluate the maximum value of the time constant of the S&H circuitry.
Questions 2
Huffman coding is a prefix-free source coding (or data compression) algorithm. Its practical applications include GZIP, PKZIP (winzip etc.), PNG, JPEG and MPEG-2. Assume that the message "Engineering is interesting." is to be transmitted over a 2-Mbps link using Huffman coding as the source code.
(a) Compute the entropy of the source.
(b) Assume that the message is source encoded using 2-ary Huffman code. Design a suitable Huffman code for the source.
(c) Compute the average length of codewords from the Huffman-encoded source.
(d) Compute the coding efficiency of above Huffman code.
(e) Assume that the Huffman encoded message is to be transmitted without any other processing (i.e. no channel coding and no compression), evaluate the time required.
Question 3
Consider a coherent BPSK receiver operating at 15oC and receiving data at the rate 1 Mbps. The system uses the waveforms s0(t) = Ac sin(2πfct) and s1(t) = Ac cos(2πfct) to transmit bit 0 and bit 1, respectively, where Ac = 0.25 μV. Assume that the energy per bit is normalised relative to a 1-Ohm resistive load. Also, assume that the transmission medium causes only AWGN. Compute the signal energy per bit, Eb.
1) Compute the signal energy per bit, Eb.
2) Compute the single-sided power spectral density of the AWGN, N0.
3) Compute the signal-to-noise ratio (i.e., bit energy to noise power spectral density), Eb/N0.
4) Compute the BER of the coherent BPSK detector.
5) Assuming that the detector operates continuously over a period of two days, find the expected number of bits received in error.
Question 4
Every multi-user communications system needs a multiple access scheme. A class of multiple access schemes of great interest to current industry is the non-orthogonal multiple access scheme (NOMA). There are multiple proposals of NOMA in the open literature. Your task here is to find a journal paper on any NOMA scheme, study it and summarize its key points in a maximum of one A4 page written in 11-point font size.