Reference no: EM132400908
Question 1:
A machine shop works 300 days per year and uses 2,600 brackets per year. These brackets are purchased from a supplier. The ordering cost per order is $22.5 and the lead time is 4 days. The holding cost per bracket per year is $1.8. Standard deviation of daily demand is 3 brackets. For a 95% service level, determine:
(i) The Economic Order Quantity (EOQ)
(ii) The Reorder Point (ROP)
(iii) The annual cost of inventory system
Question 2:
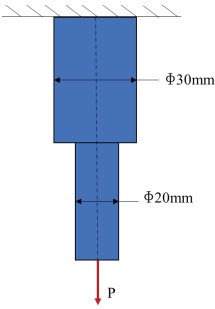
The stepped bar shown below is attached to a fixed support and subjected to an axial load. It has a circular cross section. The bar is made of AISI1020 carbon steel and the operating environment is room-temperature air. Estimate the permissible axial load P that can be safely applied on the bar. State all your selections and assumptions clearly. You may refer to the data tables available in appendix to extract appropriate data.
Question 3:
A bearing is required to support 30mm diameter rotating shaft of a heavy-duty machine. The shaft is subjected to a radial load of up to 1.6kN and axial load is negligible. The maximum estimated rotating speed is 6500rpm. A life of 7500hrs for the bearings is desired. Select and specify an appropriate deep groove ball bearing.
With usual notations, bearing life for deep groove ball bearings is given by;
L10 = (C/P)3, L10h = (106/60N)L10
Question 4:
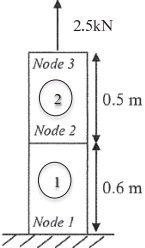
A two element bar is subjected to a tensile force of 2.5kN at node 3 as shown in the figure below. The bar has a uniform cross-sectional area of 180mm2 and an elastic modulus of 185GPa. Using finite element method, determine:
(i) Displacement at each node
(ii) Stress and strain in element 2
Given; ke = AeEe/Le or matrix format, ke = AeEe/Le 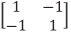
Global stiffness matrix: 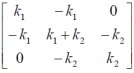
Question 5:
From the APT program given below, sketch the geometry of the resultant part and the tool path according to each statement based on your established x-y coordinate system. Clearly mark the coordinate axes on your diagram. Use 2 different colours to indicate part geometry and the tool path. You are advised to use the next page to draw a clear diagram.
PARTNO PART-07
UNITS/MM
MACHIN/MILL,02
CUTTER/15
SP=POINT/0,0,40
P1=POINT/30,20,0
P2=POINT/100,20,0
P3=POINT/100,40,0
P4=POINT/70,80,0
P5=POINT/50,80,0
P6=POINT/50,70,0
L1 =LINEJP1,P2
Cl =CIRCLEJCENTER,P3,Radius,20
L2=LINEJP4,LEFT,TANTO,C 1
L3=LINEJP4,P5
C2=CIRCLEJCENTER,P6,RADIUS,10
L4=LINEJP1,LEFT,TANTO,C2
PLI =PLANEJP 1,P2,P3
SPINDIJ700
FEDRAT/1000
FROM/SP
GO/TO,L1,TO,PL1,0N,L4
FEDRAT/350
COOLANT/FLOOD
GORGT/L1,TANTO,C1
GOFWD/CI,PAST,L2
GOLFT/L2,PAST,L3
GOLFT/L3,TANTO,C2
GOFWD/C2,PAST,L4
GOFWD/L4,PAST,L1
FEDRAT/1000
SPINDL/0
GOTO/SP
COOLANT/OFF
FINI
Question 6:
Additive manufacturing processes have been gaining popularity in recent years. Many companies are now adopting various additive technologies due to unique advantages they offer. Explain the advantages of additive manufacturing processes over traditional subtractive processes such as machining.