Reference no: EM132263433
Molecular Orbital Assignment -
This assignment consists of a series of questions based on the material covered in lectures and recommended reading. All answers should show full working, noting any assumptions made. Explain the meaning of symbols used. Where computer generated output is included, your name should appear on the print-out.
Question 1: The 1s and 2pz hydrogenic wave-functions are of the form:
Ψ1s = (1/√π)Z3/2e-|Z_r|
Ψ2pz = 1/(4√(2π)) Z5/2re-|Z_r/2|cosθ
where the distance r is in atomic units, Z is the nuclear charge. |x| is the modulus (or positive form) of some unknown x.
a) Plot the value of both LCAO-MO's for H2 along the internuclear axis. Assume that the internuclear distance is 2.5 a.u. Use a spreadsheet and calculate the value of the wave-function in uniform steps of 0.1 a.u. Mark the position of the two nuclei on your graph.
b) Plot the value of the LCAO-MO's arising from the overlap of the H 1s and F 2pz atomic orbitals along the hydrogen fluoride (HF) internuclear axis. Use a spreadsheet and calculate the value of the wave-function in uniform steps of 0.1 a.u. Mark the position of the two nuclei on your graph. Assume that the internuclear distance is 2 a.u. and that the atomic orbital coefficients are those given below:
ψ+ = 0.19ψH + 0.98ψF
ψ- = 0.19ψH - 0.98ψF
c) Compare the graphs obtained in parts (a) and (b). Comment on where the electron density resides in each molecule.
Question 2: a) The structure of benzene (C6H6), optimized using the HF/STO-3G level of theory and basis set in Gaussian09, is given in the standard orientation in Table 1 (in attached file). The optimized MO's from this calculation are listed as atomic orbital coefficients in Table 2. Use these data to identify all MO's with π-symmetry. For each π-MO provide (i) a sketch showing all the localized AO's in the wave-function and (ii) a sketch of the MO. Label your sketches with the MO number and identify and label the HOMO and the LUMO. Be sure to sketch both occupied and unoccupied π MO's and indicate any changes in phase in your sketches. Example sketches for formaldehyde are shown below.
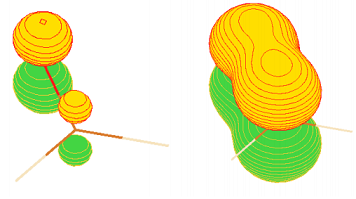
b) Use the data in Table 2 (in attached file) to estimate the Ionization Potential of benzene in units of electron volts. Explain how you derived your answer.
Attachment:- Assignment Files.rar