Reference no: EM13799361
1. TRUE or FALSE: 'In a market where the forces of demand and supply are free to fluctuate unimpeded, the equilibrium price is the only price that can last. Explain.
2. An increase in supply and an increase in demand will...(select the best option, and explain your choice):
(a) increase price and increase quantity
(b) decrease price and increase quantity
(c) affect price in an indeterminate way and decrease quantity
(d) cancel each other out and not have an impact on either price or quantity
(e) affect the price in an indeterminate way and increase quantity
3. Assume coffee beans are sold in a purely competitive world market. Describe the impact, ceteris paribus, of each of the following on a graph.
(a) a severe drought in one of the major coffee-producing nations (Brazil)
(b) a rise in the incomes of consumers
(c) an expectation of a bumper crop in Brazil
(d) a report that links heart disease to the consumption of caffeine
(e) a rise in the price of tea
CASE STUDY
Assume that Coglin Clothing Company is producing T-shirts in a purely competitive market. Show the impact on market price and quantity, ceteris paribus, of each of the following on a graph. Make sure you explain the equilibrating process.
a. an improvement in technology
b. increase in cotton prices
c. cheaper labour
d. the product is more fashionable now
e. the price of product Y (a substitute for X) falls
f. an expectation of a fall in income of consumers
1 An increase in the price level results in a decrease in the quantity demand of an inferior good only.
2 Assume that there is a fixed supply in the market. A higher price will result from a change in demand brought about by a rise in income.
3 A change in demand occurs when a hairdresser raises the price of haircuts and the salon experiences a decline in the number of customers.
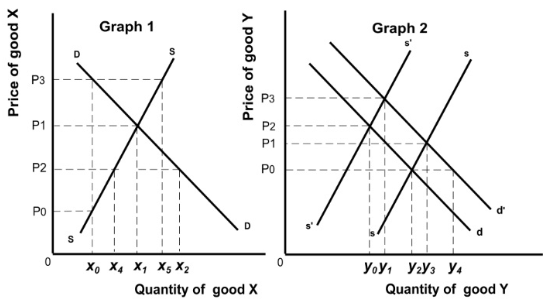
4 In Graph 1 below price P3 is unsustainable because excess supply in the market would drive the price down. The surplus would eventually shrink to zero.
5 In Graph 2 below imagine that suppliers are prepared to supply along curve ss and demand curve is d. Ceteris paribus, an expectation of increase prices in the future would result in a new equilibrium price equal to P1.
6 Imagine that the demand and supply curves in Graph 2 depict equilibria that exist before and after the simultaneous occurrence of a decrease in prices of raw materials coupled with increased preference for good Y. The original equilibrium must be at P2 and Yo.
7. Price elasticity of demand measures the responsiveness of quantity demanded to changes in price.
8 Normal goods are the only goods that have negative price elasticity of demand.
9 Price elasticity of demand rises when the number of substitutes increases or as the purchase of the good uses up more and more of the consumer's budget.
10 The price elasticity of supply for a linear supply curve is positive.