Reference no: EM132463888
ECON 4140 Game Theory - Loyola Marymount University
Question 1. Player I's payoff matrix in a game is
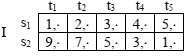
Part a) Find the maximin and minimax value for player I and the corresponding maximin and minimax strategies?
Part b) Does the matrix have a saddle point? Why or why not?
Part c) Find player I's security value and security strategy and describe what strategies player I fears player II may use here. Solve and show graphically. Also show where the maximin and minimax values are in your graph
- explain how you could find the minimax and the maximin in the graph alone (what would you need to identify?)
Question 2. Player I's payoff matrix in a game is
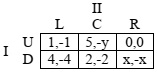
a) Determine the security value and security strategy for player 1 if x=1.
b) Determine the security value and security strategy for player 1 if x=3.
c) Determine the security value and security strategy for player 1 if x=5.
d) In what case, if any, does the game have a saddle point for player I? Explain.
e) Find player II's security value and security strategy if x=y=3.
f) Determine the mixed strategy NE if x=y=3 and compare expected outcomes for both players with the security strategy. In your own words, explain what the difference is between the approaches of a NE strategy and a security strategy.
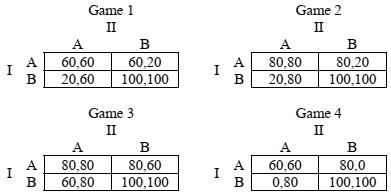
Question 3. Consider the following four games. What are the NE in each game? Comparing the games with each other, in what games do you think do players choose which NE more/less frequently than in another game? Explain your answer.
Question 4. For the scenarios below determine the reaction functions to their own strategy for each player, plot them (separately), and determine whether the Brouwer Fixed Point Theorem applies to each of them.
a) Consider the following normal-form game G = {N , S1 x S2 , (ui)i∈N } with N = {1, 2} , S1 = S2 = [0,1], u1 (s1 , s2) = s1 + 2s1s2 - 2s12 and u2(s1, s2) = s2 - s1s2 - 0.5s22
b) Change player 2's utility function to u2(s1, s2) = 1.5s2 - 2s1s2 - 0.5s22
c) Now change player 2's utility function to u2(s1, s2) = 2s2 - 4s1s2 - 0.5s22.
d) [Extra Credit] Can you determine whether the NE is stable based on the reaction functions you have drawn in a) - c)? If so, how? If no, why not?
Question 5. Consider a Cournot duopoly with market demand P (Q) = 140 - Q .
a) Assume both firms have marginal cost c = c1 = c2 = 20 (no fixed cost). Derive the firms' reactions functions and plot them. Calculate the NE and show in your graph.
b) Now assume that c2 = 20 and firm 1's marginal cost is c1 = 20, q1 ≤ 30 or 80, q1 > 30. Derive the firms' reaction functions and plot them. Find the NE and show in your graph.
c) Now assume that c2 = 20 and firm 1's marginal cost is c1 = 20, q1 ≤ 30 or 40, q1 > 30. Derive the firms' reaction functions and plot them. Find the NE and show in your graph.
d) Now assume that c2 = 20 and firm 1's marginal cost is c1 = 20, q1 ≤ 30 or 0, q1 > 30. Derive the firms' reaction functions and plot them. Find the NE and show in your graph.
e) Compare the four scenarios and explain the differences in outcomes. Any challenges along the way?
Question 6. Consider the following "Battles-of-the-Sexes" game:
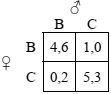
a) Find the mixed-strategy NE. Plot the reaction functions in a large-scale and precise graph.
b) Now, assume that λ = 0.1 . Determine the QRE reaction functions and carefully plot them in your graph (plug in some values, like 0, 0.1, 0.2, etc., or use excel or some other program). Indicate the QRE in your graph.
c) [Extra Credit] What do the QRE reaction functions look like if λ = 1 and λ = 10 ?
Question 7.
a) Describe game 1 below formally and draw the tree for game 2.
b) Indicate the (pure) strategy sets for all players in each game.
Game 1
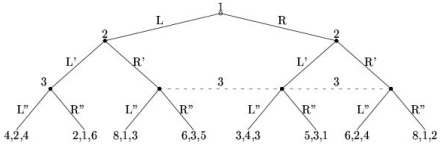
Game 2: G = {N , H , P,(Ii )i∈N , (ui )i∈N } with N = {1, 2},
H = {Φ, A, AC} ∪ Z where Z = {B, AD, ACE, ACF}, P(Φ) = P( AC) = 1 and P( A) = 2 ,
I1 = {Φ,{AC}} and I2 = {{A}}, u1 (B) = u2 (B) = 2 , u1 (AD) = u2 ( AD) = x ,
u1 (ACE) = u2 ( ACF ) = y , u1 ( ACF ) = u2 ( ACE) = 1
Make sure you always explain and derive everything, as well as draw carefully and clearly label everything, where applicable - this holds for all problems sets and everything else you do, whether it is explicitly stated again or not.
Note: Need only 1-3 Questions.